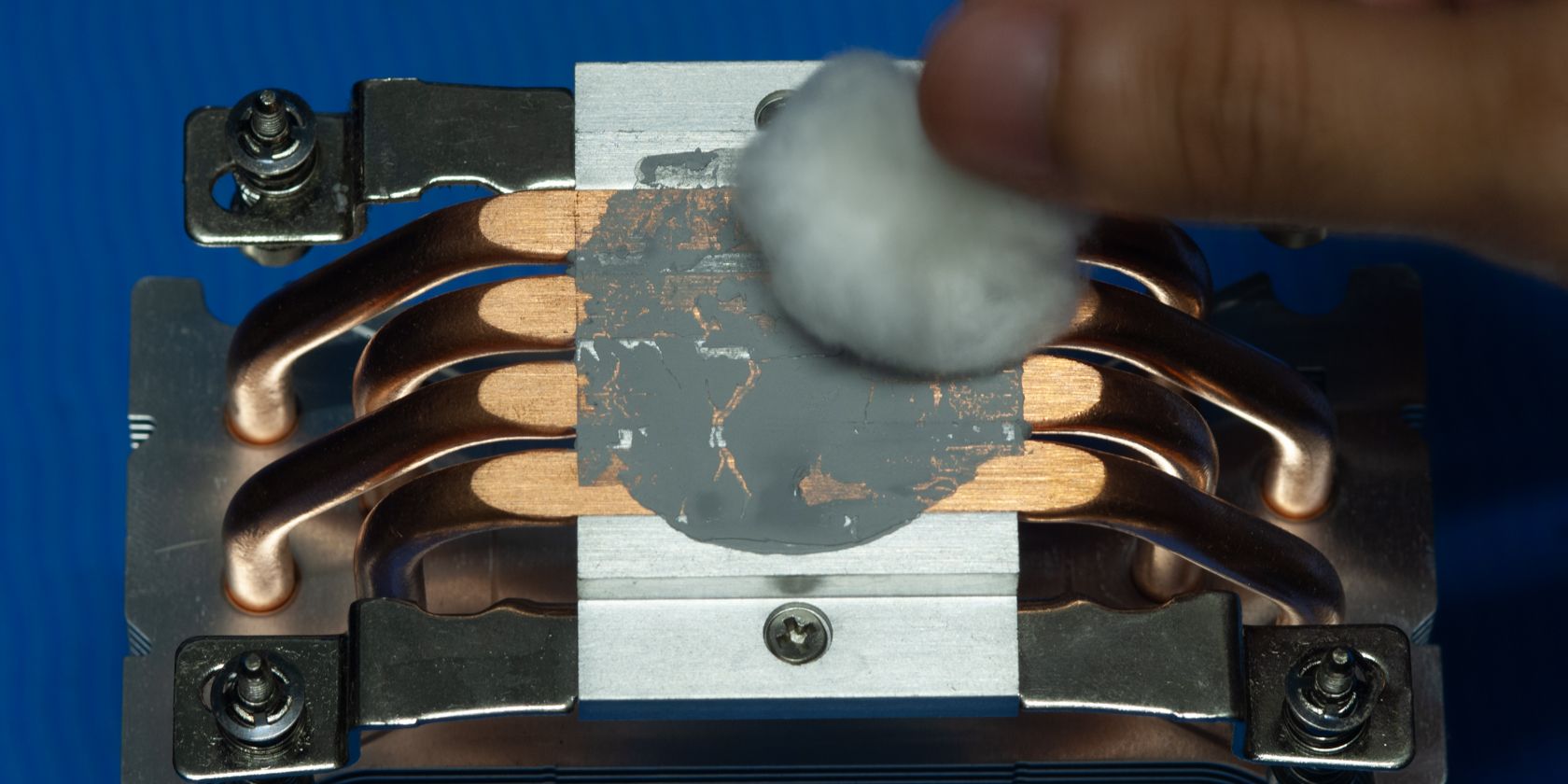
What Is CPU Thermal Throttling?
