These networking modes include NAT, bridged, and host-only networks.
So, what exactly are NAT, bridged, and host-only networking modes?
How do they work, and which should you use?
What Is NAT?
A virtual DHCP server is automatically created whenever a virtual machine is made.
What Is a Host-only web connection?
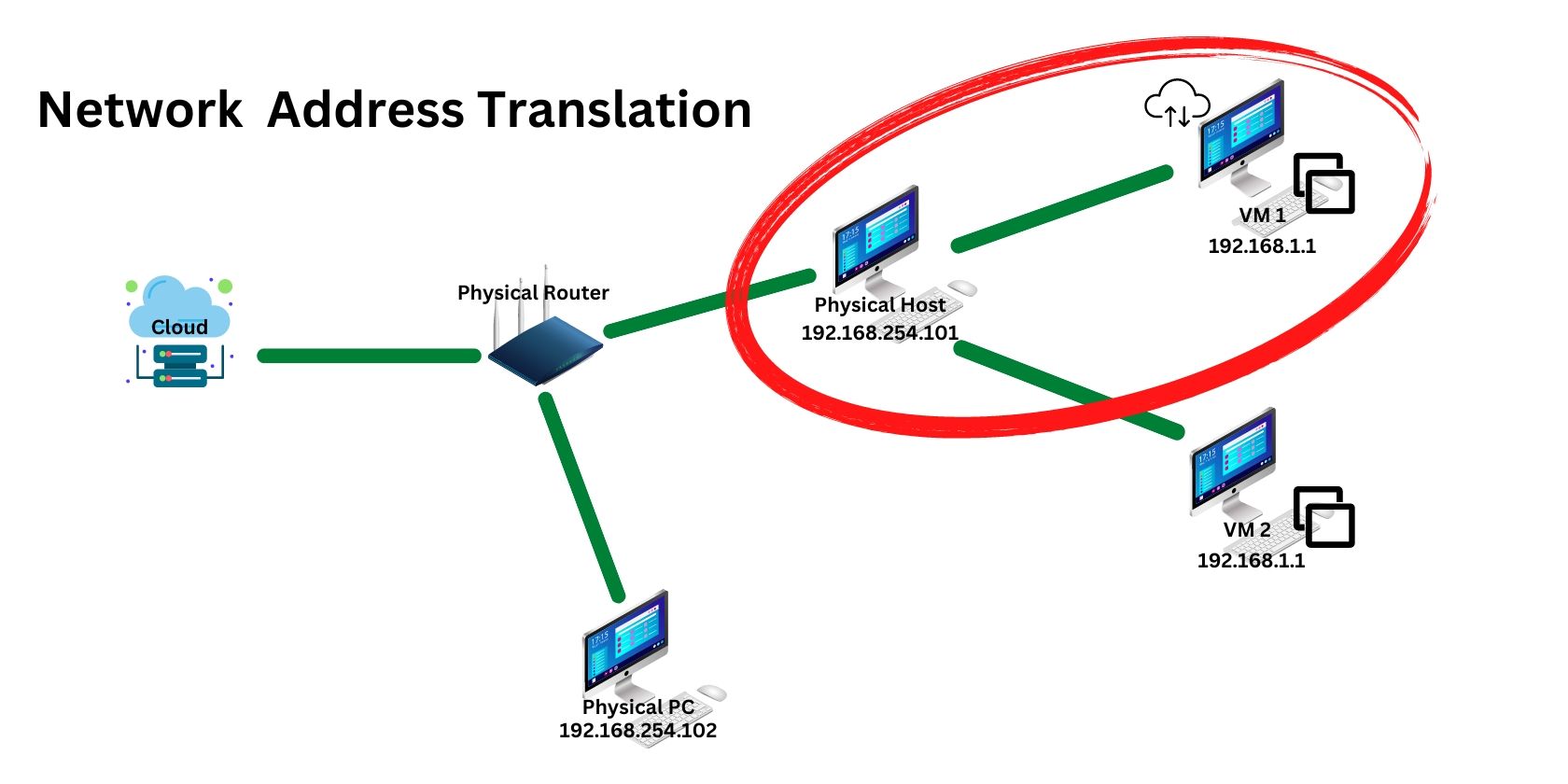
A host-only web link provides the highest level of web link security in exchange for very limited networking capabilities.
A host-only networkuses a virtual DHCP serverfrom the host machine to give a unique IP address to each VM.
What Is a Bridged connection?
A bridged online grid is the most permissive of all online grid connection types.
