A database relationship describes the connection between different database tables.
The relations determine how to store and retrieve data.
Django works well with relational database systems (RDBMS).

It, therefore, supports database table relationships.
The types of relationships depend on the requirements of your app and the data it models.
Good relations between Django models and the database improve data maintenance.
That includes improving query performance and reducing data duplication.
Database Relationships
Relational database systems support three types of database relationships.
These relations are one-to-many, many-to-many, and one-to-one.
The throw in of database relation affects your tool’s use cases.
Django modelsrepresent database tables in the app.
You must create good relations between tables to create a good database system.
Database relations determine how to store and present data in your app.
To understand database relations, start bycreating a Django projectnamedHoods.The app will be a neighborhood social web connection.
It will manage various neighborhoods' social activities, security, and businesses.
Residents can register, sign in, and create profiles.
They can also create posts and business adverts for everyone to see.
To get started, create a database that will store all neighborhood data.
Then, you will create the Profile, NeighborHood, Business, and Post models.
To create the models, you must determine the relationship the database tables need.
The two records depend on one another.
In this case, theProfile modeldepends on theUser modelto create resident profiles.
So there can only be one profile for each resident registered on the app.
Also, without a user, a profile cannot exist.
Django’s User modelis a built-in authentication model in Django.
You don’t have to create a model for it.
Instead, import it fromdjango.contrib.auth.TheOneToOneField()on theProfile modeldefines a one-to-one relationship.
Theon_delete=models.CASCADEargument prevents the deletion of one of these records.
You must delete the records from both tables.
you might use the Django admin interface to visualize the relationship in your app.
To access to Django admin, you must register as an admin user known as asuperuser.
Once you’ve done so, start the server.
initiate the admin page in a web app using the URL http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin.
You will see the admin page where you could sign on with the credentials you created earlier.
Once logged in, you will see theGroupsandUsersobjects.
The Django authentication framework manages these two models.
At the bottom, you will see theProfile model.
Open theProfilemodel and proceed to add a profile.
The OneToOneField() data pop in allows you to create profiles for authenticated users.
This is how the app administers one-to-one relationships.
It is also referred to as a many-to-one relationship.
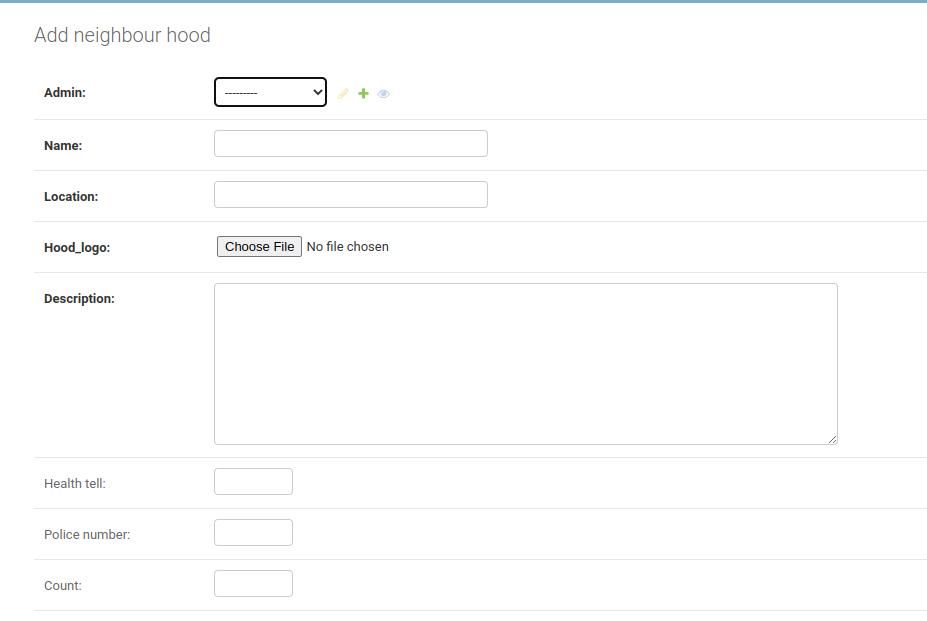
In your case, one admin can create several neighborhoods.
But each neighborhood can only belong to one admin.
you’re free to use the ForeignKey data jot down to define such a relationship.
Django has an in-built admin interface.
You don’t have to create a model for it.
The admin has the right to manage content and visualize the app from the admin panel.
The model that accommodates many records will have theForeignKey.
It defines the relationship as one-to-many.
The code below shows where to place the key.
For anyone to create a neighborhood, they must have admin rights.
And one neighborhood cannot have many administrators.
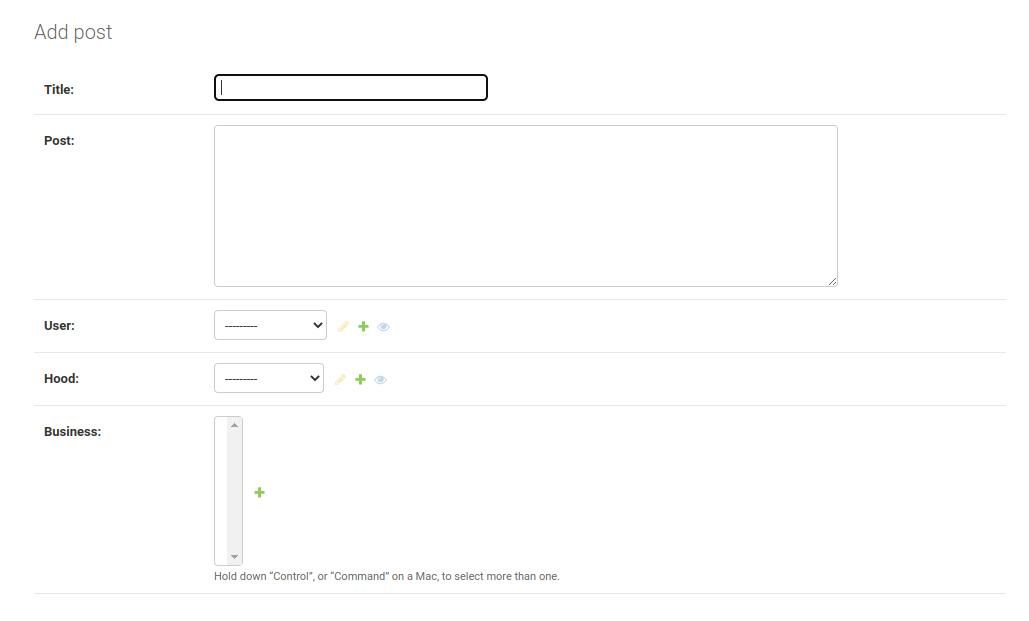
Many-to-Many Database Relationships
In many-to-manyrelationships, many records in one model associate with others in another.
For example, thePostandBusinessmodels can have several records of each other.
Users can make several business adverts in their posts and vice versa.
However, creating many-to-many relationships can lead to inaccurate data.
In other frameworks, you would have to create a new table to join the two tables.
Django has a solution for this.
Django has a comprehensive system that makes connecting and operating relational databases easy.
Django features make it easy to store and retrieve data from related tables.
It has in-built APIs that connect and create database relations for your app.
Database relationships determine the behavior of your tool.
Whether you use one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many relationships depends on you.
With Django, you might configure and test features without breaking your program.
Use Django to secure database systems and optimize your developer experience.