Youll probably have heard the word from Big Tech companies like Meta, Microsoft, and Google.
But what exactly is it?
What will it look like?

And how could it change our lives?
The metaverse is a online grid of 3D virtual reality worlds that are currently under construction.
When theyre complete, these spaces will be enabled by both existing and emerging technologies.
Plus a few that havent even been invented yet.
So, grab your VR goggles and lets go!
It will be characterized by decentralized networks and significantly greater user empowerment.

This environment is typically accessed through specialized equipment; usually a VR headset with a built-in screen.
In some cases, users may also wear sensor-fitted gloves that enable tactile feedback.
AR offers the potential to merge digital experiences with our physical surroundings.

Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchains use consensus mechanismsor pre-defined algorithmsto collectively verify the validity of changes.
Cryptocurrency
A digital currency that uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions.
Unlike fiat currencies, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized platforms (e.g.

blockchain) and are not governed by any central authority.
Unlike cryptocurrencies, each NFT has unique metadata and an identification code.
This identifier is recorded on a blockchain to signal the ownership of a particular digital asset.
Avatar
A 3D model or a 2D icon representing a user in a virtual environment or game.
Avatars provide users with a personalized virtual identity and help to facilitate user interaction in virtual worlds.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
The ability of computers or machines to perform tasks that usually require human intellect.
AI can interpret and learn from data or human language, recognize patterns, and solve complex problems.
Interoperability
The ability for different systems, devices, or applications to operate in conjunction with each other.
In the metaverse, interoperability would allow for a seamless experience as users navigate between different platforms and experiences.

What Is a Metaverse?
Picture the metaverse as a sprawling, virtual-reality landscape.
Using VR and AR technology, youll step into a universe thats rich, interactive, and multi-dimensional.
More than 100 years later, the Philco Corporation would create Headsight, the first motion-tracking head-mounted display.
Augmented reality started to emerge towards the end of the same decade.
Ten years later, wed get MUD1, considered the oldest virtual world in existence.
This text-based game introduced shared virtual spaces and laid the groundwork for what was to come.
The development of digital worlds and VR started to take off through the 80s and 90s.
Technology company VPL Research released the first consumer-ready VR goggles and gloves in 1988.
Then, in 1992, Neal Stephensons Snow Crash introduced the term metaverse into the English lexicon.
Once we had a name for this budding new world, things really got interesting.
By 2009, Bitcoin had emerged as the first decentralized digital currency.
Another important development took place in 2018, when Axie Infinity introduced play-to-earn mechanics in its virtual worlds.
As we reached the second decade of the 21st century, things began to progress even more quickly.
Decentraland launched on the Ethereum blockchain in 2020, providing a decentralized platform for virtual environments.
Microsoft also introduced Mesh, a mixed reality (MR) platform.
Most recently, in 2023, Apple entered the mixed-reality headset market with the release of Apple Vision Pro.
What Does the Metaverse Look like Today?
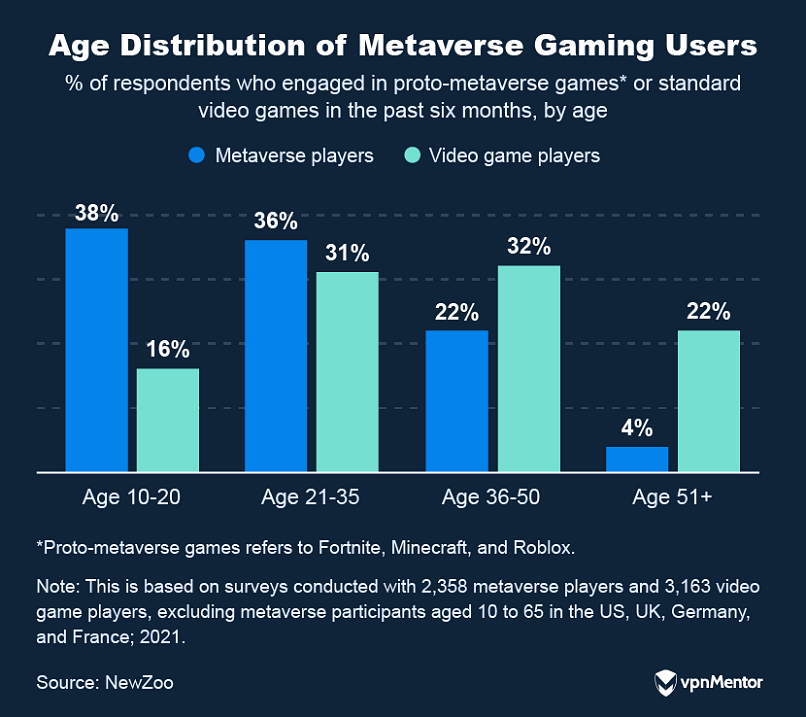
The metaverse industry is currently a bit like a digital Wild West.
A factor thats affecting how quickly the metaverse can be fully realized.
This, in turn, is affecting how people currently view and use these platforms.
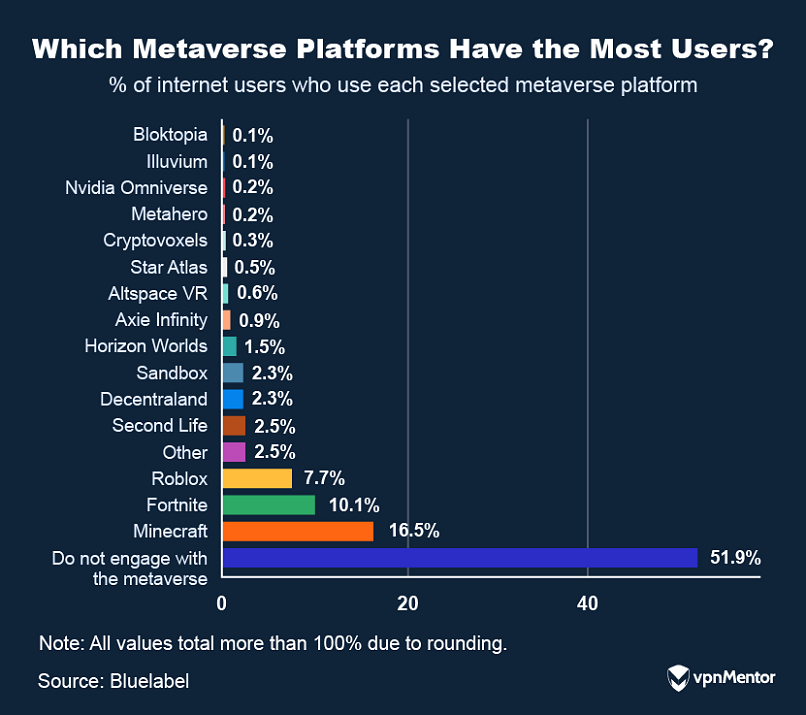
Only about 0.05% of the worlds population uses the metaverse each month.
Businesses believe that it will take at least five years for these worlds to become widely used by consumers.
We explore these in more detail in the Challenges Presented by the Metaverse section below.

