Blockchain and cryptocurrencies are a vast and complex landscape.
Many cogs go into this machine, including something known as a Merkle tree.
Merkle trees play a key role in blockchain functionality, but what exactly does it do?

How does a Merkle tree work, and why is it so important in blockchain technology?
How Does a Blockchain Work?
Before getting into the dynamics of the Merkle tree, it’s important to understandhow blockchains work.

Image Credit: Azaghal/Wikimedia Commons
Transactions on a blockchain cannot be altered or deleted.
Instead, using aprocess called hashing, data is encoded through mathematical algorithms.
These algorithms can convert any length of characters into a fixed, encoded length.
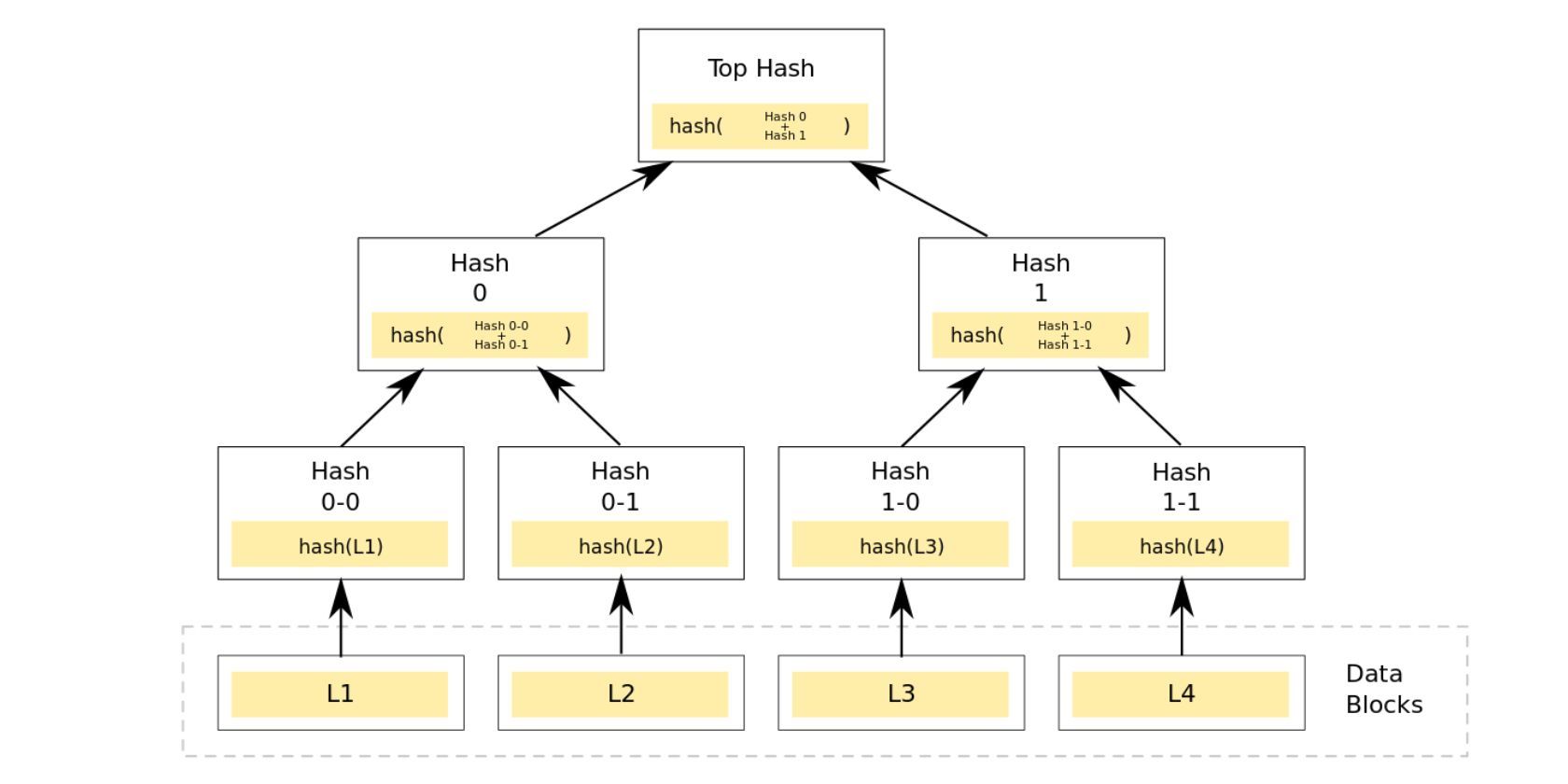
Image Credit: Azaghal/Wikimedia Commons
When recording transactions on a blockchain, Merkle trees play a crucial role.
But how does a Merkle tree work?
What Is a Merkle Tree?
The name “Merkle tree” has two origins.
Merkle also invented cryptographic hashing, which is used in the Merkle tree.
The second part of “Merkle tree” stems from its structure.
In short, a Merkle tree streamlines the process of storing transactional hashes on a blockchain.
Using a Merkle tree, the validity of the data can be quickly assessed through one final hash.
This simplifies the data storage process but also maintains security integrity.
Merkle trees also don’t require many computational resources.
So, using Merkle trees helps in mitigating this issue.
So, how does it work?
How Does a Merkle Tree Work?
Below is a diagram of how a Merkle tree works.
Looking at this Merkle tree diagram, things look a little complex.
But the process of Merkle tree hashing is quite straightforward when broken down.
There are a couple of steps that go into the Merkle tree process.
The branches are also sometimes referred to as non-leaf nodes.
The initial transactions from each node are hashed in pairs, with one hash remaining as the outcome.
The root is essentially the culmination hash of all the individual hashes of transactions stored within the block.
One Merkle tree is required per block, meaning each block has one Merkle Root data field.
Within a block exists something known as a hashMerkleRoot.
Can Blockchains Function Without Merkle Trees?
Without Merkle trees, cryptocurrency blockchains require more resources and time to carry out key processes.
What’s more, Merkle trees play a big role in data verification.
This nifty cryptographic process allows blockchains to operate seamlessly without the need for excessive usage of resources.