But have you ever wondered what cache is and how it’s different from RAM?
You see, both RAM and cache are volatile memory storage systems.
On the other hand, the primary memory systems supply data to the CPU when turned on.
But why have a memory system on the computer which can’t store data when it’s turned off?
Well, there is a big reason why primary storage systems are quintessential for a computer.
Regarding numbers,secondary storage systems like SSDs have an access time of 50 microseconds.
Image credits:Tosaka/Wikimedia commons
Therefore, primary memory systems are almost 3,000 times faster when compared to secondary storage systems.
Here is how data moves through the memory systems in a modern computer.
To store this data, random access memory uses a dynamic memory cell (DRAM).

This cell is created using a capacitor and a transistor.
If the capacitor is fully charged, it is said to store a 1.
On the other hand, when it’s discharged, it is said to store 0.
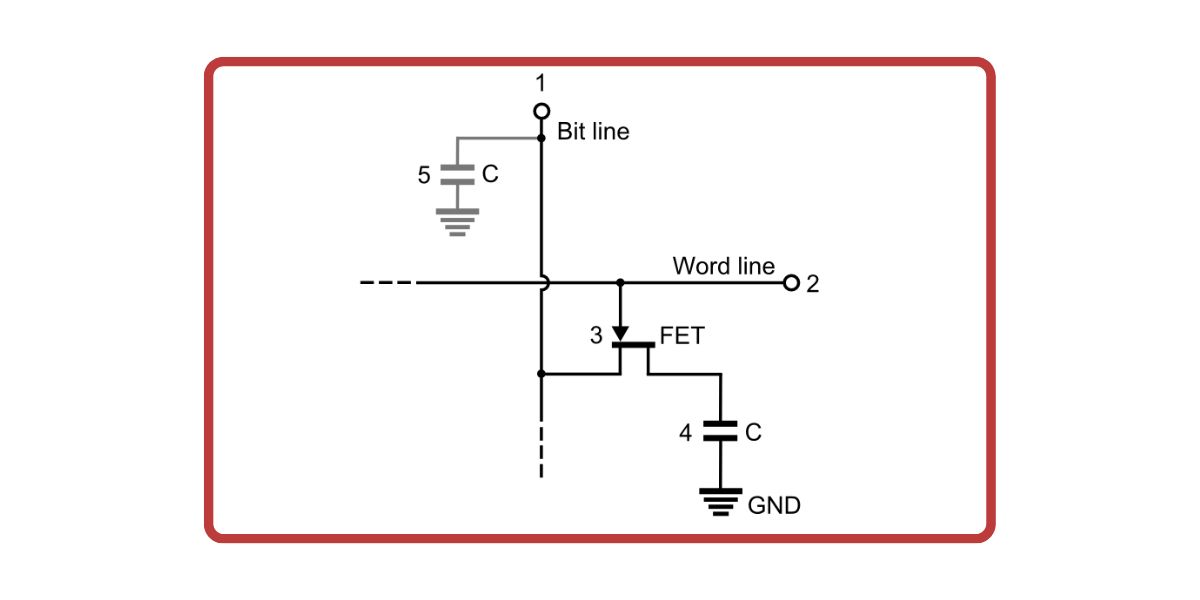
Image credits:Tosaka/Wikimedia commons
Although the DRAM cell is capable of storing charges, this memory design comes with its flaws.
Due to this, data stored in the RAM can be lost.
Due to the reasons mentioned above, RAM only supplies data to the CPU every 17 nanoseconds.
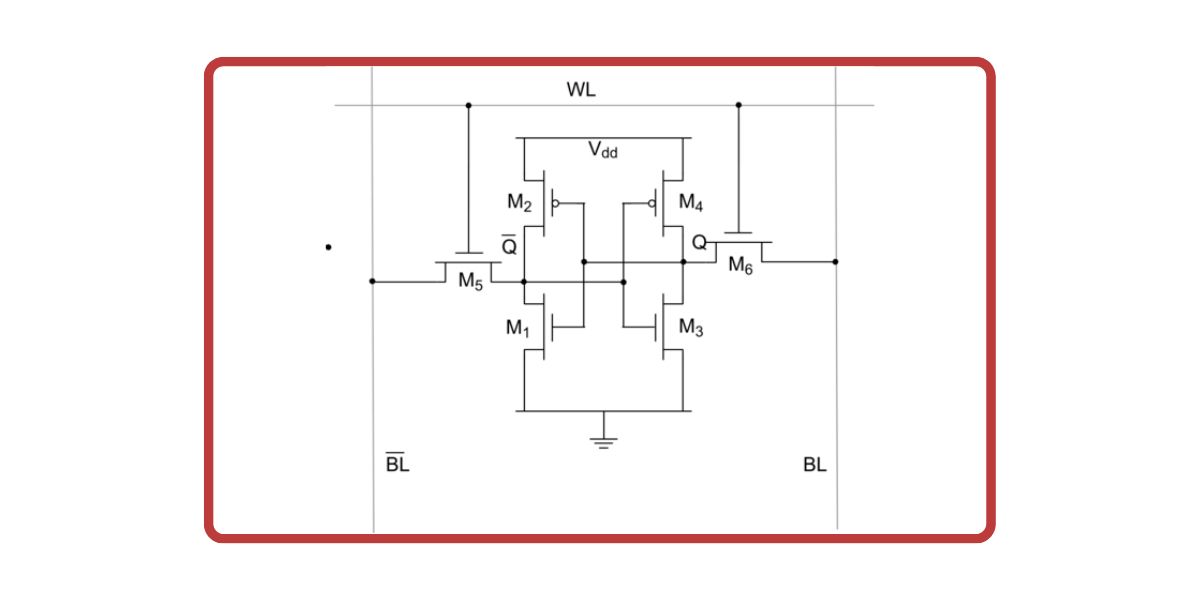
Image credits:Abelsson/Wikimedia Commons
At that speed, the CPU can’t reach its peak performance.
To solve this problem, we have cache memory, another temporary storage system much faster than the RAM.
First and foremost, cache memory is not present on the motherboard.
Instead, it is placed on the CPU itself.
Due to this, data is stored closer to the CPUenabling it to access data faster.
In addition to this, cache memory does not store data for all the programs running on your system.
Instead, it only keeps data that is frequently requested by the CPU.
Due to these differences, the cache can send data to the CPU at astonishingly fast speeds.
Furthermore, compared to RAM, cache memory uses static cells (SRAM) to store data.
Instead, it uses a set of 6 transistors to store information.
That said, cache memory, too, has its flaws.
For one, it is much more costly when compared to RAM.
This is substantially larger than the DRAM cell’s single-capacitor design.
Comparison metric
RAM
Cache
Function
Stores program data for all applications running on the system.
Stores frequently used data and instructions required by the CPU.
Due to its low memory density, cache memories store data in the range of Kilobytes or Megabytes.
Cost
Fabricating RAM is cheaper due to its single transistor/capacitor design.
Fabricating cache is costly due to its 6-transistor design.
Location
RAM is connected to the motherboard and is far away from the CPU.
Cache is either present inside the CPU core or shared between cores.
Speed
RAM is slower.
An outstanding balance between both memory systems is quintessential to getting the most out of your PC.