It allows a VM to online grid with other VMs and all physical machines on the physical online grid.
A bridge adapter provides each VM with a unique IP address within the physical data pipe subnet.
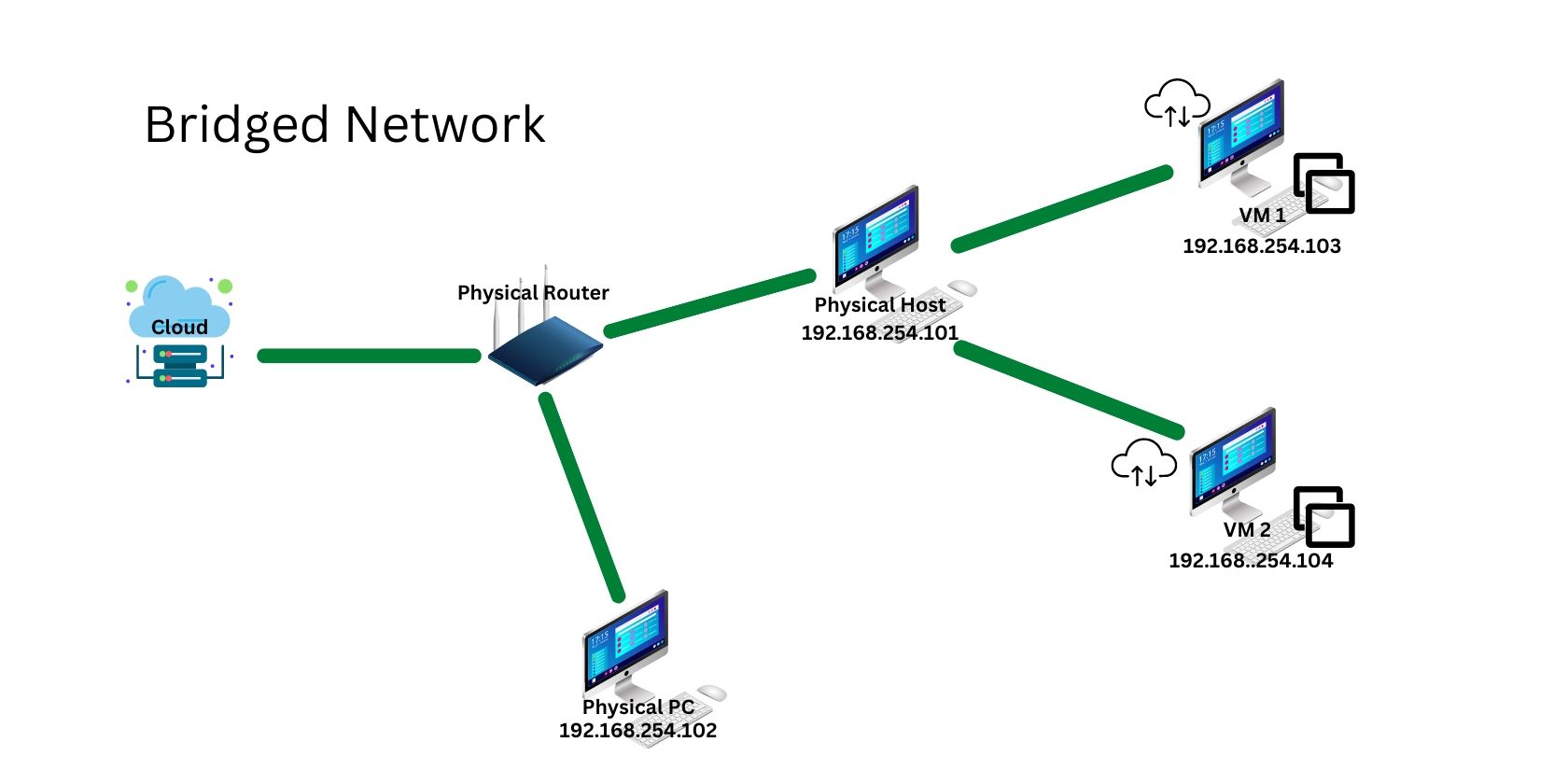
VMs get their IP address not from a virtual DHCP server but from the physical router in your connection.
Depending on the connection mode, your virtual machine will have varying degrees of networking capabilities.
Besides, setting the correct web connection mode is easy and can be done in a few seconds.

The important thing is that it’s crucial that you understand which web link mode better fits your needs.
There are many practical applications for using a virtual machine.
Many of these applications are usually in the form of testing, education, development, and hosting services.