What Could the Metaverse Look like in the Future?
Technologies Shaping the Metaverse
The metaverse is an evolving digital universe, shaped by cutting-edge technologies.
Lets look at how these technologies enable unique interactions within virtual worlds.
This contrasts traditional cloud computing, where data must be transferred to distant centers for processing.
Robust online grid infrastructure, including technologies like 5G and edge computing, is the foundation of the metaverse.
Imagine being in PixelVerse, talking to a friend from Japan.
Web 3.0 is the third evolution of the internet; i.e.
the interface that allows users to access documents, applications, and multimedia online.
Its envisioned to be a decentralized version of cyberspace, offering users more control, security, and connection.
This concept is crucial for understanding the underpinnings of the metaverse and the technologies that enable it.
In PixelVerse, the principles of Web 3.0 come to life.
This marks a significant shift from the more centralized and corporate-controlled Web 2.0.
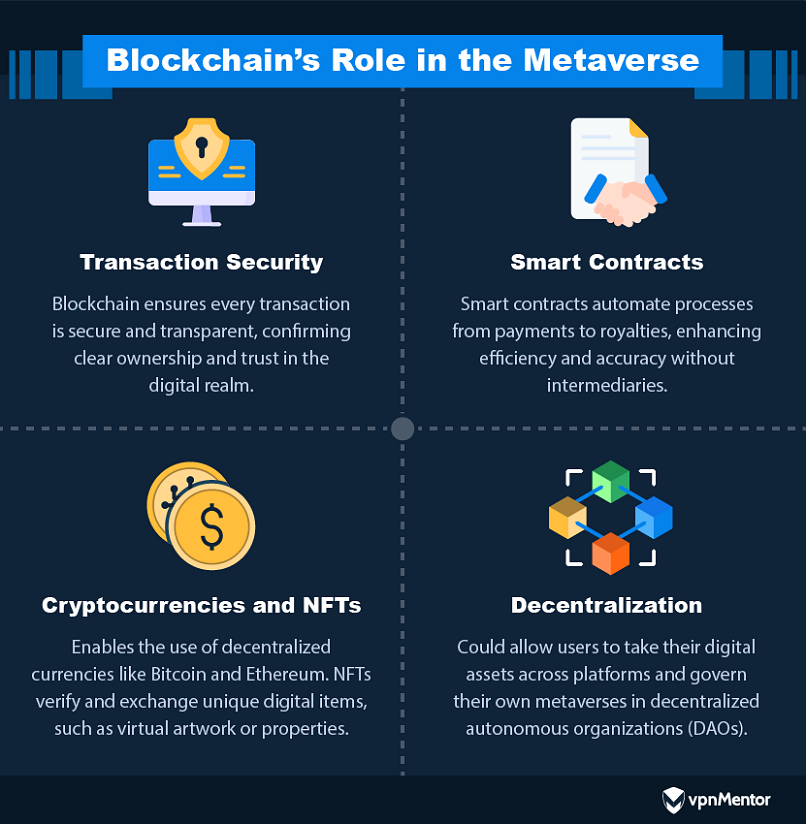
Blockchain technology and smart contracts are at the core of the metaverses transaction system.
Blockchain acts as a decentralized ledger, recording transactions securely and transparently.
Smart contracts, which operate on this blockchain infrastructure, are automated agreements.
The integration of blockchain and smart contracts is essential for facilitating transactions with cryptocurrencies and NFTs in the metaverse.
They represent a shift towards more user-driven financial interactions in virtual environments.
In the metaverse, NFTs act as a means to authenticate and trade these digital assets.
Their legal status is still being defined in the physical world.
Lets consider PixelVerse for a minute.
You opt to use Bitcoin for the transaction.
This purchase, and the transfer of ownership, is recorded on the blockchain as an NFT.
This technology is required for tasks such as language translation, sentiment analysis, and conversational interfaces like chatbots.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) significantly enhances user experience in the metaverse.

