Every auto manufacturer strives to be innovative.
The constant development of new technologies pushes the boundaries of whats possible.
In the past five years, major advancements have been made in electric vehicle efficiency.
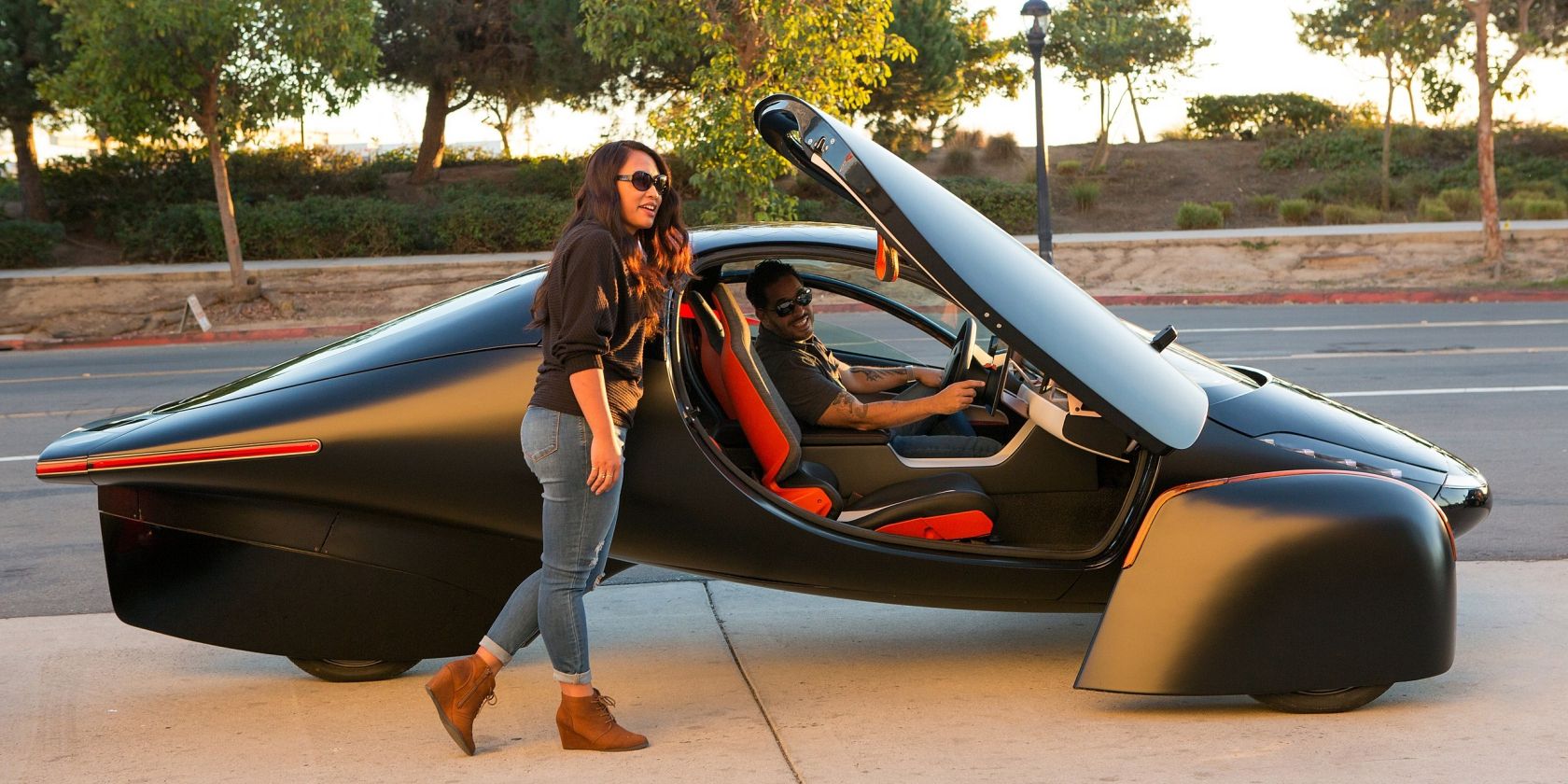

