The answer can be a positive “yup!”
if you don’t mind some instability during the first weeks of using your new PC.
Before We Begin…
Properly overclocking or undervolting a CPU requires a lot of trial and error.
In the process, some crashes are inevitable.
Also, keep a full OS backup handy, just in case.
Thus, we should follow suit.
Proceed at your own peril.
What Is Undervolting?
The short version is that undervolting is the opposite of overclocking.
Theoretically, this also leads to a drop in performance.
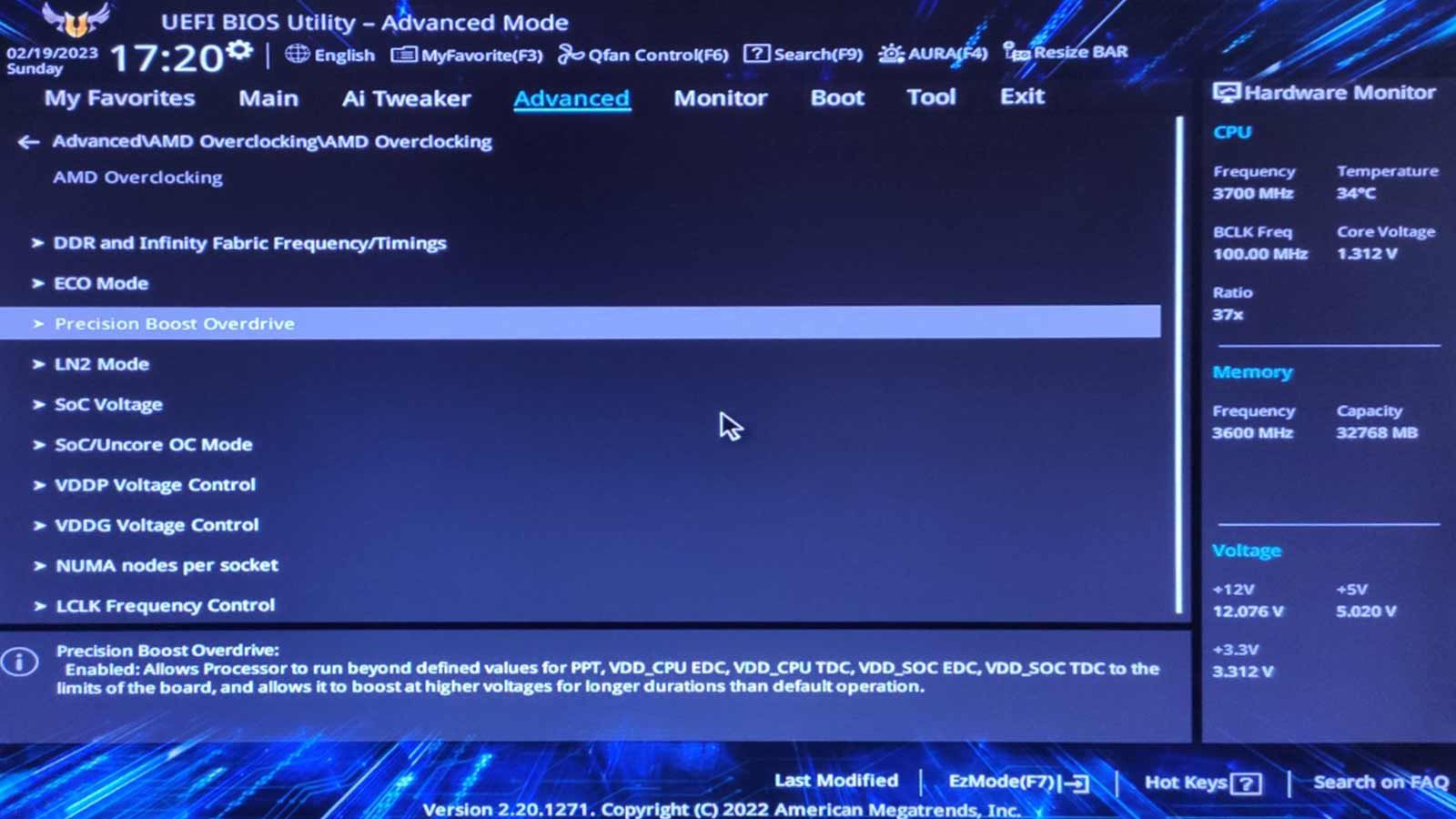
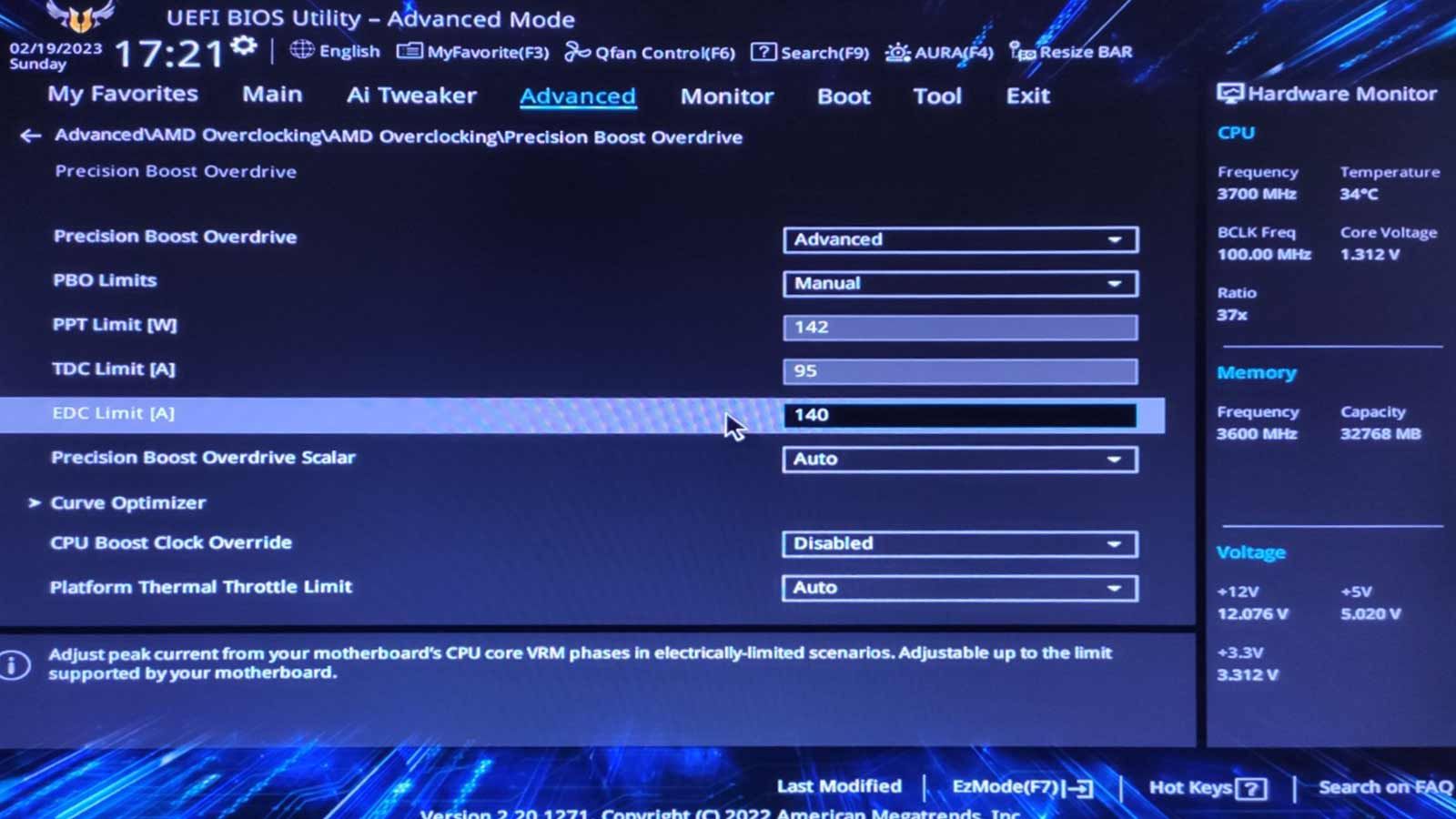
What Is PBO?
Unlike typical overclocking, it doesn’t lead to a higher CPU frequency.
And also, unlike “classic” undervolting, it doesn’t lead to a drop in performance.