It integrates into avatars, enabling them to mimic real-world gestures and emotions in real time.
NLP is a crucial AI component that enables computers to understand and generate human language.
It uses algorithms to interpret speech or text, facilitating natural interactions between users and the virtual environment.

Imagine youre exploring a bustling virtual marketplace in PixelVerse.
As you interact with various NPCs, AI brings these characters to life with dynamic responses and realistic behaviors.
As you move through the marketplace, other NPCs react to your presence and previous interactions.

Moreover, IoT technology enables you to control real-world devices from within the metaverse.
As you enjoy the virtual sunshine, the weather shifts, and it starts to rain.
Thats thanks to IoT technology.

It represents a broad spectrum of technologies that merge digital and physical worlds to enable immersive experiences.
Augmented Reality (AR)
AR involves overlaying digital content onto the real-world environment to enhance it.
Think Pokemon GO, where digital objects are added to the real world but not integrated into it.

Imagine youre exploring a virtual mall in PixelVerse.
You spot a pair of jeans youve been eyeing.
Using SC, you enter the shop for a virtual try-on.

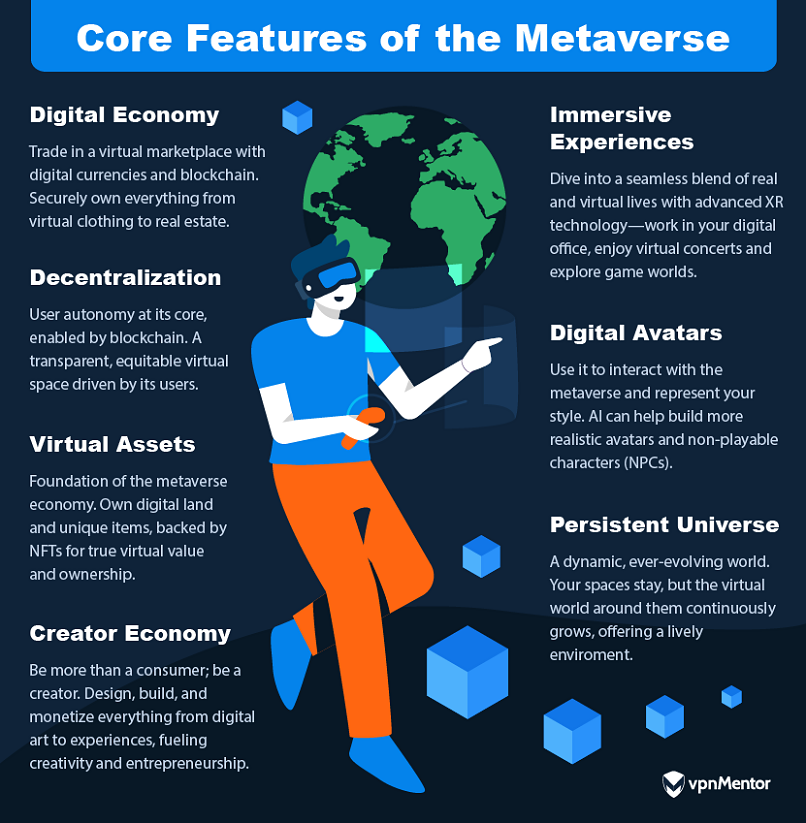
Each aspect plays a crucial role in making the metaverse a rich, multi-dimensional experience.
Emerging technologies that aim to make interacting with virtual content more realistic, like XR, are key here.
Combining work, education, and entertainment into a single digital space is also essential to driving these experiences.