Image Credit: ApteraMotorsMedia/Wikimedia Commons
American EV maker Aptera has been pursuing electric vehicle efficiency since 2006.
The Long History of Electric Vehicles
The history of electric cars is often disputed.
Davenport created a small locomotive powered by two electromagnets that ran on a track.
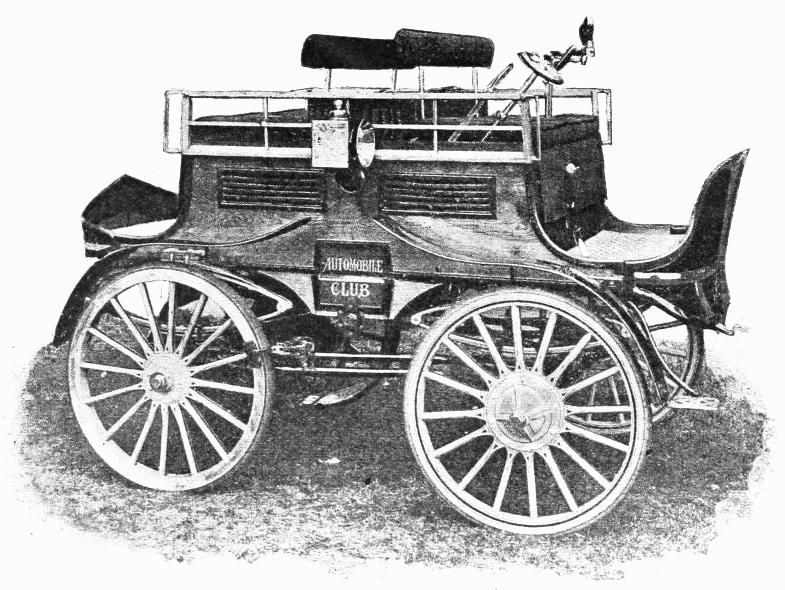
Image Credit: Tokumeigakarinoaoshima/Wikimedia Commons
A notable breakthrough came in 1997 with the Toyota Prius Hybrid, followed by the Tesla Roadster in 2008.
2011 marked Chevrolet’s entry into the EV market when it introduced its plug-in hybrid Volt EV.
The Volt used technology developed by the US Department of Energy.
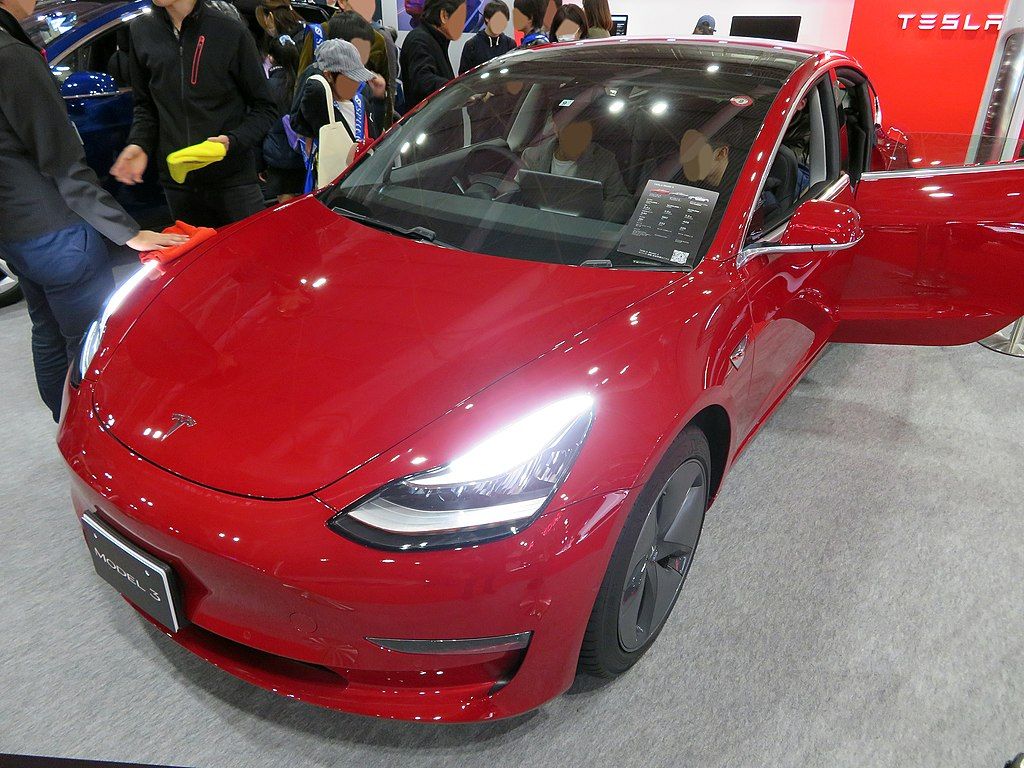

