Unfortunately, nothing better reminds you of this setup than when you might no longer connect to a website.
The cause may be somewhere on your side, on the websites side, or somewhere in between.
And the best way to figure out where the problem sits is by using Traceroute.
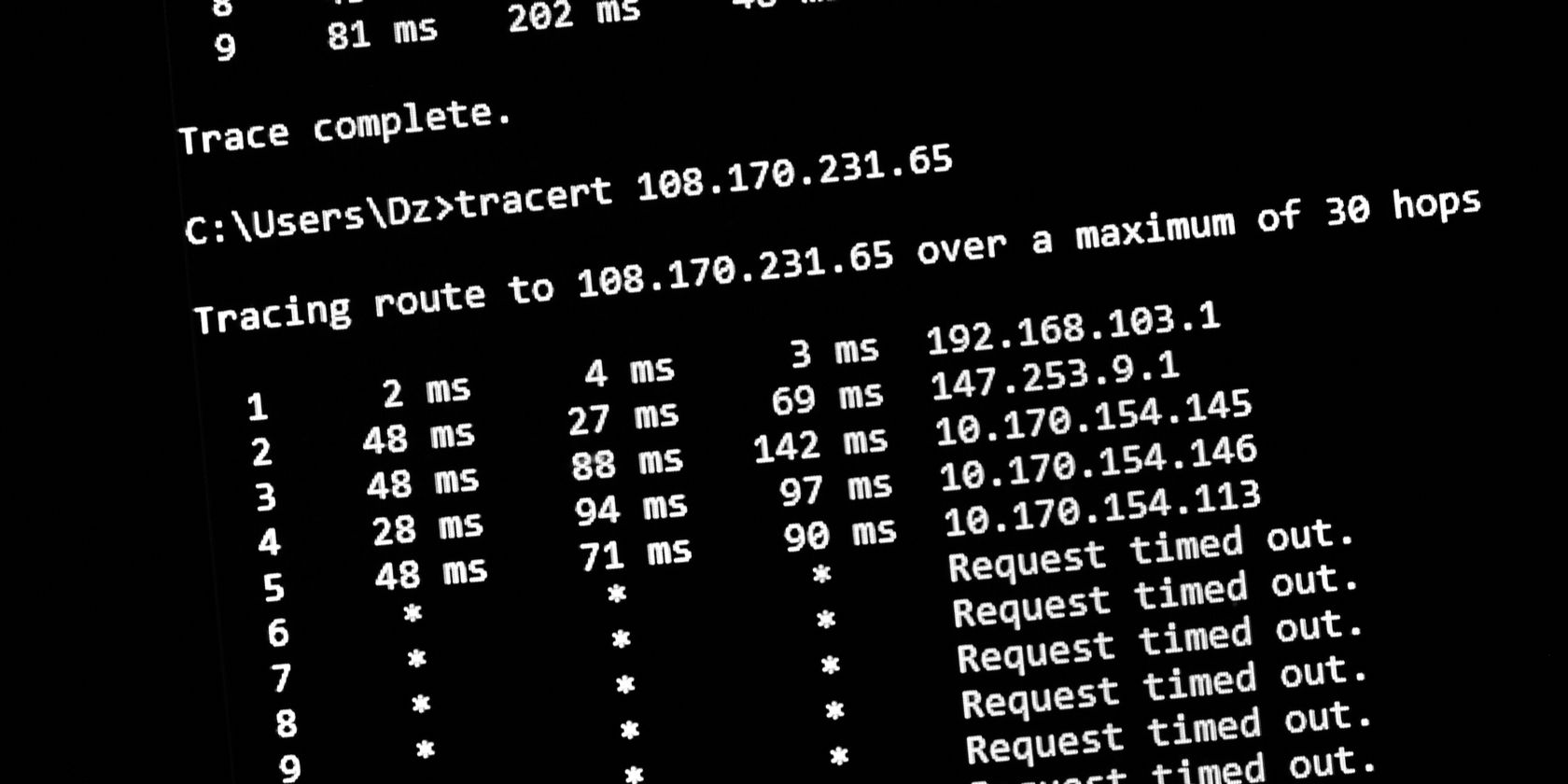
Image Credit: dennizn/Shutterstock.com
What Is Traceroute?
Every modern operating system can trace a route.
Once youve initiated Traceroute, it sends packets towards your set destination.
