DSPs are slowly becoming a staple of every modern audio product, so what exactly is a DSP?
Why are they important, how do they work, and how do they affect your listening experience?
What Is a DSP?

Image Credit:deepsonic/Flickr
DSP is an acronym for Digital Signal Processor.
As the name implies, a DSP is a microprocessor specifically designed for audio signal processing.
A DSP is basically a CPU optimized only to solve audio processing problems.

Image Credit:Ginoweb/Wikimedia Commons
Common DSP Uses
DSPs are used in all kinds of daily audio electronics.
Audio processing such as EQ and ANC requires the manipulation of these 1s and 0s to achieve wanted results.
A microprocessor such as a DSP is required to manipulate these binary numbers.

Image Credit:Ginoweb/Wikimedia Commons
Like any microprocessor, a DSP uses a hardware architecture and an instruction set.
Hardware architecture dictateshow a processor operates.
DSPs often use architectures such as Von Neumann and Harvard Architecture.
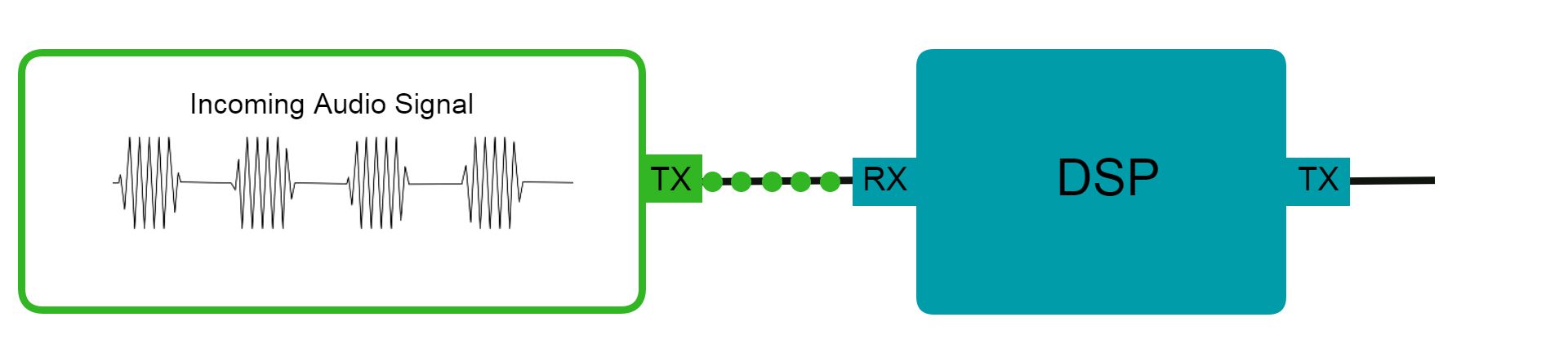
An ISA is what determines what operations a microprocessor can do.