Image Credit: Tokumeigakarinoaoshima/Wikimedia Commons
Today, nearly every automaker has a hand in producing electric vehicles or battery packs.
Improving on previous technologies to produce the most efficient EV ever.
Types of Electric Vehicles
There are four main types of electric vehicles.

Image Credit: Calreyn88/Wikimedia Commons
These include:
Battery Electric Vehicles
Battery-electric vehicles run on batteries rather than internal combustion engines.
An example of this is the Tesla Model 3.
An external charging port connected to a large battery pack drives a DC electric motor.

Image Credit: Rutger van der Maar/Wikimedia Commons
These are also recharged by grid-connected electrical sockets and regenerative braking.
Both systems are joined to a regenerative braking system.
The battery pack is only recharged by regenerative braking.
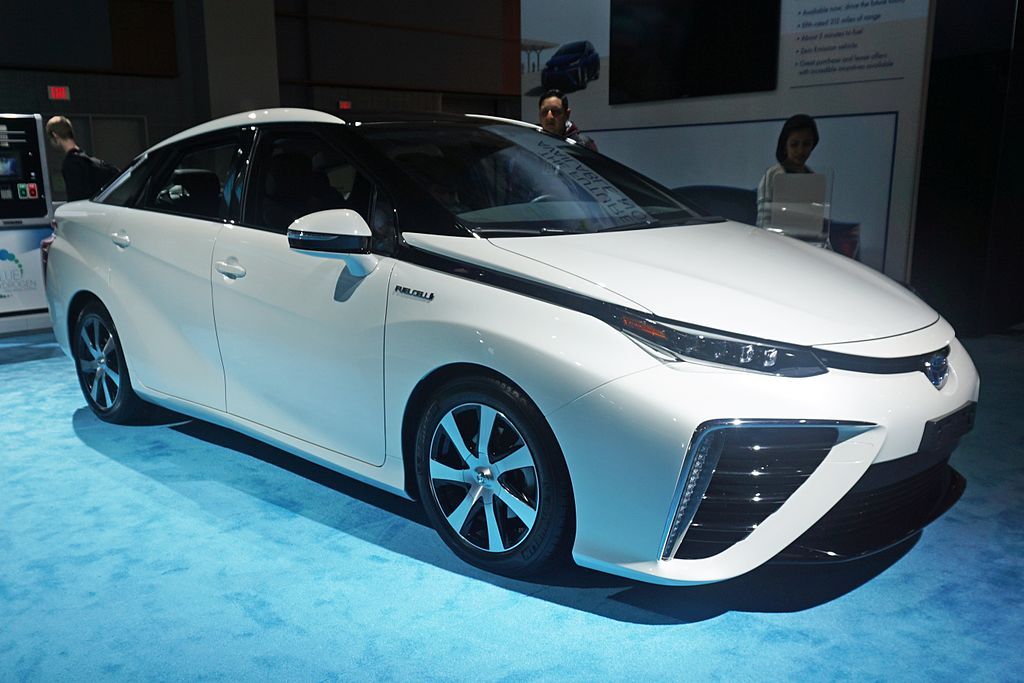