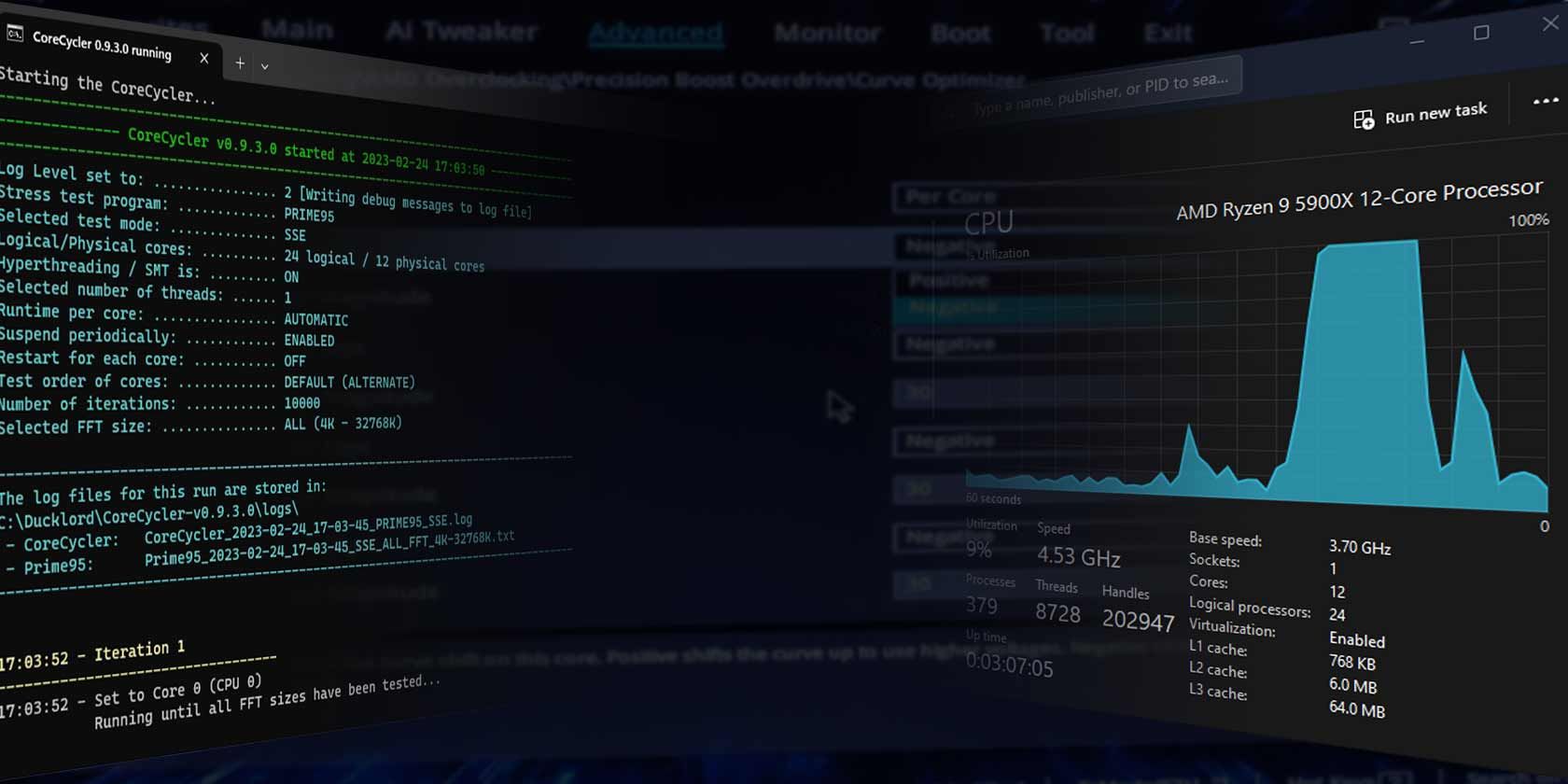
What Is CoreCycler?
Doing that lets you easily pinpoint which core is unstable with your current hardware options.