The more power your CPU is pulling, the more heat it generates.
Since overclocking pushes the CPU to reach higher clock speeds, it pulls more power and generates more heat.
Image Credit: Jhet Borja
To be clear, thermal throttling itself isn’t a bad thing.
How Does CPU Thermal Throttling Impact Performance?
The effect is especially notable on portable devices as they tend to have smaller power budgets and cooling solutions.
Image Credit: Jhet Borja
It can also lead to games outright crashing in extreme situations.
That’s a significant loss in performance.
The CPU’s power draw was also significantly reduced.
Ideally, your CPU should be running at 50-60 Celsius (122-140 Fahrenheit) when under no load.
Depending on your specific CPU load and degree of throttling, the mileage may vary.
How to peek if Your CPU Is Throttling
Checking for CPU thermal throttling is actually quite simple.
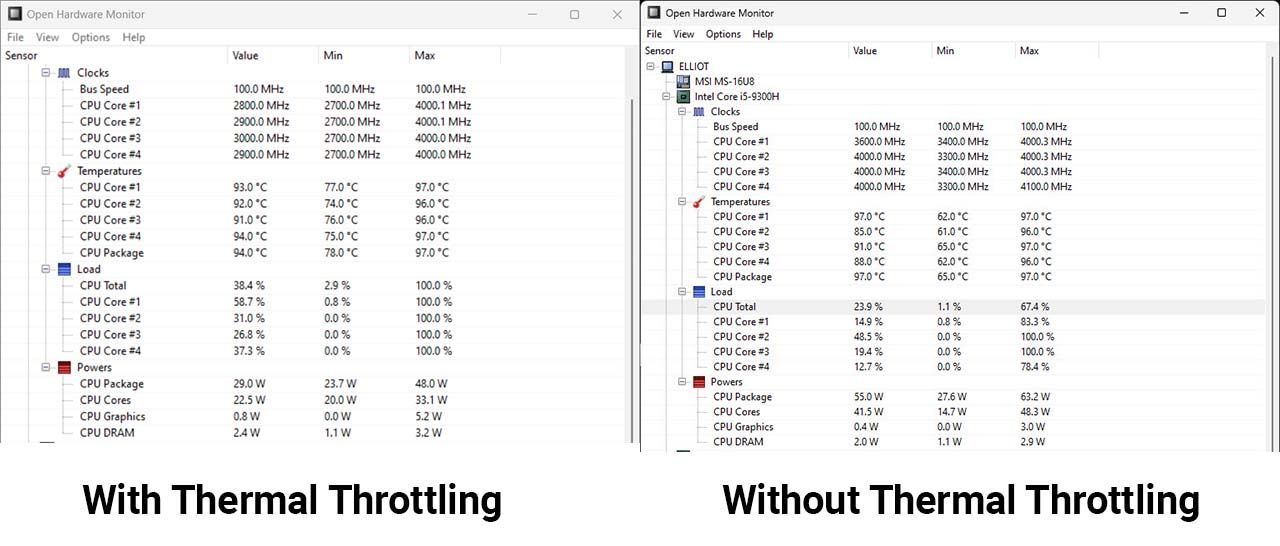
This will result in a performance loss and is a pretty solid indication of your CPU being thermally throttled.
Dust is the number one enemy of your box.
This also applies to water-cooled systems.
Image Credit: Jhet Borja
Thermal repasting can also help, as your thermal paste can dry out over time.
Or if you’re done with thermal paste,liquid metal is also an option.
But it is easier said than done for most of us.
Alternatively, you’ve got the option to also undervolt your CPU.
Undervolting involves lowering your CPU’s power consumption while maintaining consistent core and memory clock speeds.
That said, it does require some technical know-how.
These methods also extend to other PC components and can also be used toprevent thermal throttling on your GPU.
It’s not that hard, after all.