As a programmer, you will often find yourself performing an action or task repeatedly.
This can be tedious and time-consuming, especially when working with a large or complex code base.
Automating them with functions is a more effective approach to performing such tasks.
Functions allow you to write the code logic once and use it anywhere in your program.
What Is a Python Function?
In Python, a function is a block of code used to perform a specific task.
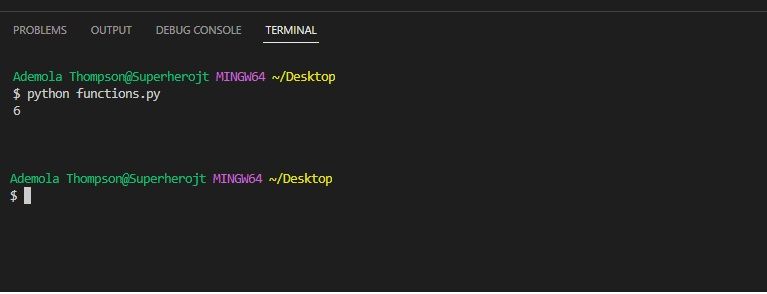
A function can take in arguments as input and return output values.
When the function is called multiple times, it returns a different output for each case.
A useful system for this function will be a calculator app.
Defining a Function in Python
Python has many built-in functionsavailable for developers to use.
However, these built-in functions are not always enough to meet the demands of most projects.
To meet custom demands, you have to define your custom functions.
Defining custom functions is common practice in programming.
you might write whatever logic you want your function to perform.
Understanding Function Arguments
In previous examples, the functions have taken arguments to perform actions.
The arguments in these examples are known as required or positional arguments.
Each argument represents a corresponding parameter.
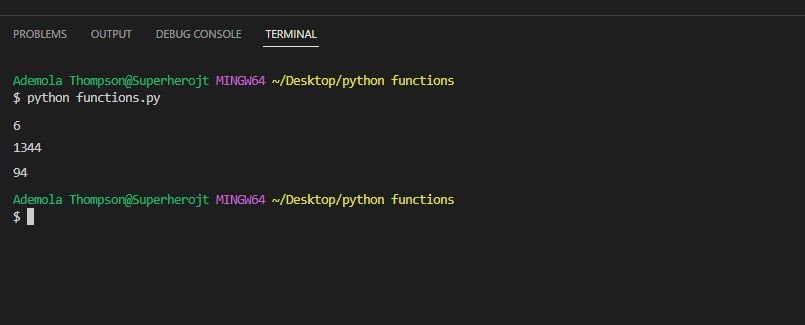
In the first function call, numbers1, 2,and3representa, b,andcaccordingly.
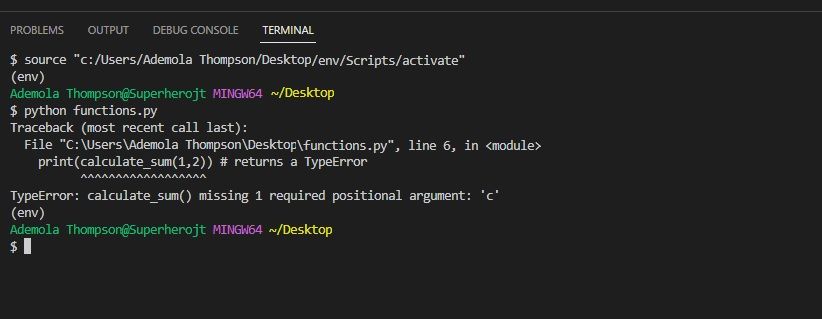
Positional arguments are compulsory.
If you dont add them, you will get aTypeError.
They are optional arguments and dont need to follow a specific order.
Python lets us use*args and **kwargsto specify keyword arguments.
Doing this will not get an error if you forget to add a value when calling the function.
you could specify default values for as many arguments as you want but ensure you do this wisely.