What Is PPA?
The world of free and open-source software (FOSS) relies on individual contributions.
Note that you shouldn’t confuse PPA on Linux with the medical condition Primary Progressive Aphasia.
Sometimes, these applications may not be merged with the official repository of the software.
This is where PPA comes to play.
Ubuntu allows developers to create PPAs and host them onLaunchpad.
Users can search for a package or repository on this site and add its PPA to their system.
How Are PPAs Different From Standard Repositories?
PPAs allow users to easily install and update software not provided by the official repositories of their Linux distribution.
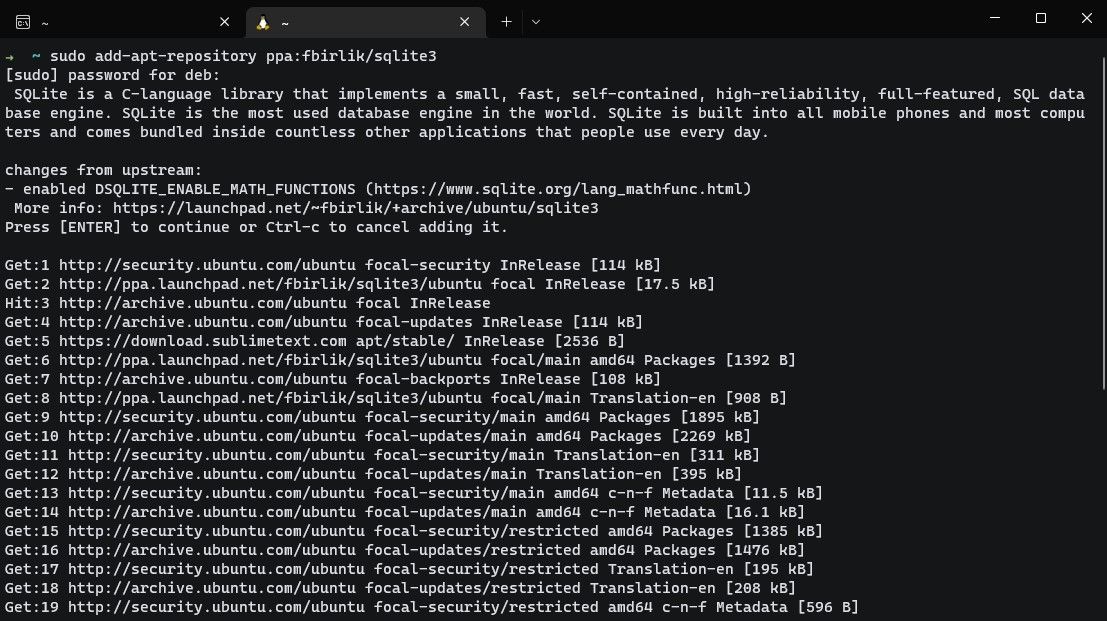
The default package manager on a distro generally manages these repositories.
Thankfully there’s a command that does all the work for you.
you’re able to now download software from that PPA using the default package manager on your distro.
PPAs are often created and maintained by third-party individuals or groups rather than the operating system’s official developers.
This can increase the risk of security vulnerabilities or other issues with the packages in the PPA.
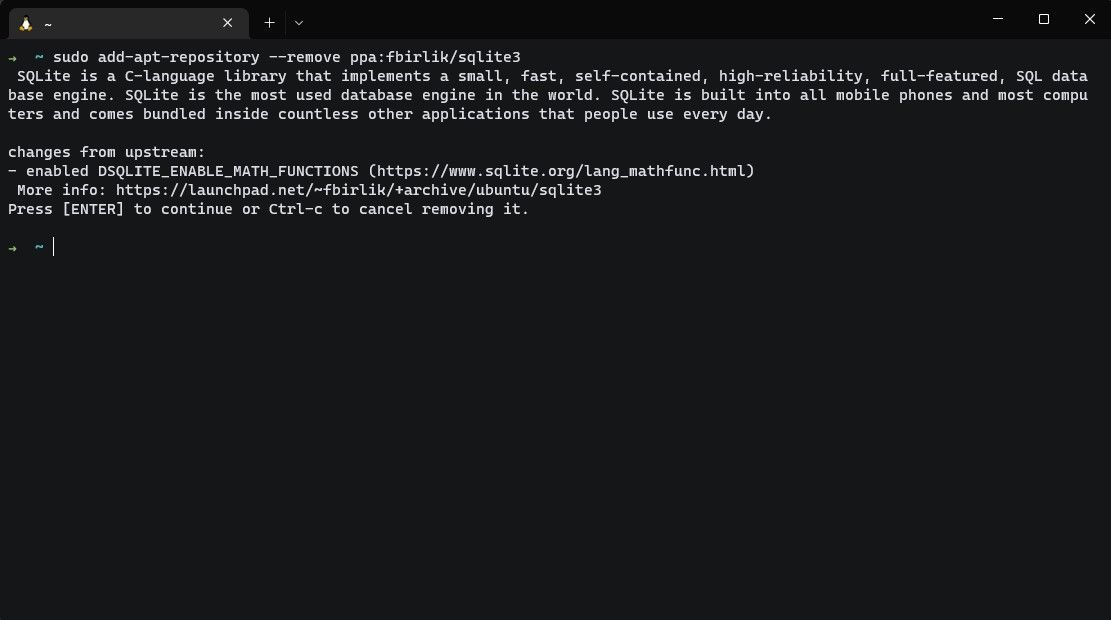
To test whether the process worked, try installing software that is part of the PPA you removed.
The package manager should throw an error.
Advantages of Using PPAs on Ubuntu
There are several advantages to using PPAs.
Let’s glance at a few of them:
PPAs are great when used with caution.
However, since these packages are not officially supported, sometimes, they may end up breaking your system.