Here’s everything you gotta know about fstab and file systems on Linux.
What Is a File System?
Some common file systems include NTFS, FAT, ext4, etc.

The ext4 (extended filesystem version 4) is prominent on Linux and Unix Systems.
Each line is delimited by white spaces and contains the following six sections:
1.
File System
It contains the gear or file system the system should mount at boot.
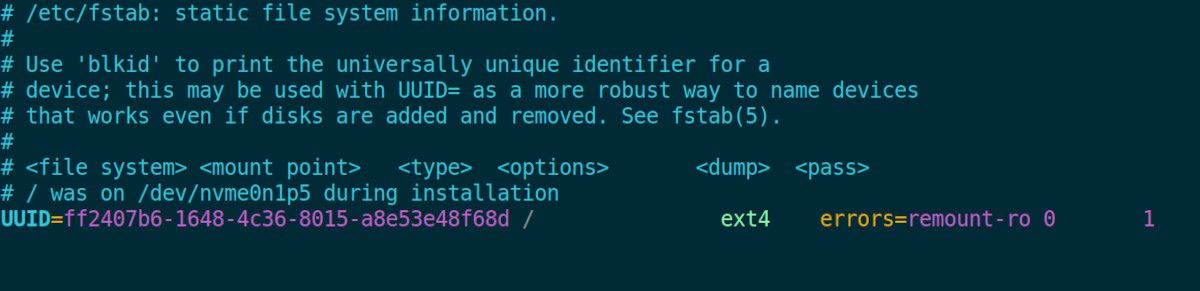
The mount command also utilizes fstab tomount a hard drive or any storage deviceswhenever you run appropriate mounting commands.
Mount Point
The mount point specifies the directory on which a storage unit should be mounted.
The system needs to mount each file system in the correct directory.
Options
A comma-separated list of mount options for the listed storage equipment.
The options control how your system mounts and uses the file systems.
Some common options include:
5.
Dump
This flag indicates whether the dump utility should back up the file system.
The default is 0, which means do not back up.
The fsck utility on Linux systems checks and repairs file system consistency.
The default value is set to 0, which means do not check the file system.
Mounting Storage Drives on Linux
File systems play an integral role in your Linux system.
Without a proper file system, it would be hard to manage and organize data on your PC.