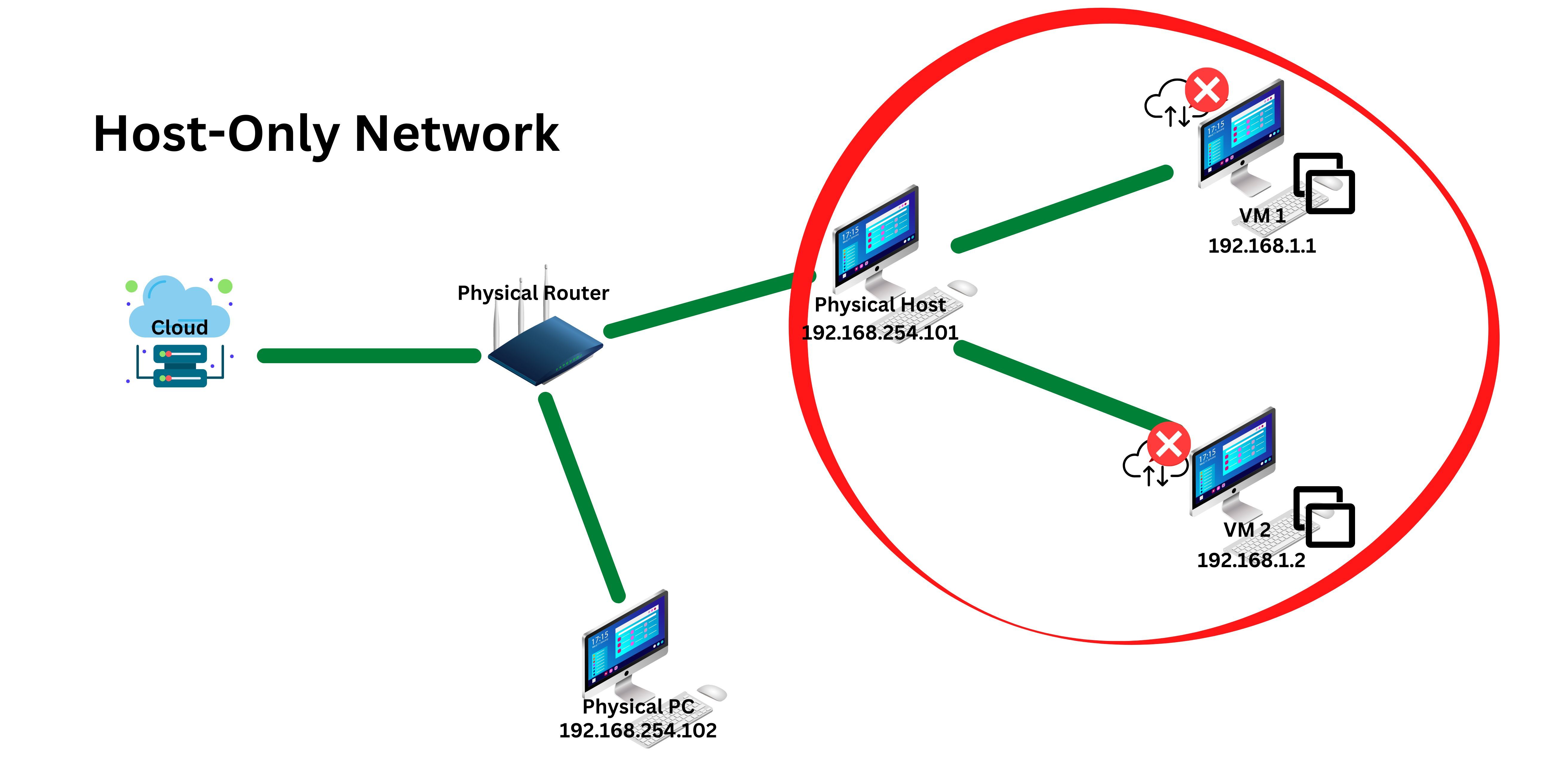
VMs configured to use NAT are invisible to physical machines and other VMs hosted by the host machine.
This mode grants full connection connectivity at the expense of having the least amount of security.
A bridged data pipe only allows connection to the host and other VMs.
To tailor fit your connection mode, it’s possible for you to mix and match connection modes.
This is possible as hypervisors often give VMs four to eight web connection adapters.
So, it’s possible for you to use multiple data pipe modes when necessary.
You would combine NAT and host-only data pipe modes to create such a connection.
And that’s basically all you’re gonna wanna know about VM networking modes.
Hopefully, you’re able to now use and customize your VM networks.