Well, let’s find out.
What Is Beamforming, and Why Do You Need It?
Before getting into beamforming and its advantages, it’s important to understand how traditional Wi-Fi routers transmit data.

You see, a traditional router uses radio waves to transmit data.
The router uses several antennas to create these waves and send them to your rig.
These ripples created by the router enable your equipment to connect to the internet.

That said, these waves get weaker in intensity as they travel longer distances.
You see, Wi-Fi routers that do not support beamforming send waves in an omnidirectional pattern.
But how does your router focus these beams of energy?

And how does it know your devices' location?
How Does Beamforming Work?
As explained earlier, your router uses antennas to generate radio waves.
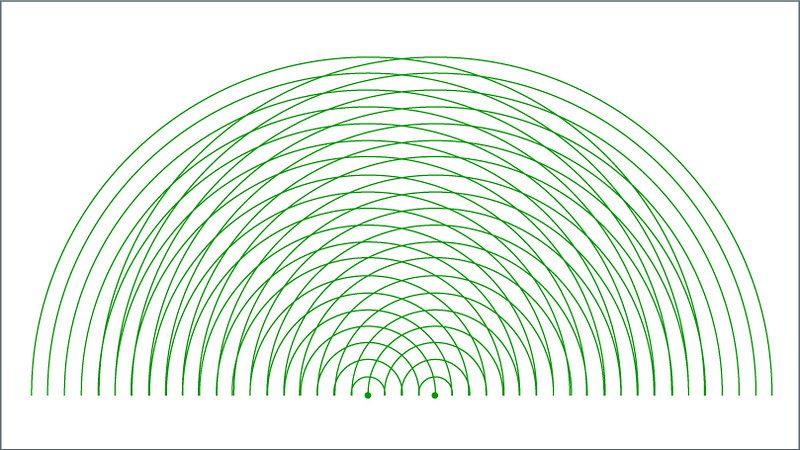
In most cases, these antennas can radiate energy in a uniform pattern.
Therefore, to create directed beams, routers use the concept of interference.
Simply put, interference refers to the variation in wave amplitude when two or more waves collide.

This variation in wave amplitudes can either be positive or negative based on the phase of the waves.
It is this variation in wave intensities that enables beamforming.
This difference in time and phase helps steer the waves toward your deviceimproving Wi-Fi strength.
This brings us to the second questionhow does your router know your gear’s location?
Well, to understand that, we have to look at the types of beamforming.
There are two ways your Wi-Fi can perform the task at hand.
Therefore, for explicit beamforming to work, both the router and your gadget should support it.
Explicit beamforming works by transmitting special beamforming data packets to your machine.
The machine uses this data to calculate the steering matrix.
Implicit Beamforming
Unlike explicit beamforming, implicit beamforming works even when your unit does not support it.
Instead, the router tries to understand signal patterns reaching the rig using acknowledgment frames.
The acknowledgment frame asks the router to resend the data if the data is not received.
That said, it also enables technologies like MIMO.
Short forMultiple Input Multiple Output, MIMO enables your router to send multiple data streams to your unit simultaneously.
Not only this, the multiple transmission of data streams increases data rates as well.
Understanding MU-MIMO
Both MIMO and beamforming improve the efficiency of Wi-Fi transmission exponentially.
That said, even after all these improvements, Wi-Fi has a flaw.
It can’t transmit data to multiple devices at the same time.
That said, Wi-Fi 6 tries to solve this problem.
Which Technologies Does Your Wi-Fi Support?
Nothing comes close to Wi-Fi when it comes to technical jargon.
Beamforming increases signal strength and enables features like MIMO and MU-MIMO.
These features improve the rate at which your router transmits data making it faster.