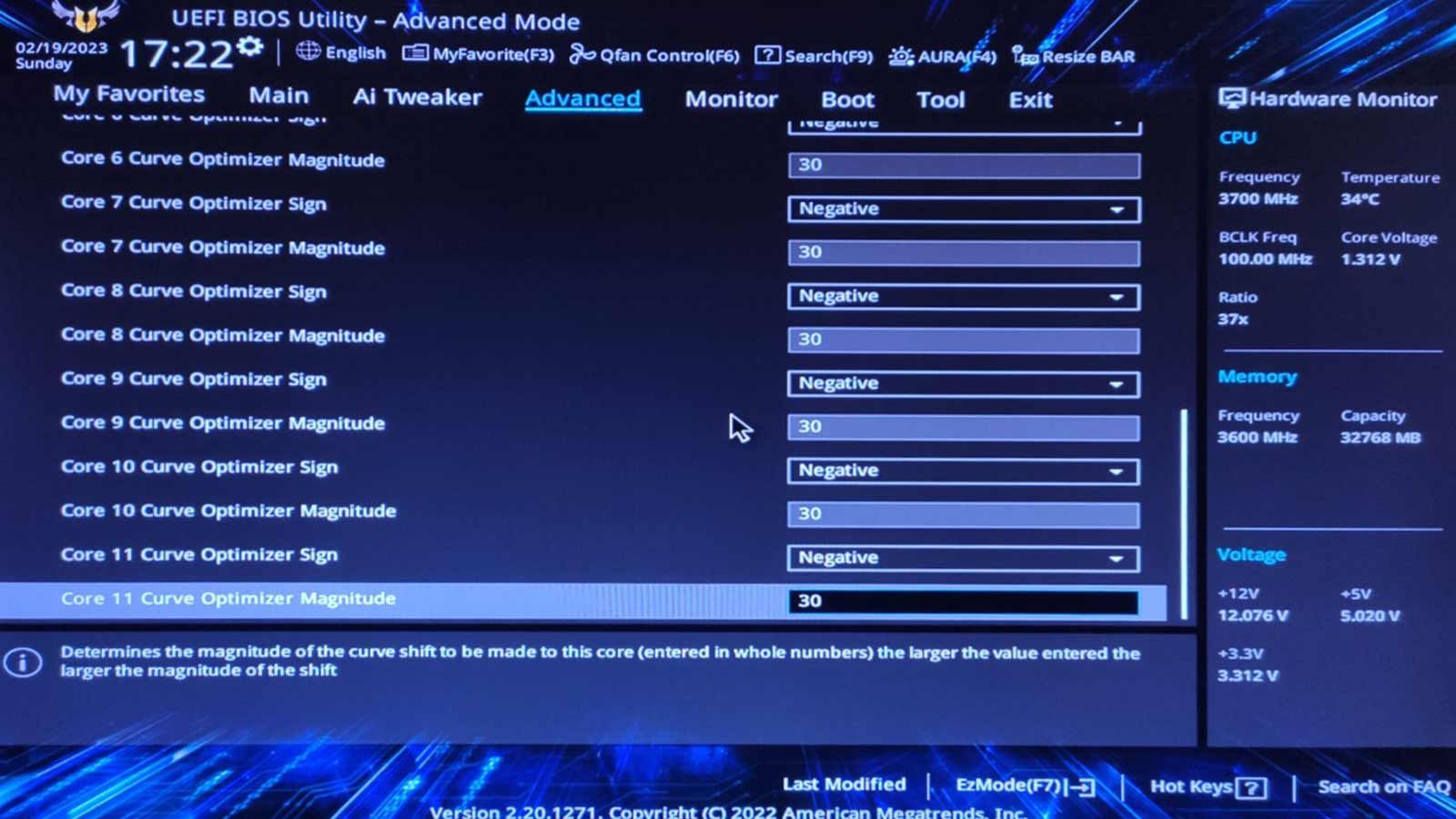
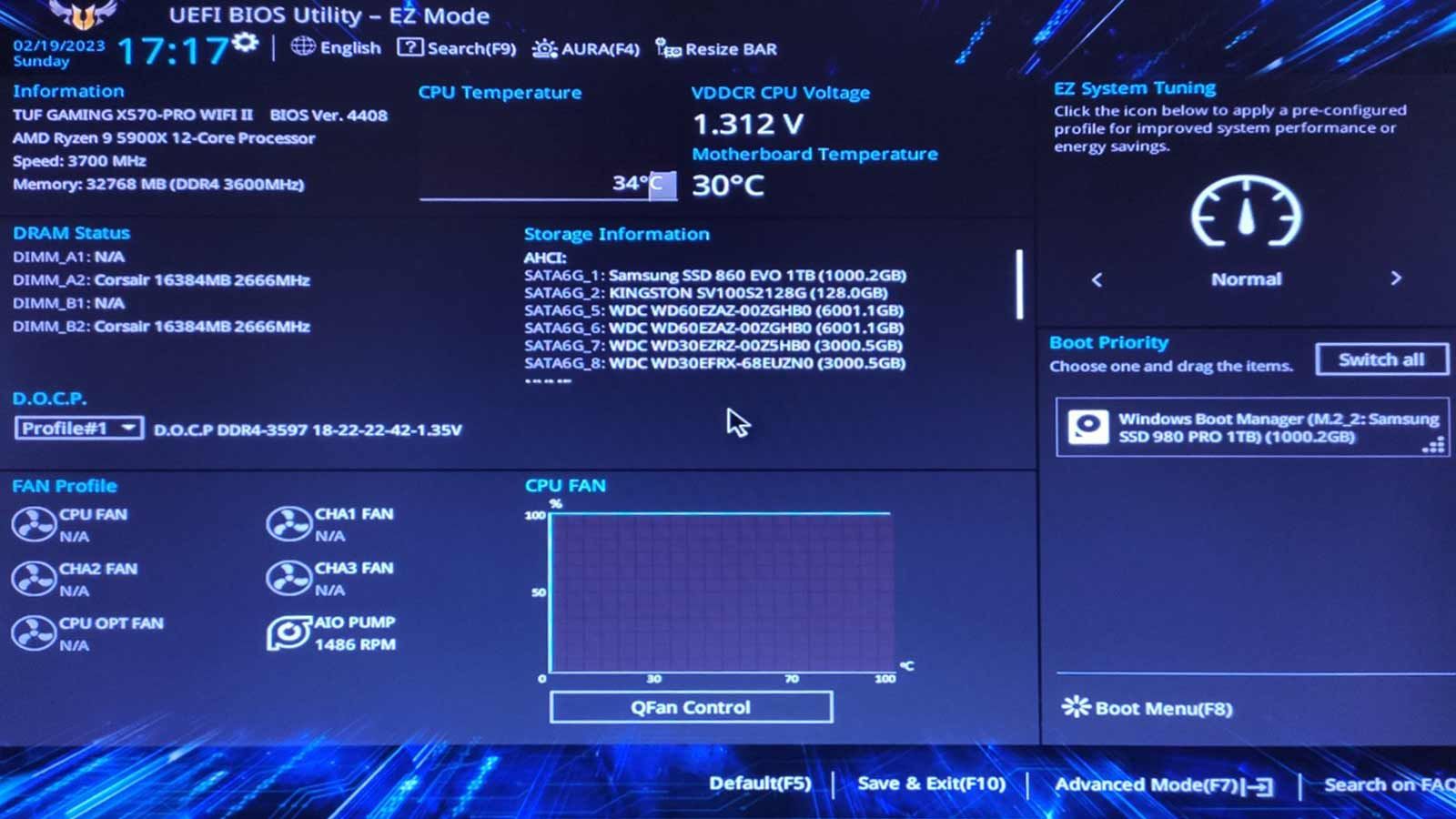