Artificial intelligence plays a pivotal role in this immersion.
The concept of a persistent world is also integral to the metaverse experience.
They enable secure, automated transactions and digital marketplaces where virtual goods can be exchanged.

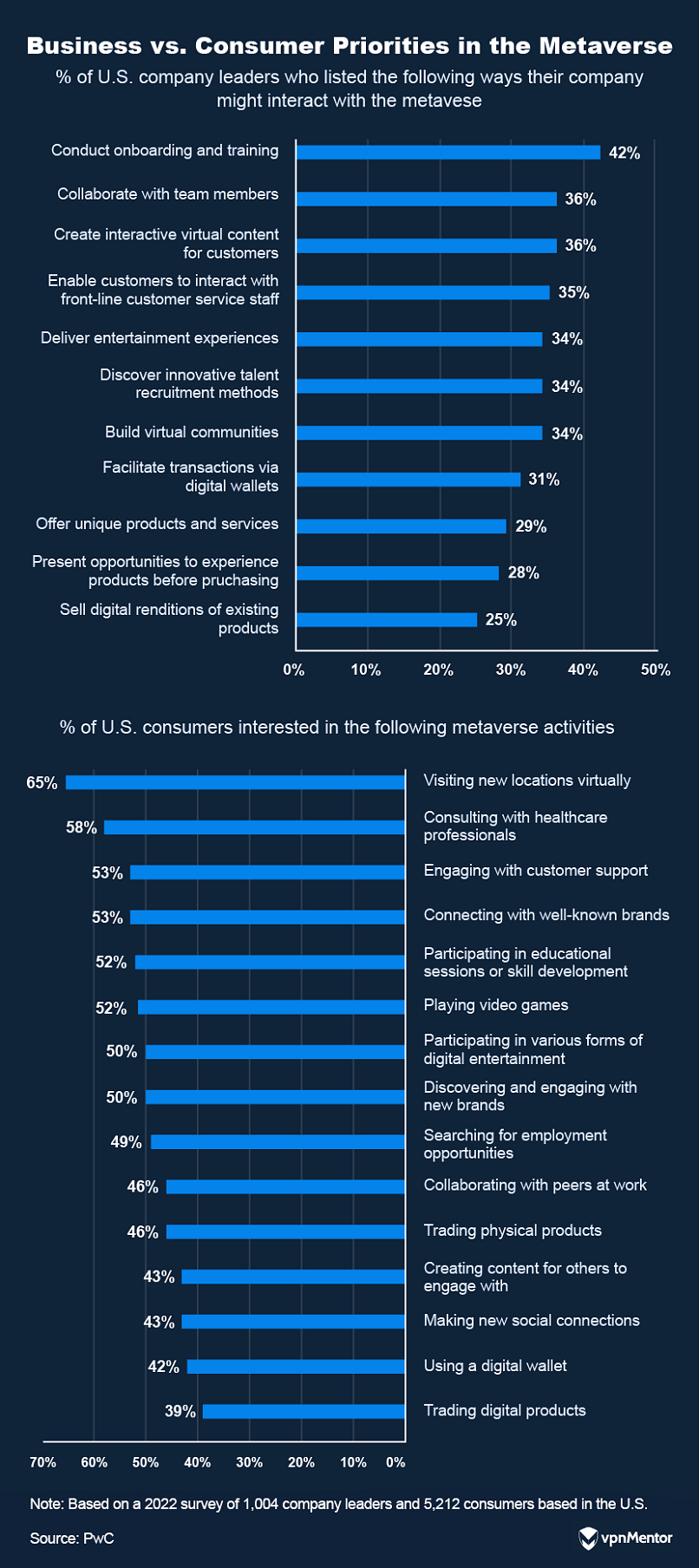
Within the metaverse, the digital economy is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing user engagement and technological advancements.
This growth represents a shift in how value and ownership are perceived in the digital age.
Virtual assets, including digital land, play a pivotal role in the metaverses digital economy.

