One such thing is pixel binning.
But does it, really?
Let’s learn what pixel binning is, why it’s used, and how it works.

See, smartphones face a big problem when it comes to cameras: size limitation.
A camera sensor is basically a plate of millions of pixels that capture ambient light.
So, the more pixels there are, the more light they can capture to produce a better image.
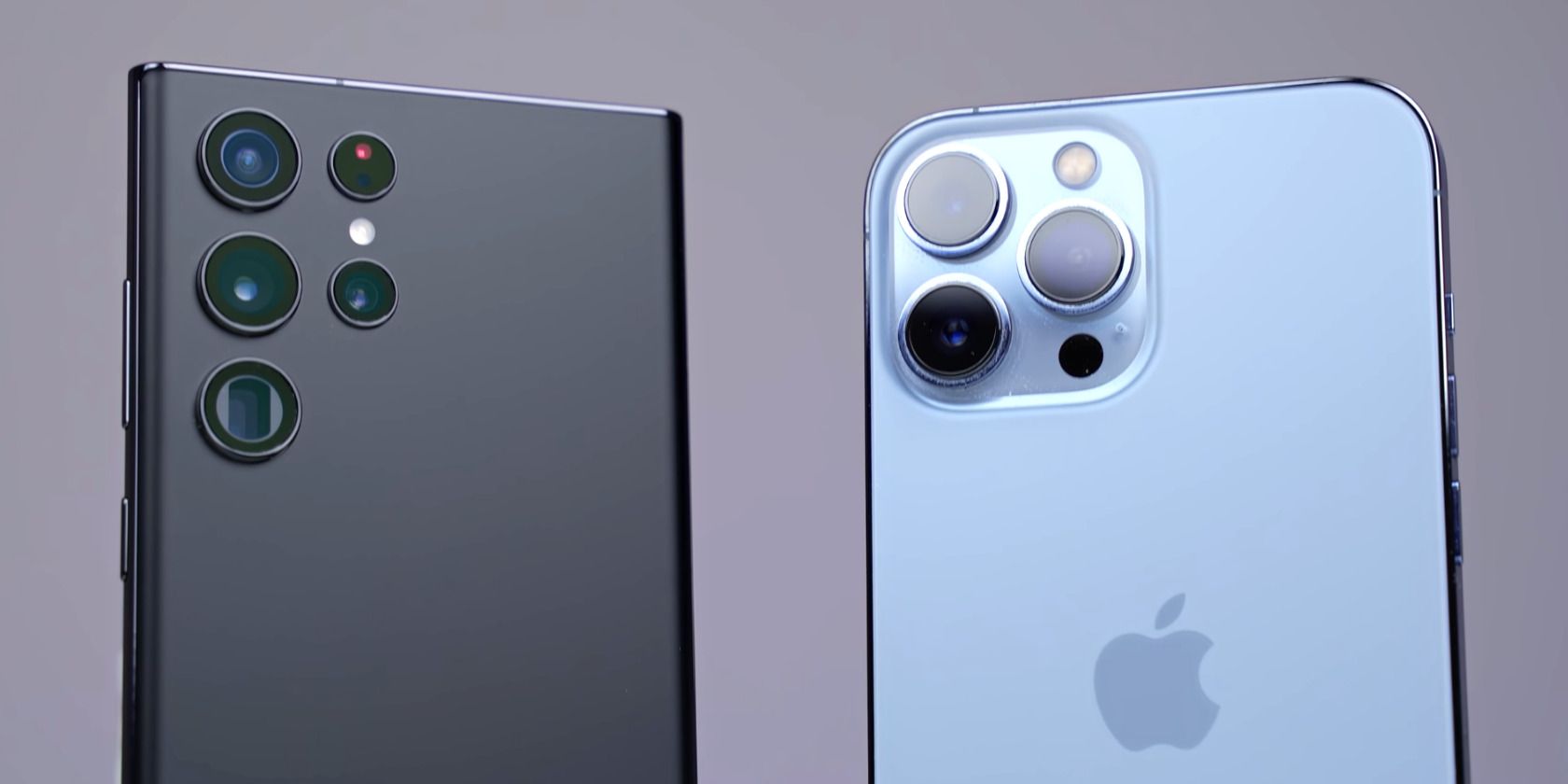

Image Credit: SuperSaf/YouTube
This light is then converted and used to produce the image you see on your screen.
To overcome this limitation, tech companies came up with a clever workaround.
What Is Pixel Binning?
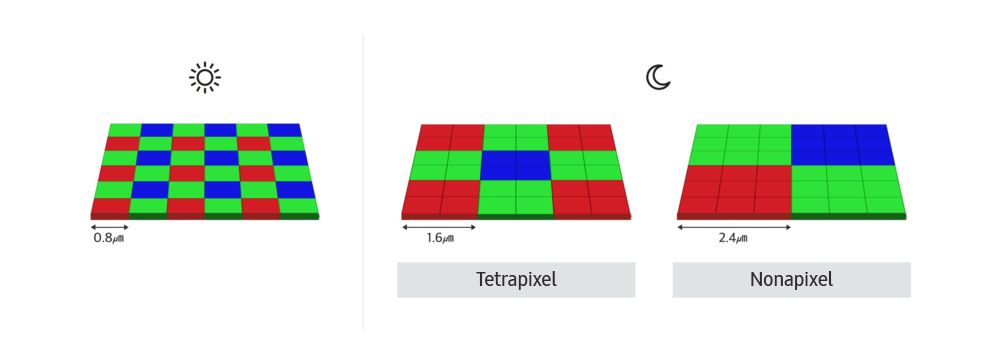
Image Credit:Samsung
How Does It Work?
Let’s understand this with an example using theiPhone 14 Pro Max and Galaxy S22 Ultra.
In contrast, shooting at full resolution adds excessive workload and takes much longer to process.

Also, remember that megapixels and megabytes are not the same things.
For example, the Galaxy A53 has a 64MP camera and does 4-in-1 pixel binning to give 16MP shots.
This is unnecessary because a larger individual pixel will always capture more raw light.
This is whyphotos from Samsung phones look over-processedsometimes while the ones from iPhones look more natural and consistent.
The number of megapixels determines the maximum image resolution that your phone is capable of shooting in.
Megapixel count tells you nothing about color science, white balance, dynamic range, or anything as such.
A smaller photo can be processed immediately.