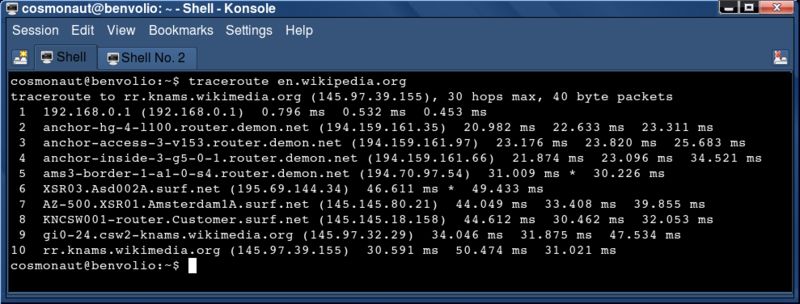
Running the traceroute command on Linux.
This is really handy if youre trying to find a fault on the online grid.
you’re able to then use this information to better diagnose what’s going wrong.
How Does Traceroute Work?
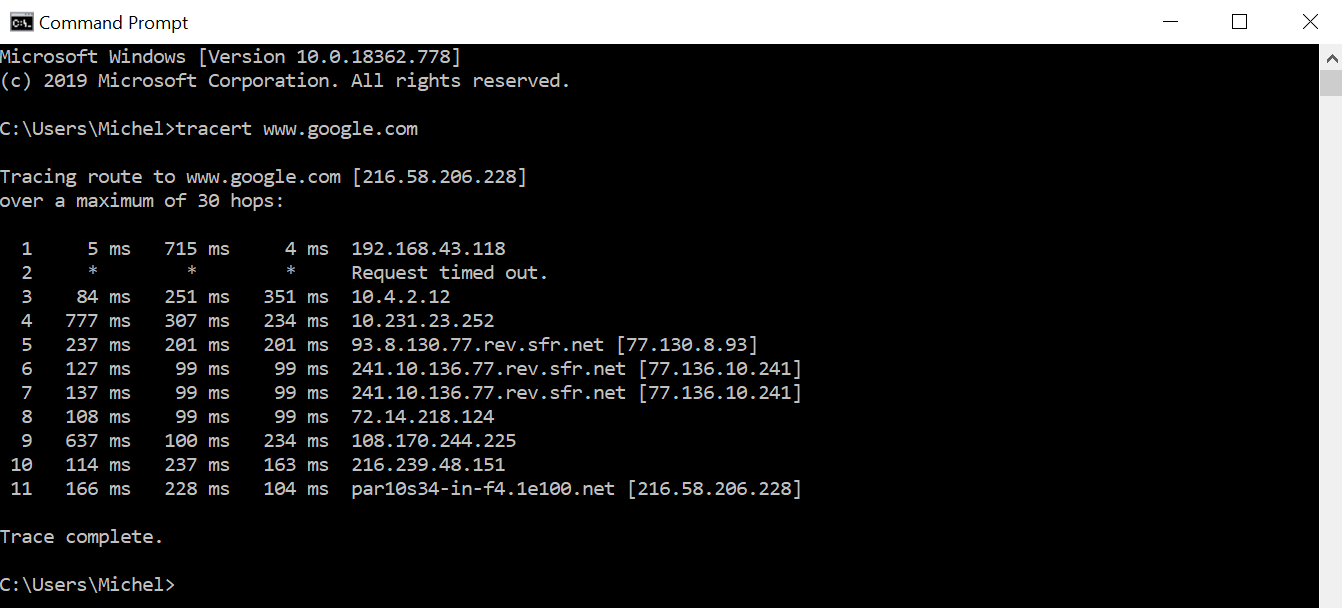
Image Credit: Michel Bakni/Wikimedia Commons
Traceroute is a handy way to diagnose web connection errors.
However, Traceroutes invention is all thanks to a clever exploit using a packet’s “Time-to-Live” variable.
What Is a Packet’s “Time-to-Live”?
Unfortunately, networks can be finicky things.
If this value ever hits 0, the packet is deemed “dead” and is destroyed.
When the packet is sent off on its journey, it will make multiple stops across different servers.
Every time it arrives at a server, it subtracts one off of its TTL value.
However, if the packet does enter a loop, the TTL will eventually decrement until the packet expires.
To start, Traceroute sends out a packet with a TTL set to 1.
Your PC then logs the servers location as the first step toward your target.
What Is Traceroute Used For?
At a basic level, Traceroute lets you take a peek at how packets move around a web connection.
However, its also useful for spotting errors in the system.
Whats the Difference Between Traceroute and Ping?
Technically adept readers will spot that Traceroute sounds very similar to another handy networking tool,Ping.
However, while the two features do overlap a little bit, people use them for different reasons.
As we covered above, Traceroute helps you figure out where a packet goes once it leaves your PC.
It’s as easy as opening a command terminal and entering the Traceroute command.
On Windows operating systems, it works the same way, except the function is called “tracert.”