Image Credit: Mario Roberto Duran Ortiz/Wikimedia Commons
This means never having to plug in the vehicle under normal use.
The solar panels constantly recharge the vehicle, in addition to providing extra range while on the road.
The three-wheeled car is super lightweight and efficient.
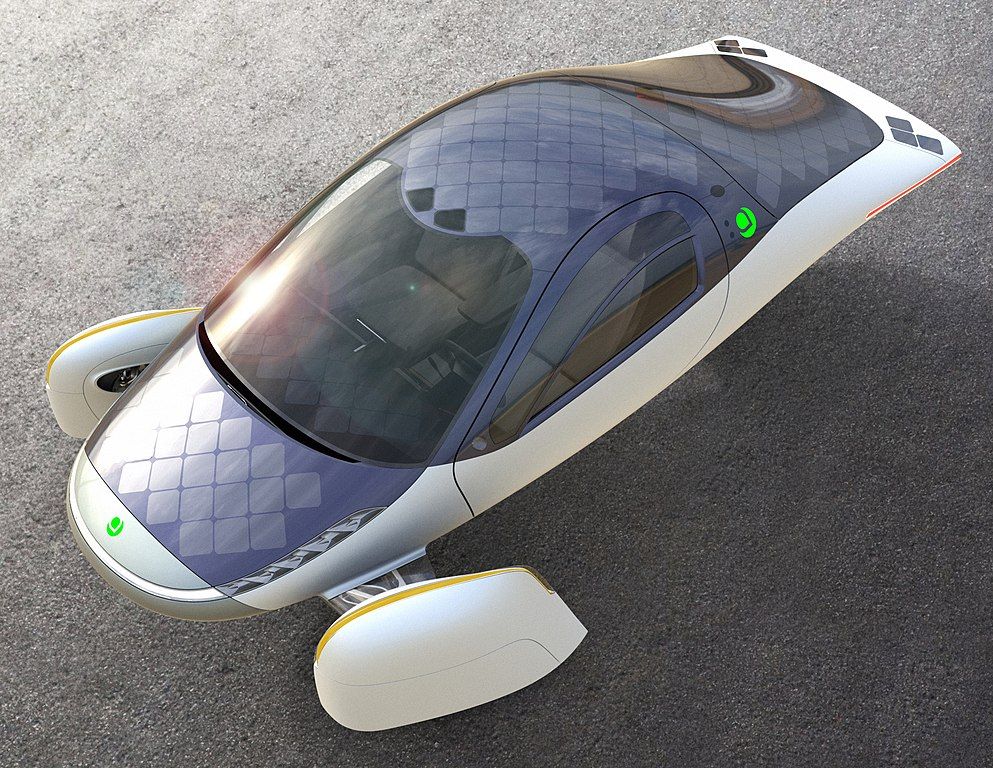

Image Credit: Aptera/Wikimedia Commons
It achieves this through a few design strategies.
It zeroes in on minimizing drag and weight, and its chassis further reduces weight and decreases roll resistance.
Because of its innovative design, the Aptera can achieve a range of up to 1000 miles.

Image Credit: Felix Kramer/Wikimedia Commons
Using only solar power, the Aptera can travel 40 miles per day under ideal conditions.
Close to the 39 miles per day average, according to the U.S. Department of Transportation.
Under normal use, you essentially get to use your Aptera without ever charging it.

Image Credit: Aptera/Wikimedia Commons
Its solar panels are designed to charge the vehicle, whether it is moving or stationary.
Compared to other EVs, this is three times more efficient according to its website.
Potential buyers are still concerned about EV prices and ranges per charge.
Aptera is the next step in EV evolution.
Efficiency is at the core of its philosophy.
It had to determine what factors hindered maximum efficiency.
These include aerodynamics, weight, roll resistance, internal components, and power.
Reduction allows you to travel farther and faster with less energy.
Reducing weight, wind drag, and the power consumed by internal components, its able to maximize efficiency.
As a result of Apteras innovation, people will be able to travel long distances with less infrastructure.
Because of its solar panels, it can also serve as a backup power source during a blackout.
There’s no denying this technology will be used in other auto manufacturers' EVs.
The only question is how much will be applied and how long it will take to reach maturity.
Now that the bar has been raised, EV makers can only push the technology forward.
Aptera will be observed closely to see how well it does.