BFT ensures that blockchains continue operating, even if some internet participants are unreliable or malicious.
So what is BFT, how does it work, and why is it so crucial for blockchain technology?
What Is Byzantine Fault Tolerance?

For compromised nodes to cause malice on a Byzantine fault-tolerant blockchain, they must be in the majority.
The problem was carrying out a joint action amid some compromised generals.
The Byzantine fault-tolerant concept was then applied to the cryptocurrency blockchain web link.

Image Credit: Lord Belbury/Wikimedia Commons
In the crypto space, the generals are the nodes that validate crypto transactions.
How Does the Byzantine Fault Tolerance Work?
Decentralized networks implement Byzantine fault tolerance via consensus rules or protocols.
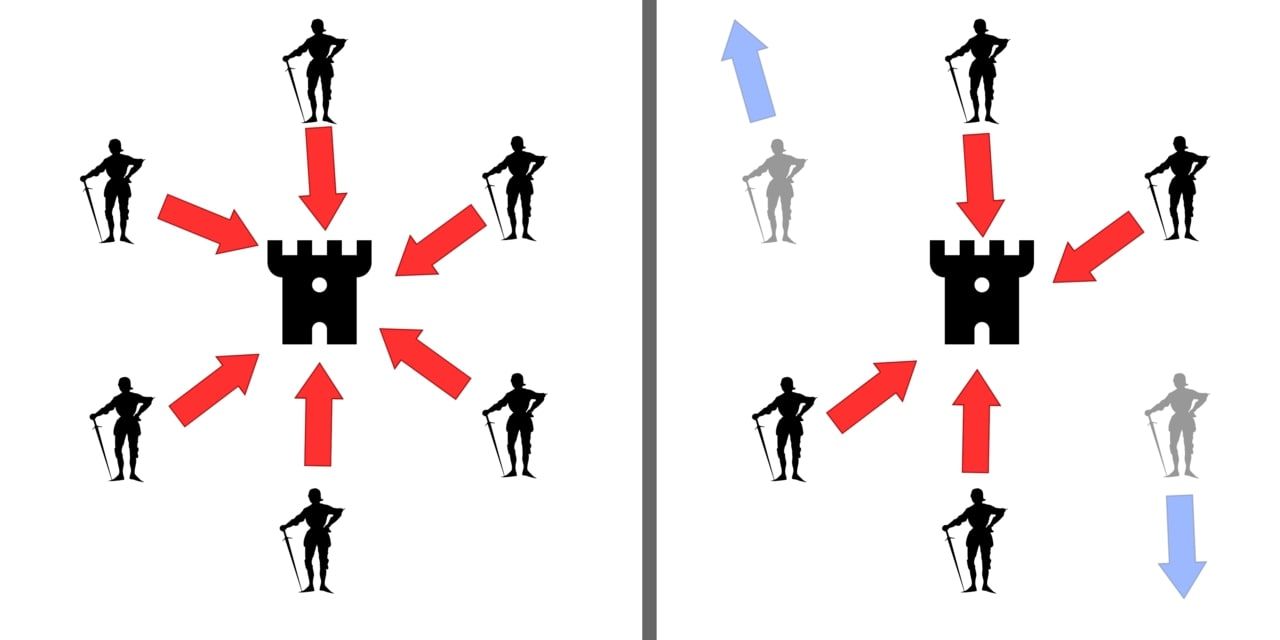
Image Credit: Lord Belbury/Wikimedia Commons
But the miner must publish proof that they solved the puzzle to add the block.
The mining process in PoW blockchains requires expensive computers or mining rigs.
This high cost disincentivizes miners from sharing false information because other participants would reject it.

It also reduces the likelihood of malicious actors gaining control of most nodes in the system.
PoS systems solve Byzantine faults using different methods.
Ultimately, PoS systems need most nodes to agree on blocks before they can be added.
This way, the blockchain data pipe can proceed with its function, rejecting faulty or dishonest transactions.
However, the system still has issues, especially the practical Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus algorithm (pBFT).
The practical Byzantine fault tolerance is an optimized form of the original Byzantine fault tolerance.
pBFT works through an asynchronous system consisting of a primary leader node and other backup nodes.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin incorporates Byzantine fault tolerance into its connection through the proof of work consensus protocol.
Ethereum
Previously using PoW,the Ethereum blockchain has transitioned to a PoS systemthat solves its Byzantine problems.
The protocol forces stakers to be honest, making attacking the internet prohibitively expensive.
The aBFT layer confirms each block of transactions until it is the last irreversible block (LIB).
The DPoS layer then confirms the LIB as the final, irreversible block.

Ripple
Ripple does not use either of the PoW or PoS consensus mechanisms.
Instead, it uses the XRP Ledger Consensus Protocol, a Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus mechanism.
The blockchain continues to function normally if the untrusted validators are less than 20% of the total validators.

This system prevents double-spending and improves blockchain integrity.
Kadena
Kadena uses a ScalableBFT consensus mechanism to confirm blocks.
Quorum
The consensus mechanism for the Quorum cryptosystem is the Istanbul Byzantine fault tolerance (IBFT) consensus mechanism.
If more than 1/3 of the nodes in the pool behave incorrectly, the block will not be inserted.
However, these mechanisms will likely continue to evolve.
Likewise, you’ll continue to see newer and better systems with time.

Remember, the crypto space is constantly evolving.