This allows you to constrain specific operations of an tool to a single method.
Each step of the algorithm that the template method defines is an inner method.
However, the template method only handles the implementation of some of its inner methods.

Subclasses usually implement one or more of the template methods inner methods.
A subclass can implement an abstract method, but it cant redefine the algorithm implemented by a final method.
So, youll often see this pattern in software frameworks that provide the blueprint for app development.
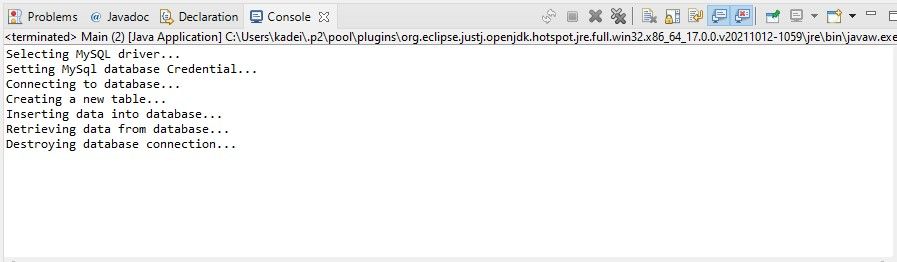
For example, you’ve got the option to connect your program to one of many database systems.
These activities are usually the same for all databases.
Therefore, the abstract Database class can implement theconnect()andcloseConnection()methods.
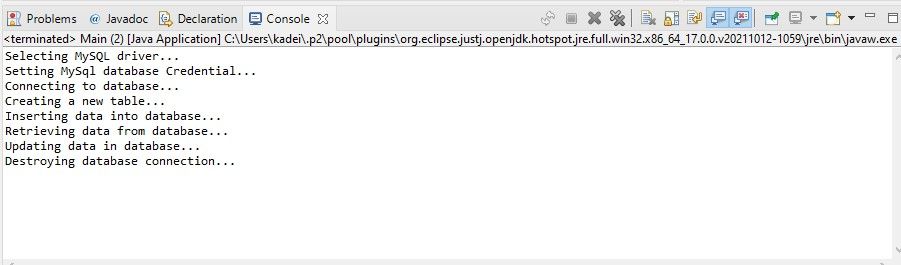
The other methods in the template method will differ based on the bang out of database.
For example, a MySQL database stores data in tables, while aMongoDB database stores data in collections.
It can also override some concrete methods.
However, it cannot touch thedatabaseTemplate()method, which uses the final keyword.
This is why the hook methods are important.
In an SQL database, youll want to create new tables, insert data, and view your data.
However, you might not want to update or delete data.
Therefore, the hook methods give subclasses the option to control these critical aspects of the algorithm.
This design pattern also supports efficient programming.
A subclass only needs to implement methods that are unique to its operation.