Subversion is an open-source version tracking system.
It keeps files in a central repository and provides version control over directories or files.
Subversion also has a server component that you might use to host your projects.

It works much like an ordinary file server.
How to Install Subversion
Subversion is straightforward to install.
You’ll need a web server if you want to get into the Subversion repository via HTTP or WebDAV.
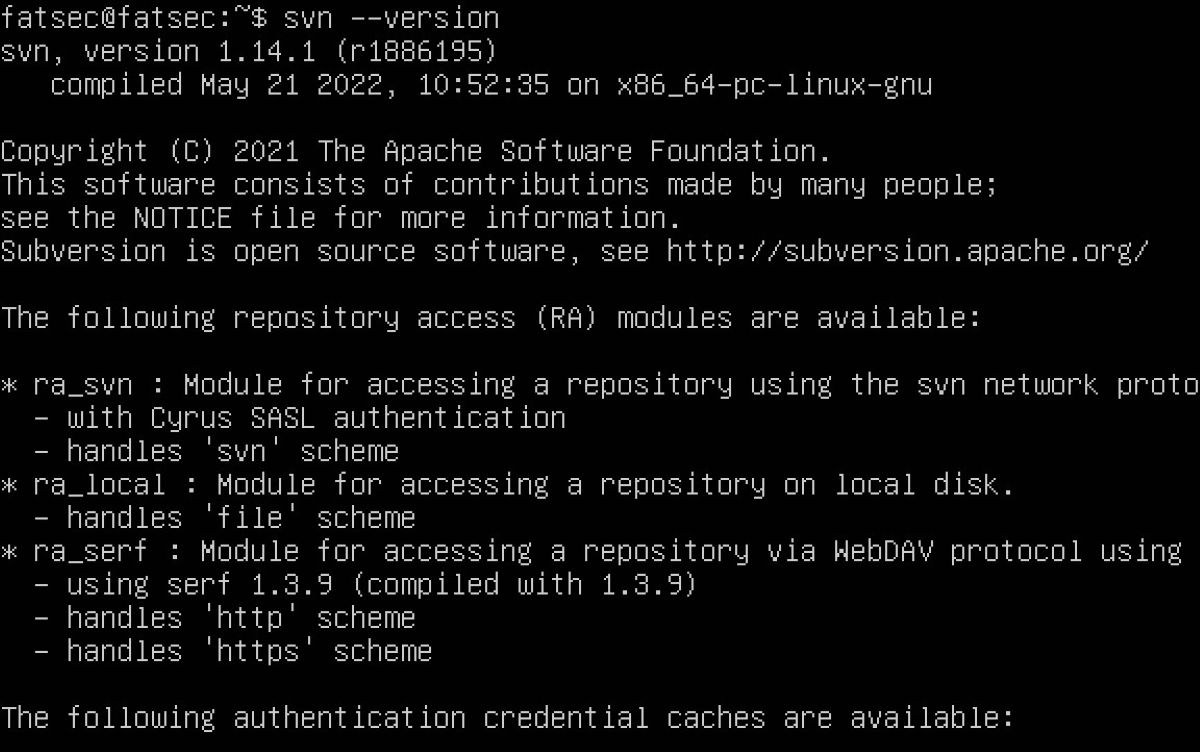
Once you’ve run this command, you could check that subversion installed correctly.
Of course, you’ll need to create a new repository for this.
you could change these values to whatever is appropriate for your circumstances.
