A processor executes programs either in User Mode or Kernel Mode.
But what is User Mode and Kernel mode, and what is the difference between the two?
Lets see what these modes are and why does a CPU needs to switch between these modes.

What Is “User Mode” in Windows?
When you boot up a program on Windows, it launches in User Mode.
Whenever a user-mode program wants to run, Windows creates a process for it.
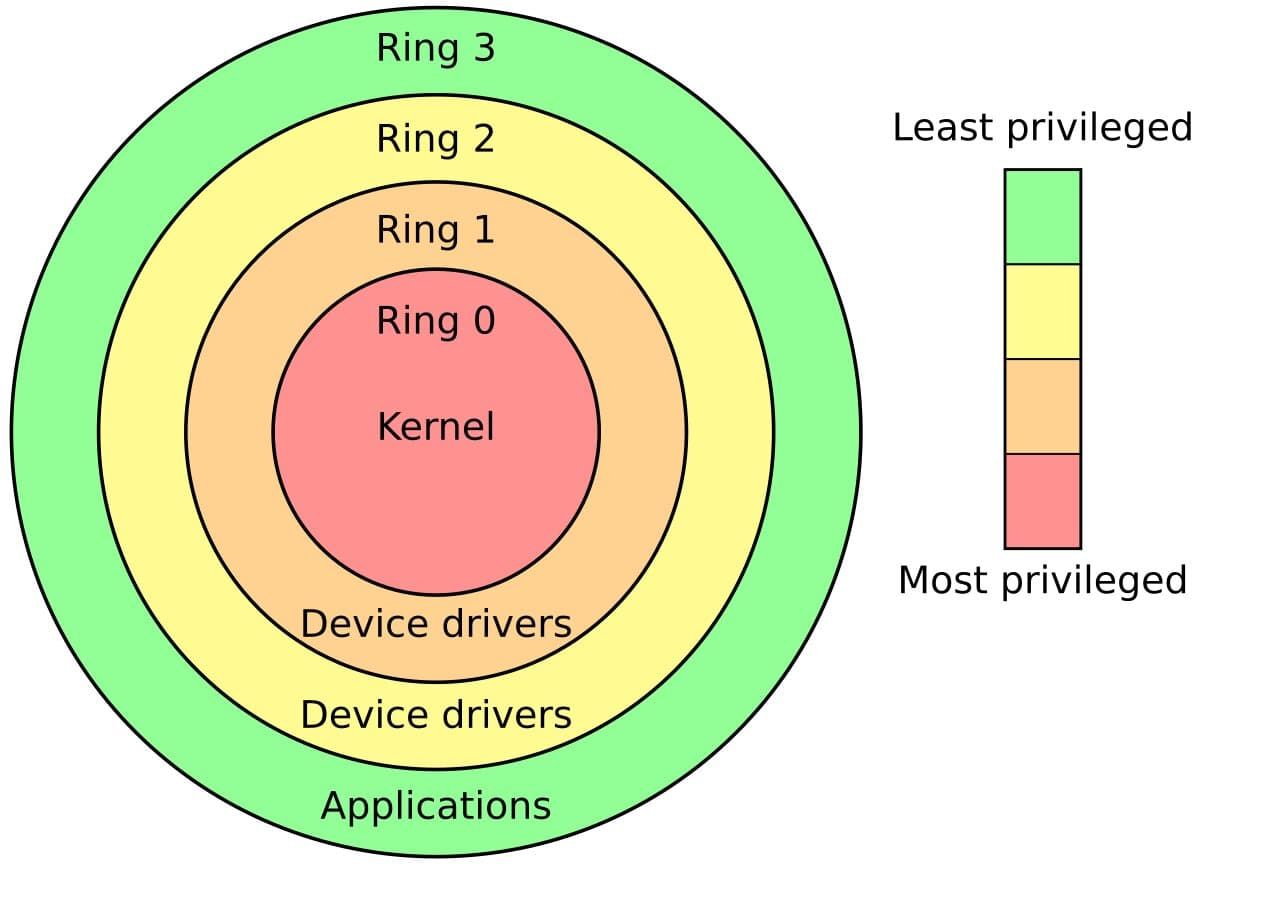
Image Credit:Hertzsprung/Creative Commons
And whenever Windows creates a process, it also creates a virtual address space for that process.
