Summary
Did you know hackers can steal your data in your RAM when your gear is off?
Cold boot attacks are a sophisticated threat that targets computer RAM, posing a serious risk to information security.
What Are Cold Boot Attacks?
Many cyber threats target software.
But cold boot attacks are a pop in of attack that is physical in nature.
The attacker’s main goal here is to cause the computer to shut down or reset.
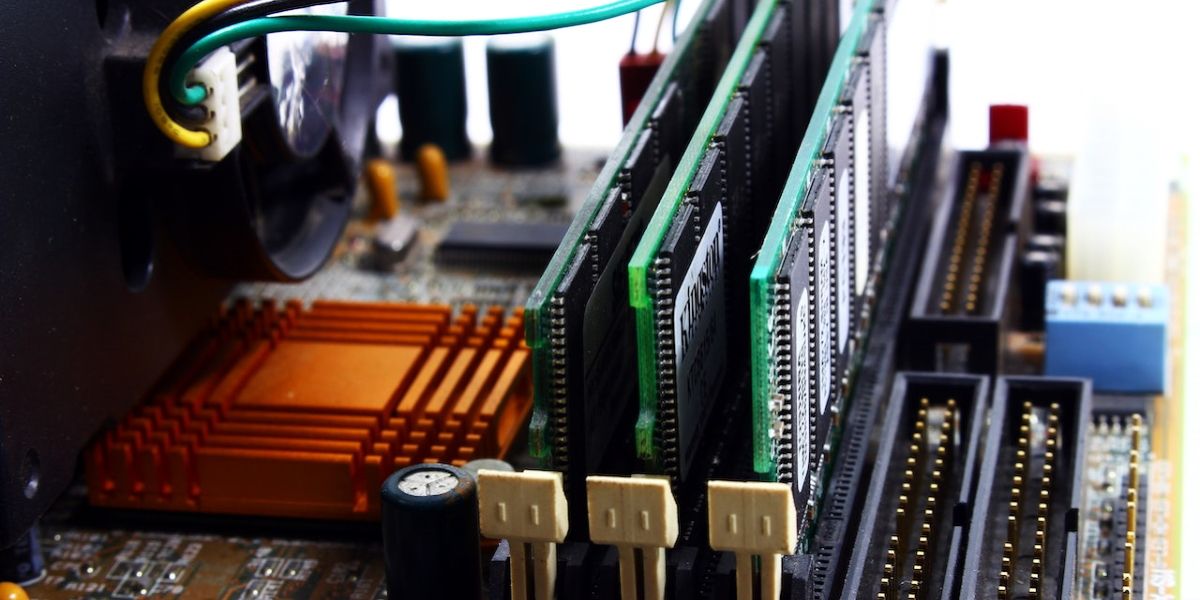

The attacker then tries to access RAM.
But, this process is not as fast as you expect.
It is possible to access data remaining in RAM, even for a short time.
Critical to a cold boot attack is the attacker’s physical access to your rig.
They usually perform this attack with a special bootable USB designed to copy the contents of RAM.
This USB allows your machine to reboot the way the attacker intended.
Cold boot attacks are a reminder that physical security is an important aspect of cybersecurity.
Still, protecting your setup from both cyber and physical attacks is always worthwhile.
How Does a Cold Boot Attack Work?
A cold boot attack focuses on a unique feature of RAM in computers.
As you’re able to imagine, if the power goes out, data stored in RAM disappears.
But it doesn’t immediately disappear like you might think.
So there is still time, albeit short, to recover your data.
This working principle underlies the cold boot attack.
Additionally, the attacker can use malware to transfer RAM contents to an external unit.
The data collected can include everything from personal information to encryption keys.
The attacker examines this data and looks for something valuable.
Speed is a very important factor in this process.
The longer RAM is without power, the more data becomes corrupted.
So, attackers need to act to maximize data recovery.
These attacks use the temporary nature of RAM and need physical access.
So, the first step is to secure your machine’s physical space.
This includes strict access controls for sensitive machines, especially in institutions.
It’s important to keep unauthorized people from accessing these computers.
Encryption keys are also usually in RAM.
It is also possible to lose encryption keys in a swift attack.
This reduces the risk of keys being extracted during a cold boot attack.
Another approach is configuring the computer’sBIOS or UEFI settingsto disallow booting from external devices like USB drives.
This can prevent attackers from using external bootable devices to dive into the RAM contents.
One method to mitigate this is using memory scrubbing techniques.
Understanding how RAM works, especially its data persistence, shows why we need dynamic, proactive cybersecurity.
Learning the working principle of cold start attacks will be useful for you to realize an important issue.
Protecting digital information is a continuous process.
Today, it is more important than ever to stay vigilant and adapt to evolving cyber threats.
Strengthening your defenses helps build a strong, resilient digital space.
This protects not only against cold boot attacks but other cyber threats, too.