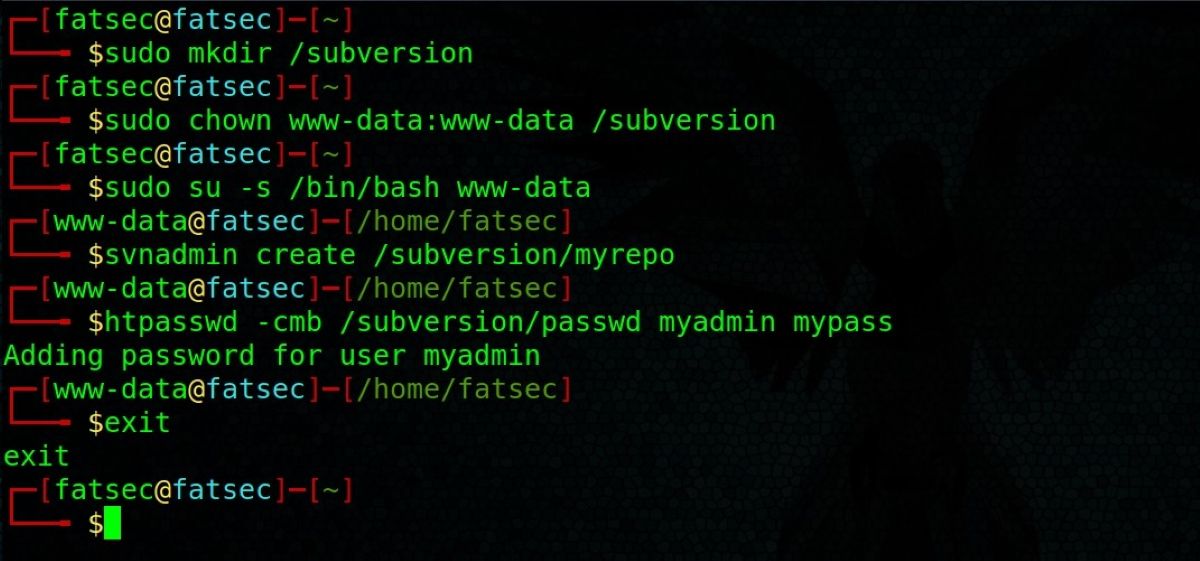
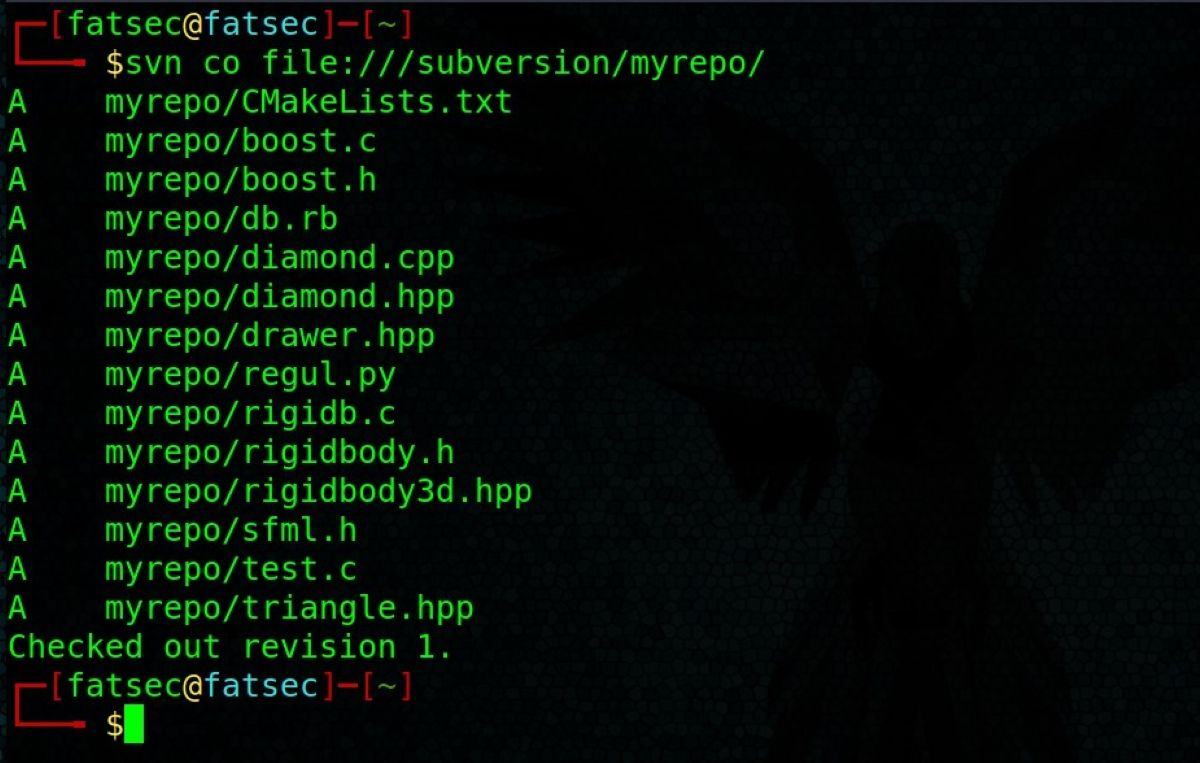
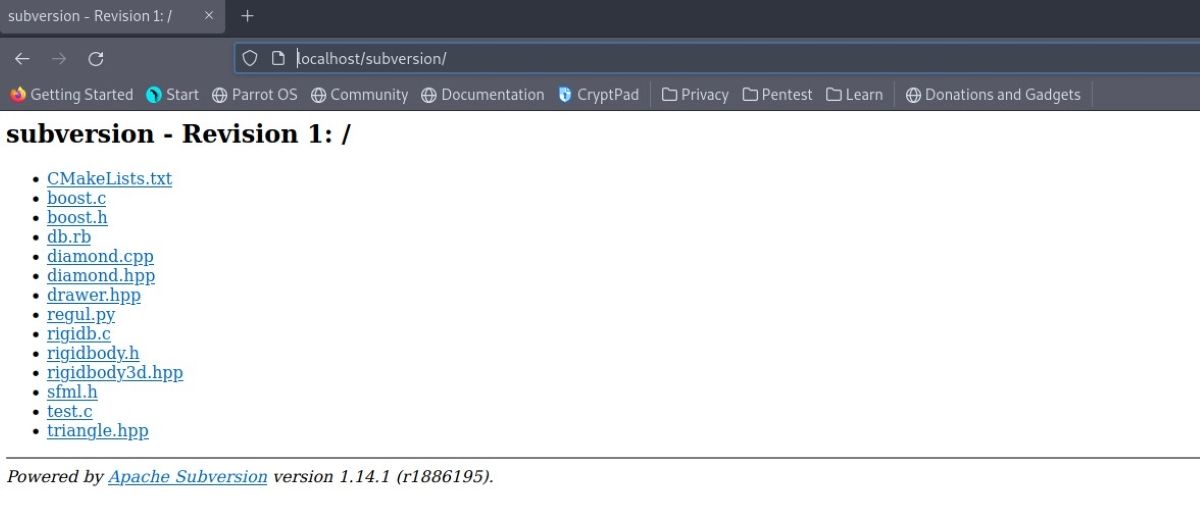
Your Subversion repository is now ready to use.
At this stage, you’re able to exit thewww-datauser by using theexitcommand.