Avirtual address spaceis the collection of logical (non-physical) addresses that Windows assigns to a process.
Processes can use these addresses to store data on physical memory.
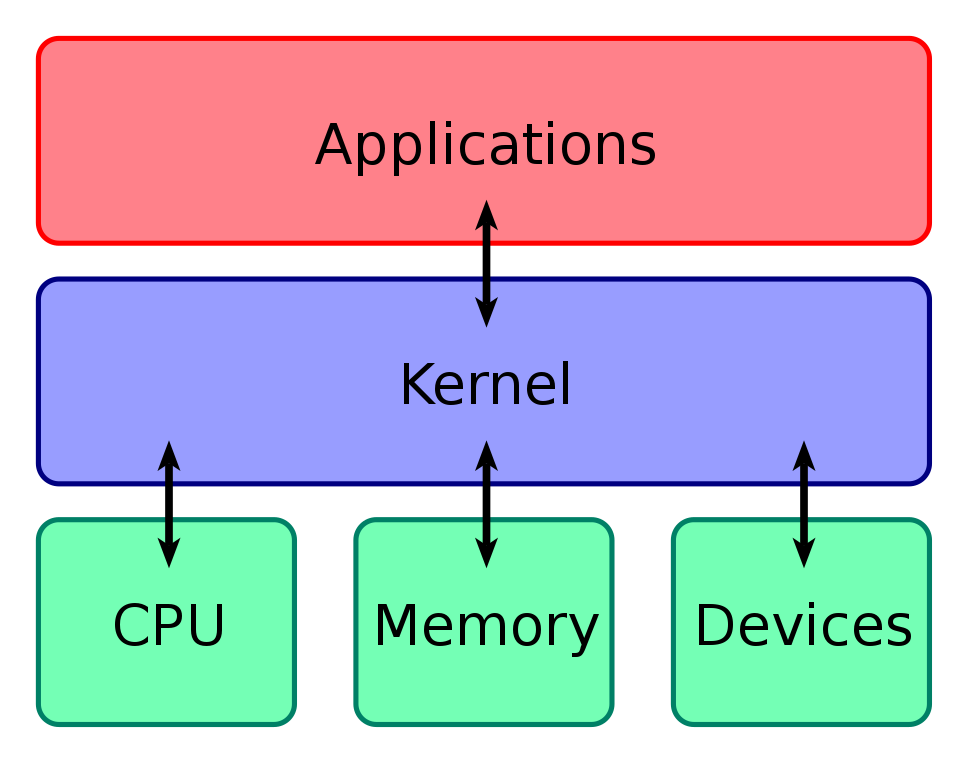
Image Credit: Bobbo/Wikimedia Commonms
Additionally, virtual address spaces are isolated.
So, one processs virtual address space doesnt interfere with another processs address space.
Windows restricts user-mode applications from accessing critical system resources directly thus making them less privileged.
Put simply, utility programs like video games run in user mode.
They are less privileged, so dont have unrestricted access to system resources.
Each user-mode tool has its own address space.
An utility cant change another applications address space.
Consequently, if one app crashes, it doesnt affect other programs running on the computer.
The kernel is the brain of an operating system.
It is the core software component that all the other components inside the OS rely on.
In short, the kernel is the most privileged piece of code running on the system.
That’s because it’s the code that directly interacts with the hardware.
Every other program that wants to use the hardware resources has to request access through the kernel.
This is called Context Switching.
What’s the Difference Between User Mode and Kernel Mode?
The key difference between User Mode and Kernel Mode is the level of privilege that each mode offers.
In User Mode, applications have fewer privileges.
So, if a program inKernel Mode crashes, it can take the whole OS down with it.
To ensure such crashes dont occur, Windows only allows some processes to run in Kernel Mode.
Applications that reside on the outermost layer are the ones with the lease privilege.
At the core of these layers is the kernel.
As a consequence, the kernel has unlimited access to OS resources.
The layered approach also protects vital OS functionality.
When programs in the upper layer crash randomly, it doesnt affect the OS.
On the other hand, when the kernel crashes, the whole OS goes down.