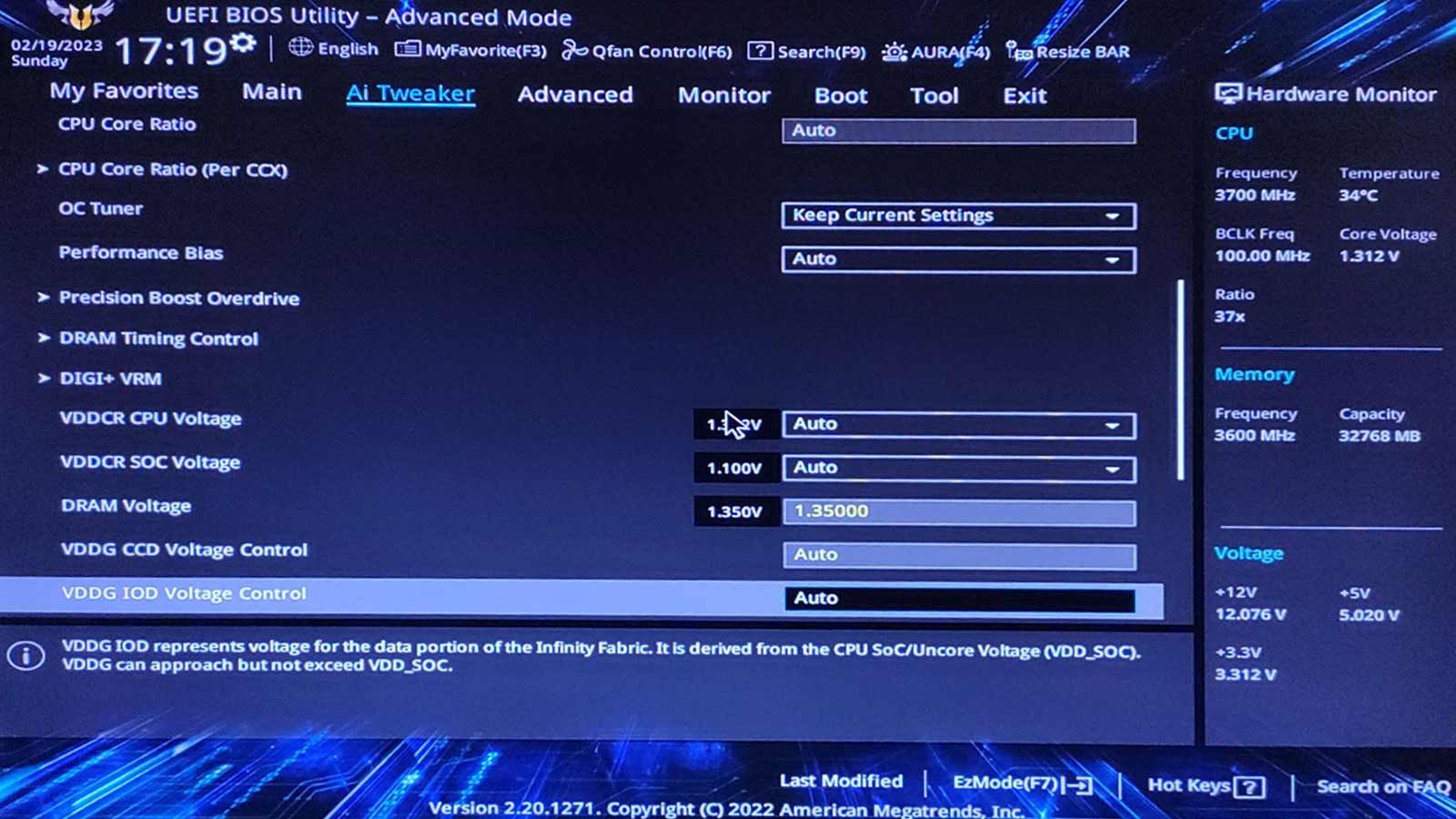
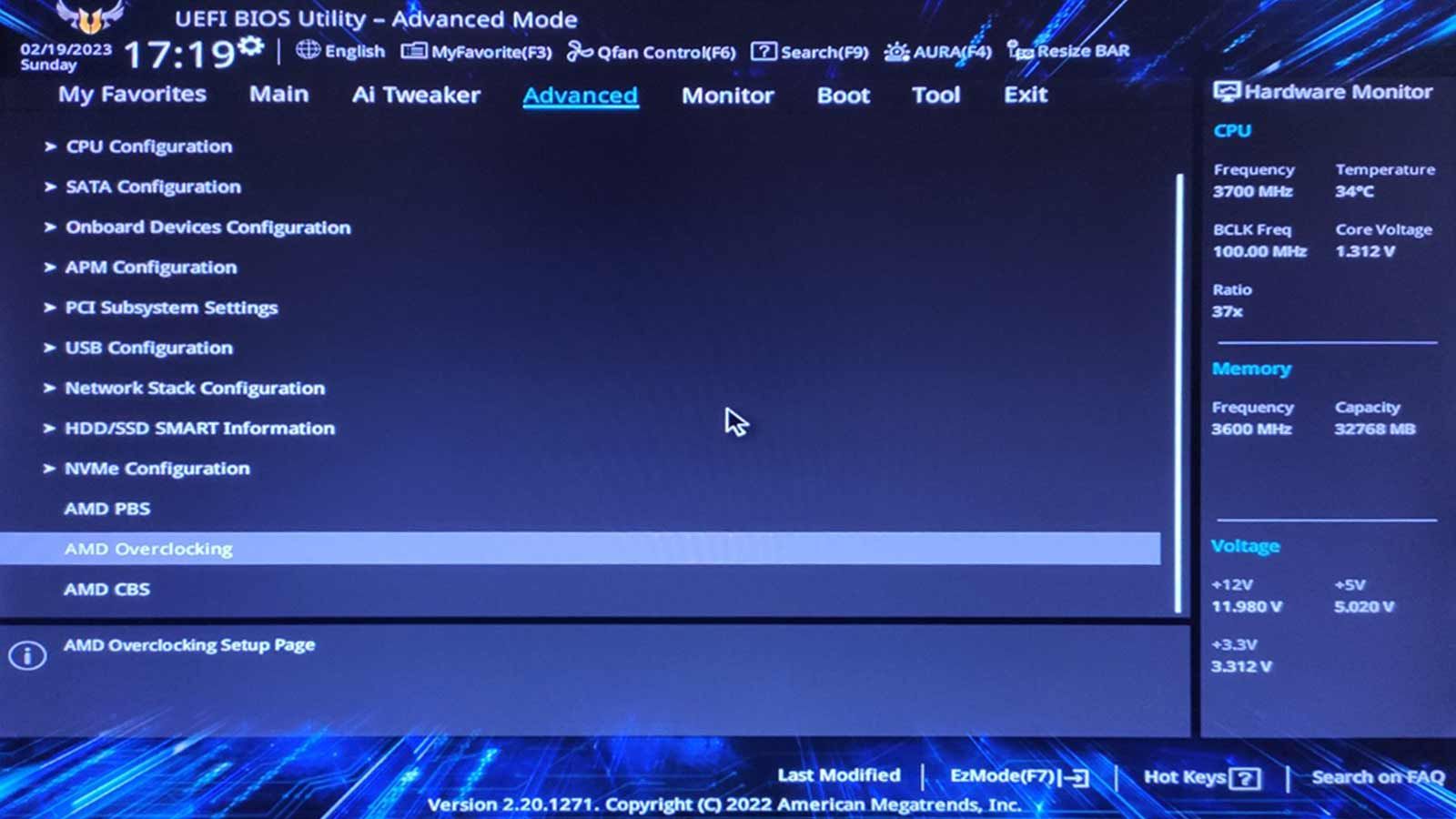
Note that the options we’ll see are in a different spot for each motherboard’s UEFI menu.