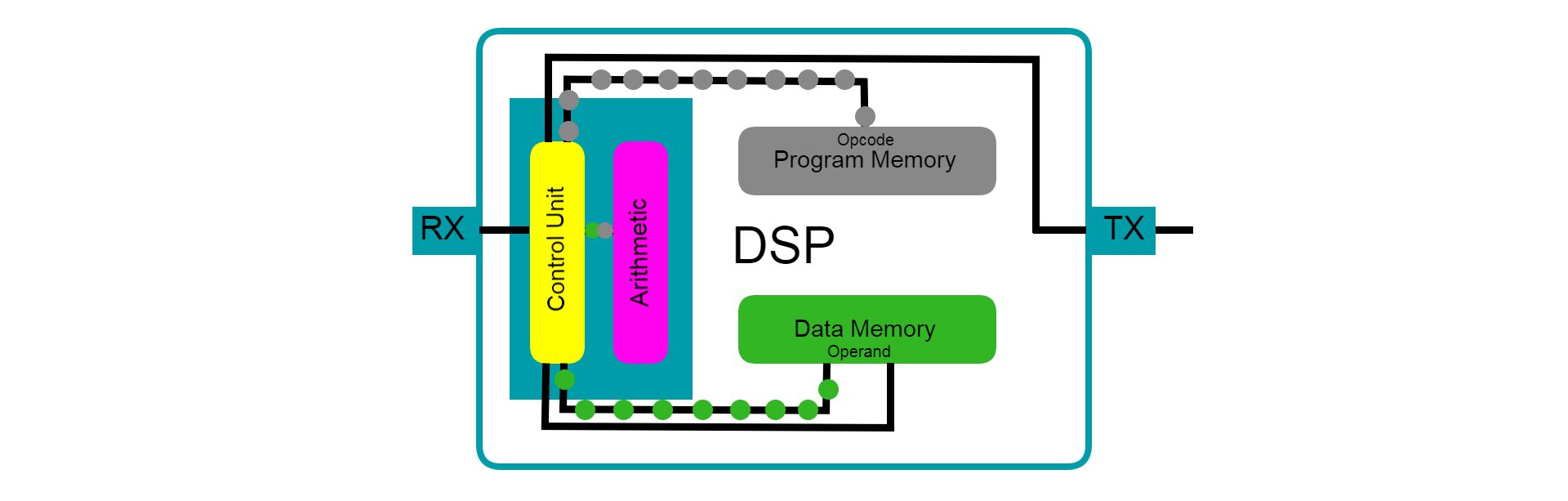
It is basically a list of instructions tagged by an operation code (opcode) stored in memory.
When the processor calls for a specific opcode, it executes the instruction the opcode represents.
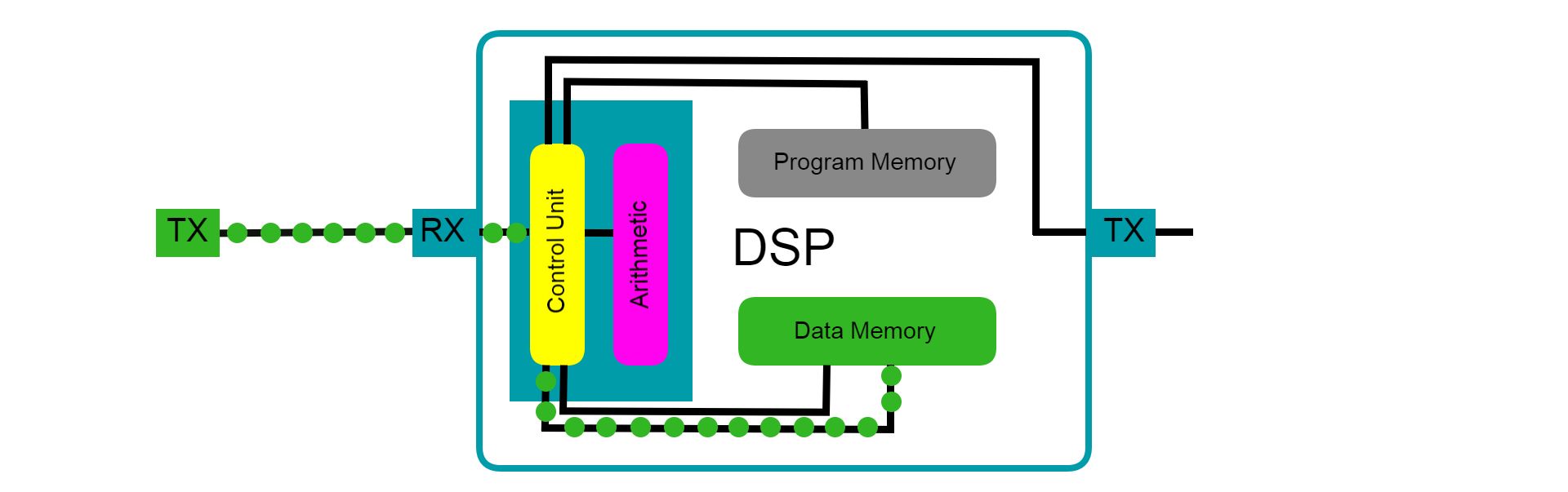
Common instruction within the ISA includes mathematical functions like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
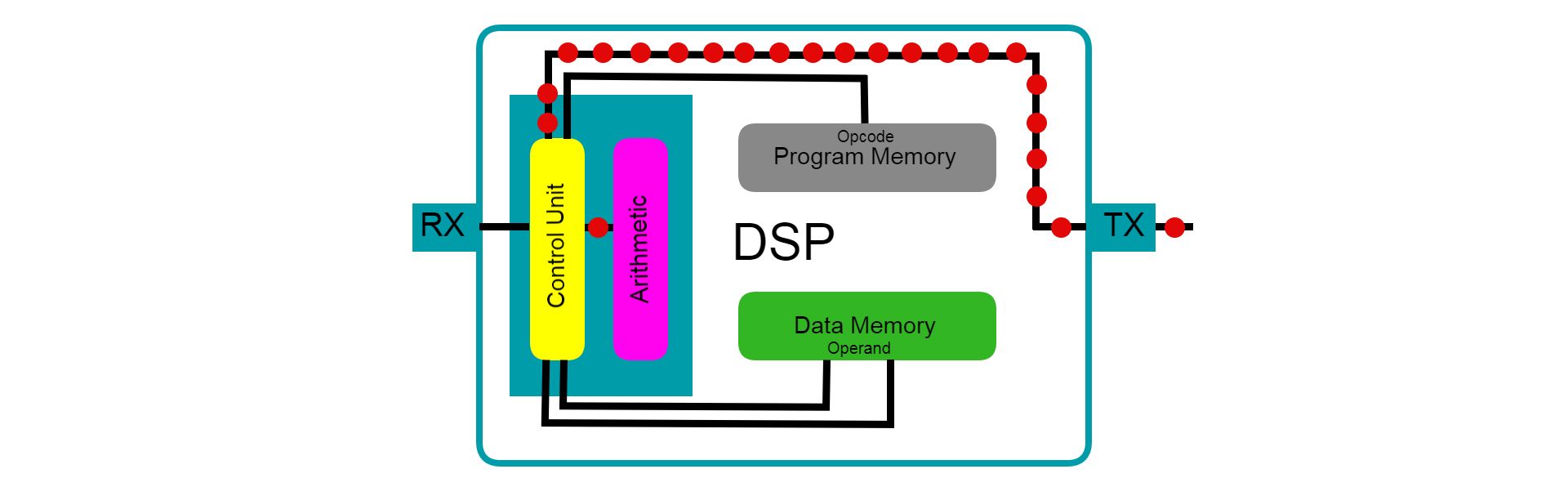
The biggest reason DSP is used over other microprocessors is real-time audio processing.
The simplicity of a DSP’s architecture and limited ISA allows a DSP to process incoming digital signals reliably.
With this feature, live audio performances can have equalization and filters applied in real time without buffering.
A DPS’s cost-effectiveness is another big reason they are used over general-purpose processors.
This makes DSPs easier, cheaper, and faster to manufacture.
Lastly, DSPs are easier to integrate with electronic devices.
DSPs Are Important Components in Modern Audio Devices
DSPs are important components of audio-related electronics.