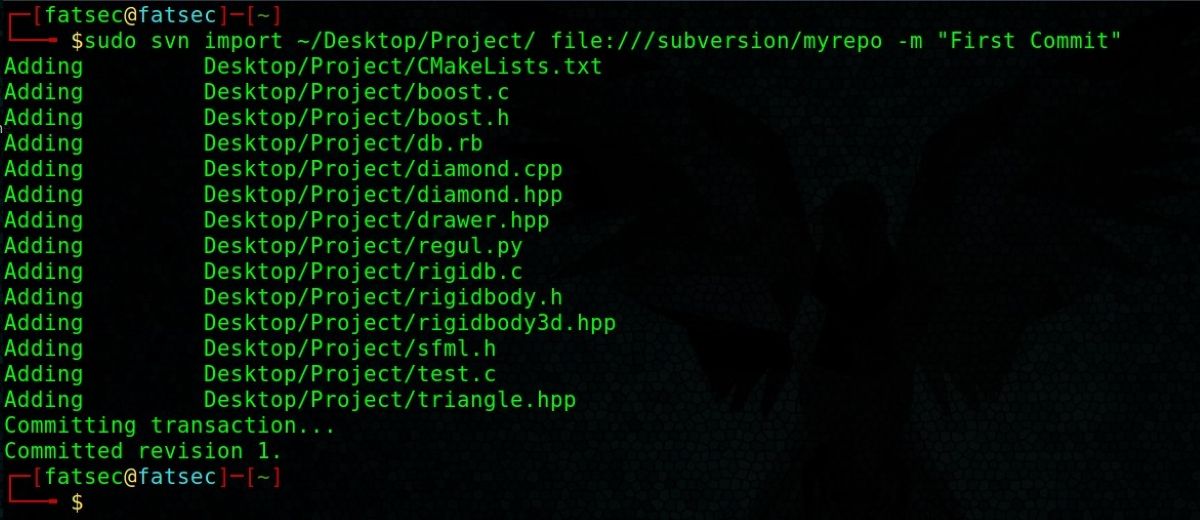
While doing this, you gotta add the commit message with the-mparameter.
you might also use the WebDAV protocol over HTTP or HTTPS, or subversions customsvnprotocol.
To give an example, the.conffile you oughta use during configuration is different.
You also need to install a digital certificate.
Because as you know, this is the working logic of theSSL encryption method.
You cancreate a digital certificateyourself, or you could install one issued by a competent authority.
Assuming you have installed a digital certificate, what you oughta do is simple.
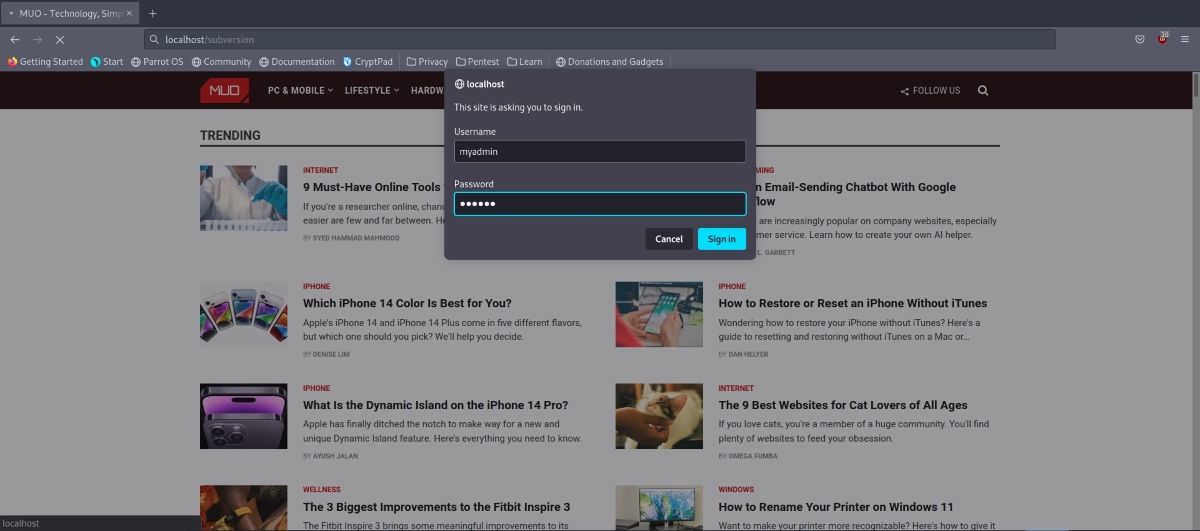
The difference in this step is the changes you will make in the configuration file.
After these changes, you’ll need to restart theapache2service.
Runsystemctl restart apache2.serviceto do so.
Why Use Subversion?
As a version tracker, Subversion remembers every change made to files and directories.
It lets you access old versions of software or documents you’re working with and find their differences.
This makes it easier to manage projects, especially if your development team is large or distributed.
There are many version control systems for Linux aside from Subversion, which you may want to consider.