Owning these assets, which are backed by NFTs, is akin to holding a piece of digital property.
For example, upon entering PixelVerse, you find the need for a virtual home.
Lets say you choose a quaint digital house, nestled in a vibrant community.

Decentralized asset holding, facilitated by blockchain technology, changes how digital assets are managed and transferred.
Blockchain enhances the security and transparency of these transactions and facilitates the fluid transfer and portability of assets.
This capability is crucial for achieving interoperability among different virtual spaces.

For example, consider a scenario where youve purchased a unique digital sweater for your avatar in PixelVerse.
Here, users are empowered to make key choices about how the virtual world operates as a collective.
For example, in PixelVerse, the community can vote on new features or changes to the virtual environment.

As players engage with this game, you earn revenue, either through entry fees or in-game purchases.
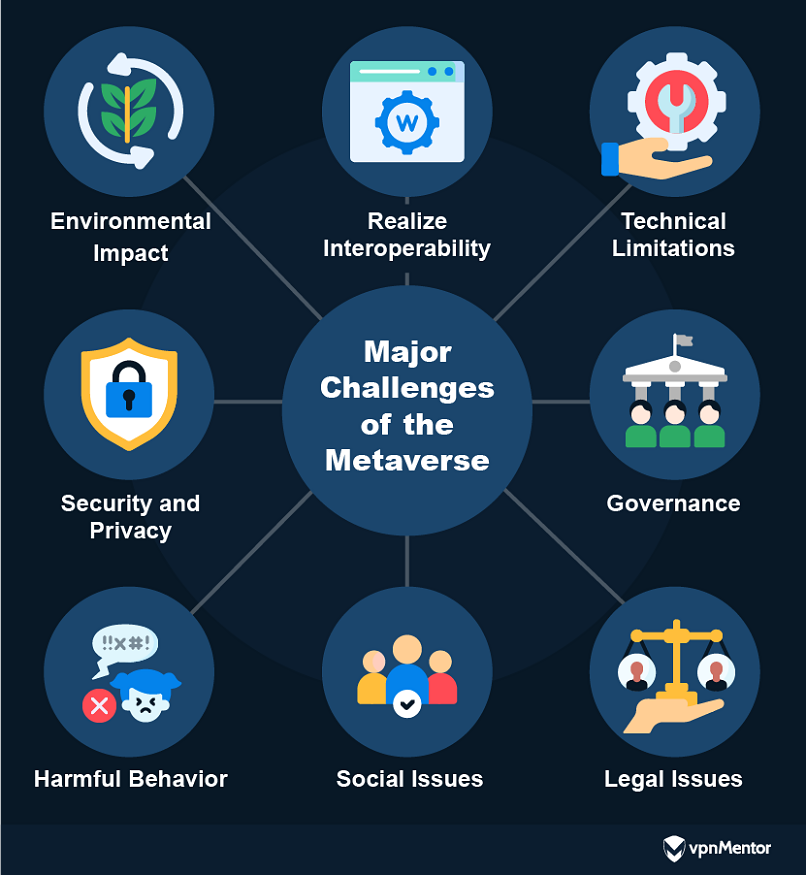
Lets take a closer look at some of the major issues and their potential effects.
Interoperability stands as a fundamental challenge in the metaverses development.

Governance
A critical issue in the metaverse is the lack of established legal governance.
Currently, there are no specific laws governing these virtual spaces.
Without clear legal frameworks, the metaverse risks becoming a lawless space, susceptible to misuse and unethical practices.

Determining which governing body should police the metaverse is another complex issue.
One major issue is unauthorized reproduction of digital assets, which often results in copyright infringement.
Imagine a digital artist in the metaverse starts creating and selling NFTs of Van GoghsStarry Night.