Also, the number of cores (and, thus, PBO values) depends on your CPU.
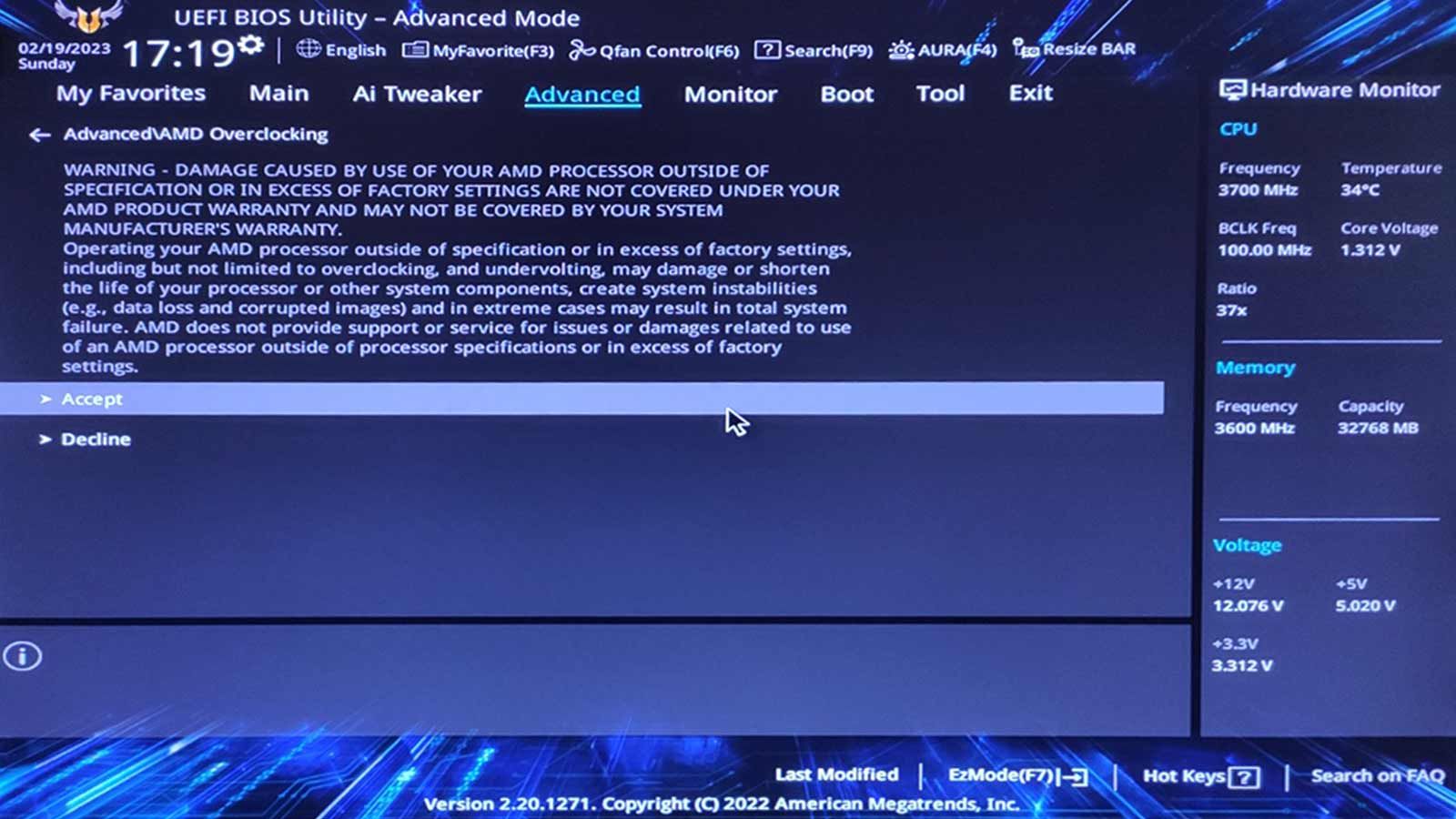
For this article, we’ll use an ASUS TUF Gaming motherboard with an AMD Ryzen 5900x CPU.