The role of NFTs complicates this legal framework further.
This can lead to misunderstandings among NFT owners.
Someone who purchases an NFT of a digital sculpture may believe they have complete rights over the sculptures design.
However, in reality, they only own the specific digital version, not the design itself.
This could lead to legal disputes if the NFT owner attempts to reproduce or modify the work without permission.
Social Issues
Essential tools like high-quality VR headsets and high-speed internet are costly and not globally accessible.
This can have significant social repercussions.
Consider a recent case where a woman was virtually attacked by a group of avatars.
The highly immersive nature of the metaverse also brings safety concerns, especially for vulnerable users like children.
Security and Privacy
The metaverses approach to security and privacy encompasses more than traditional data protection.
Users face unique cyber threats, especially concerning their digital wallets and the assets they hold, like NFTs.
In addition to financial attacks, privacy is a major concern in the metaverse.
The extensive data collection capabilities of metaverse platforms is seen as a major problem.
Users data in the metaverse is not just personal; its intimately linked to their physical and psychological attributes.
The misuse of such data could have far-reaching and severe consequences, placing individuals in a vulnerable position.
This combination leads to considerable energy demands and increased carbon emissions.
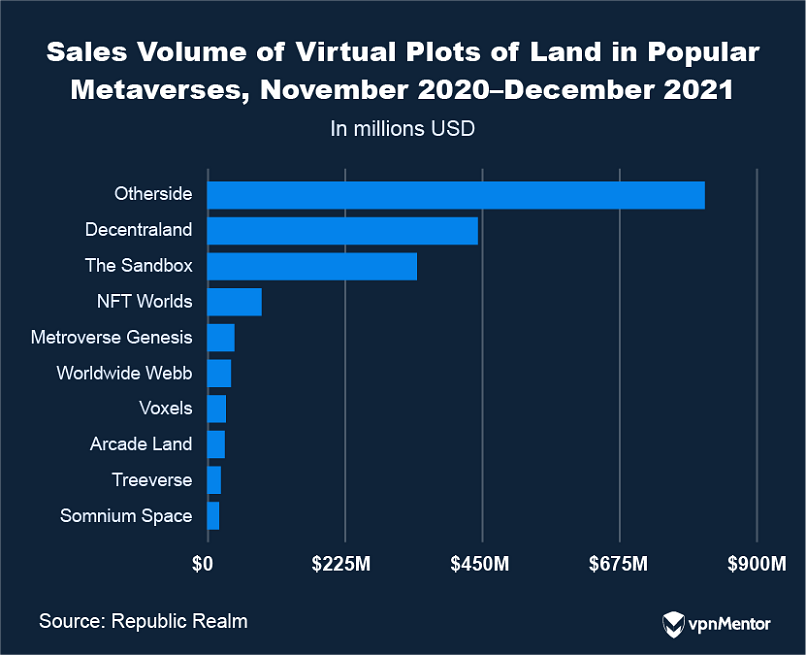
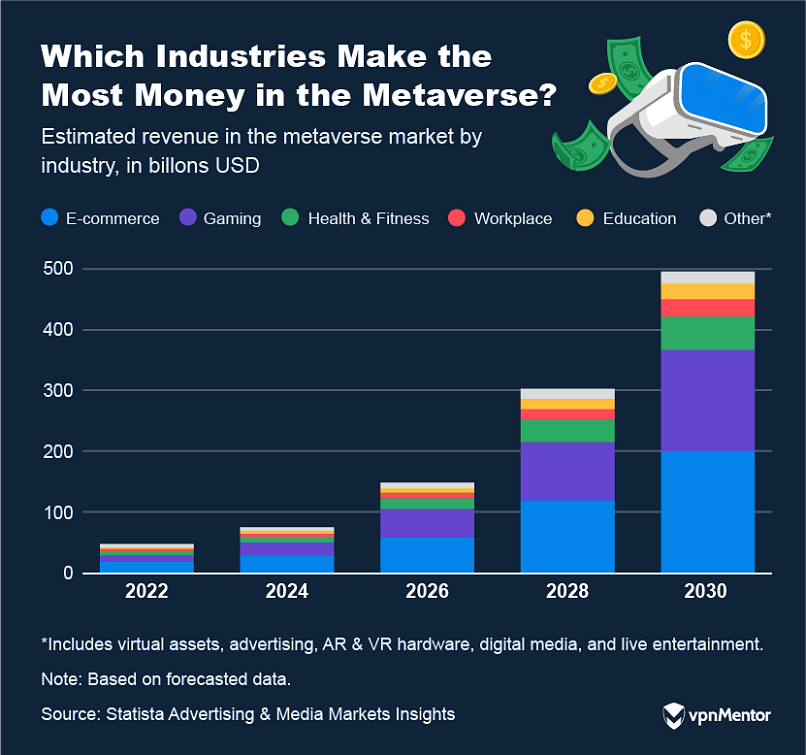
Less conservative forecasts predict the Metaverse could be valued as high as $937 billion by 2030.
When it comes to gaming, the metaverse offers distinct experiences.
Then there are blockchain-based games, which represent a unique subset within the gaming universe.
Theres another layer to blockchain gaming: play-to-earn models.
Games like Axie Infinity, Plants vs Undead, and Farmers World are all great examples of this genre.
Looking ahead, the metaverse is poised to further diversify entertainment and gaming.
We can expect experiences that are currently unimaginable.
Currently, the metaverse serves as a platform for various virtual tourism experiences.
As technologies like spatial computing advance, these virtual spaces are expected to become even more immersive and interactive.
Work and Education
The metaverse could revolutionize the realms of work and education.
This has the potential to make online collaboration much more engaging and efficient.
In the educational sphere, platforms like ENGAGE and ClassVR are combating the tedium of traditional video conferencing.
They replace 2D interactions with 3D classroom environments, making remote learning more immersive and interactive.
This would be supported by edge computing, which could enable efficient real-time data sharing and interactions.
In healthcare, the metaverse can facilitate:
Fitness and wellness in the metaverse extend beyond physical health.
Some developers are creating new tools and devices that can help users improve their mental well-being.
Companies like Peloton are investigating ways to make online workouts more interactive and social.
Users can participate in a wide range of sports and exercise routines from their living rooms.
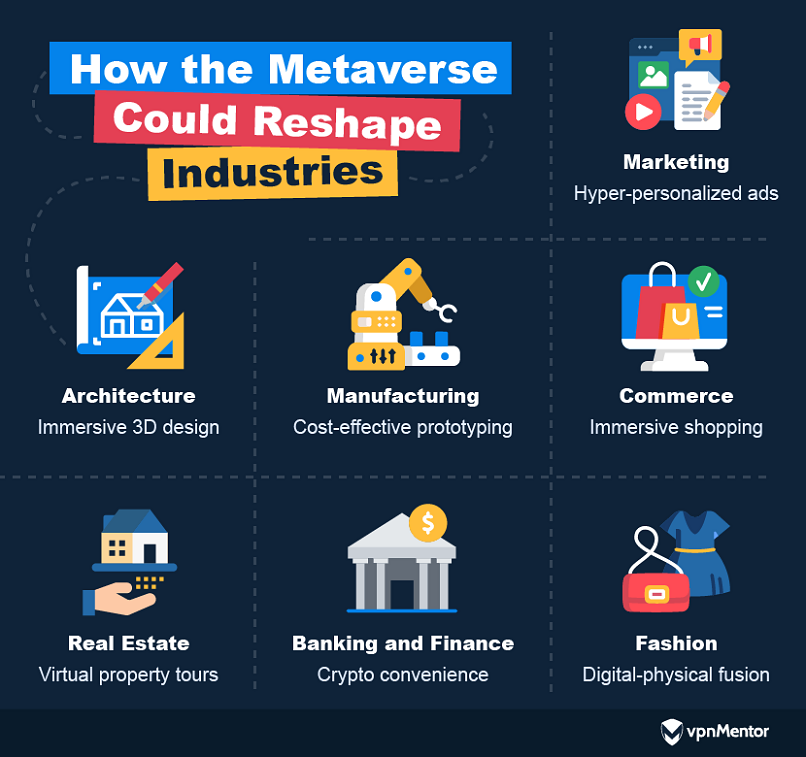
Industry
Industries are facing unique challenges as they begin to take advantage of the metaverses potential.
From marketing to architecture and manufacturing, the metaverse offers innovative solutions and future prospects.
Major Players in the Metaverse
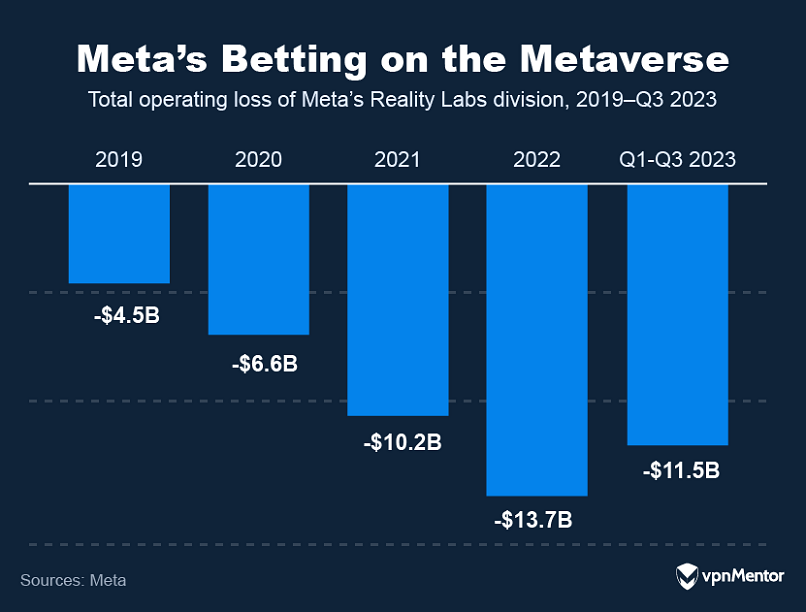
The metaverse is attracting significant attention and investment from leading technology companies.
The push towards this virtual frontier is driven by the enormous potential for growth and innovation.
Unfortunately, the company has yet to see any return on this massive investment, although it expects to.
It integrates with Hololens 2, the companys MR head-mounted display.
Controlled by eye, hand, and voice inputs, the headset overlays digital content onto the physical world.
It runs on Apples metaverse-style operating system, VisionOS, which is built around the concept of spatial computing.
Despite not actively promoting a metaverse vision, Apples actions speak volumes.
Even amid tech industry layoffs, Apples job board lists several roles focused on developing immersive experiences.
Google is primarily strengthening its position in the metaverse through AR technologies.
Several projects hint at Googles potential direction in the metaverse.
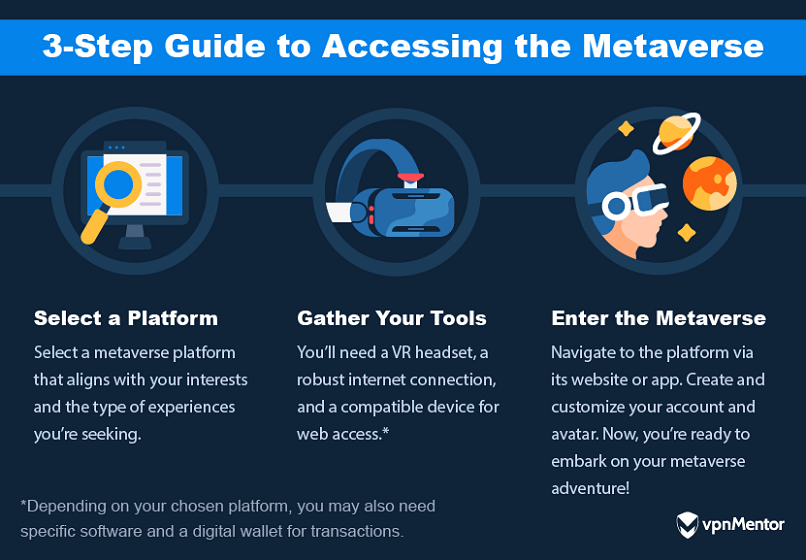
Select a Platform
Choosing the right platform is your first step in embarking on your metaverse journey.
Each metaverse platform offers a distinct experience, tailored to different interests and interactions.
Heres an overview of the best use cases for some of the most popular metaverses.
Horizon Worlds is focused on social interaction and creativity.
Users can build and customize spaces, create virtual homes, and design interactive experiences.
Its ideal for those interested in crafting and exploring user-generated environments.
Primarily catering to a younger demographic, Roblox is an excellent platform for creating and playing games.
Its also an educational tool, teaching coding and digital civility.
This platform is ideal for young creators and gamers seeking a safe and imaginative play space.
As a decentralized virtual world, Decentraland is perfect for users interested in digital real estate and community governance.
The Sandbox is a blockchain-based, play-to-earn platform.
Its a good option for gamers and creators who value asset monetization.
Its particularly popular among digital artists, offering spaces dedicated to art creation and virtual exhibitions.
Heres a look at what youll need:
3.
Enter the Metaverse
How you enter the metaverse can vary depending on the platform you choose.
For web-based metaverses (Decentraland, The Sandbox, CryptoVoxels), start by navigating to the platforms website.
App-based platforms (Horizon Worlds, Roblox) require you to download an app.
For Horizon Worlds, youll download the VR app onto your VR headset or mobile rig.
Each platform will prompt you to create a unique username.
This is your identity in the metaverse, so choose something memorable and personal.
Most metaverses offer extensive avatar customization.
Platforms like Roblox and Horizon Worlds have built-in avatar editors where you’re able to change your appearance.
In blockchain-based metaverses like Decentraland and The Sandbox, avatars can also showcase NFTs as clothing or accessories.
Once your account is set up and your avatar is ready, you might start exploring.
Each platform has its own set of controls and user interfaces.
So its important to ensure you have the right equipment to get the most out of your experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Metaverse?
The metaverse is an expansive virtual-reality landscape.
How Do You Get into the Metaverse?
Who Owns the Metaverse?
No single entity owns the metaverse.
Its a collective of various platforms and experiences thats being shaped by several major technology companies.
Is the Metaverse Free?
The metaverse offers both free and paid experiences.
Can I Enter the Metaverse without a VR Headset?
Yes, you could enter the metaverse without a VR headset.
Who Are the Biggest Players in the Metaverse?
The metaverse is attracting attention and investment from leading technology companies.
Is the Metaverse Available to Everyone?
The metaverse is technically available to everyone, but it isnt universally accessible in its current form.
How Many Metaverses Are There?
There are multiple metaverses under development.
What Are the Disadvantages of the Metaverse?
just, comment on how to improve this article.