The menu options we’ll refer to are for that motherboard’s UEFI menu.
We also assume you’re using your motherboard UEFI’s default values.
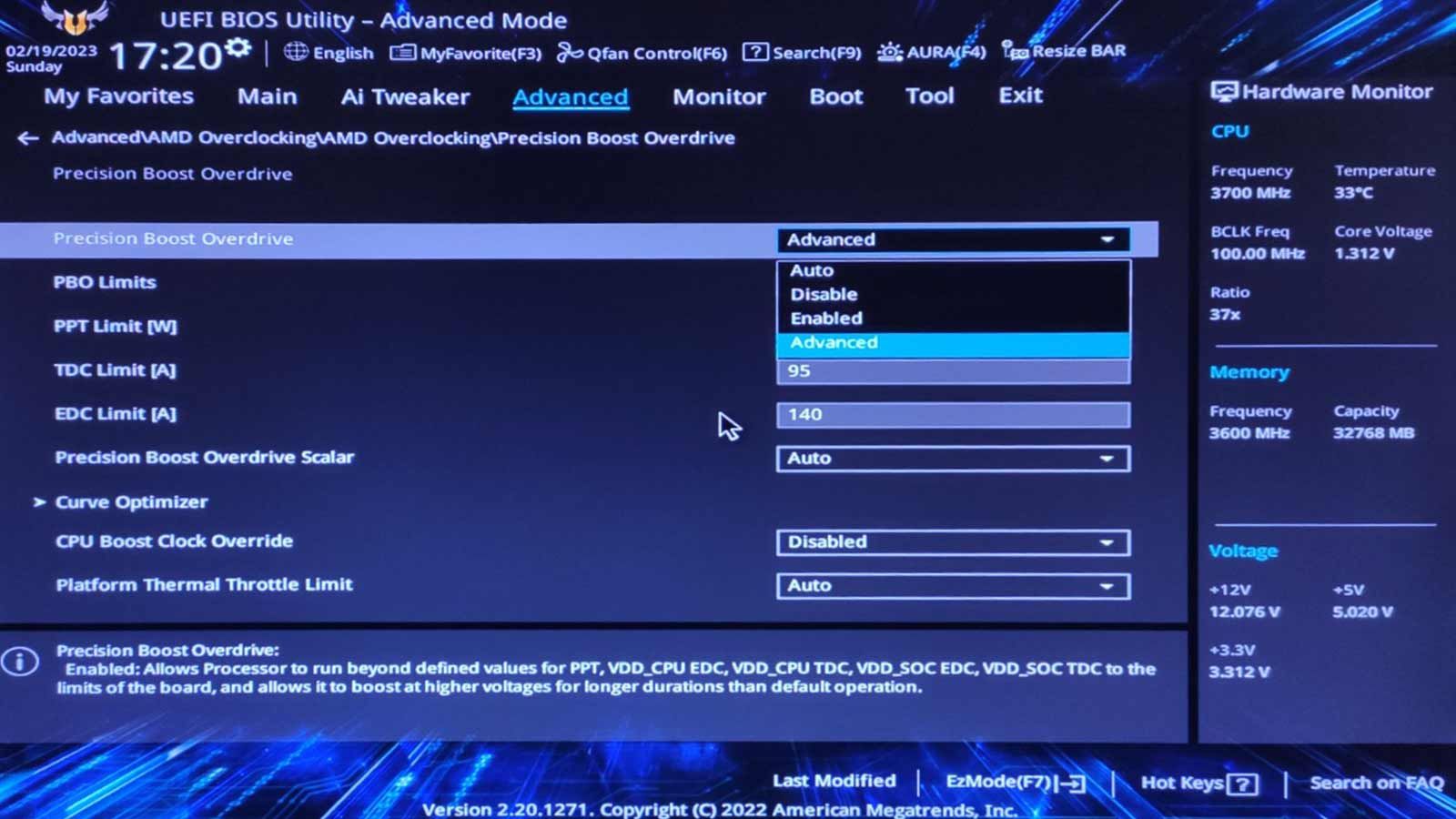
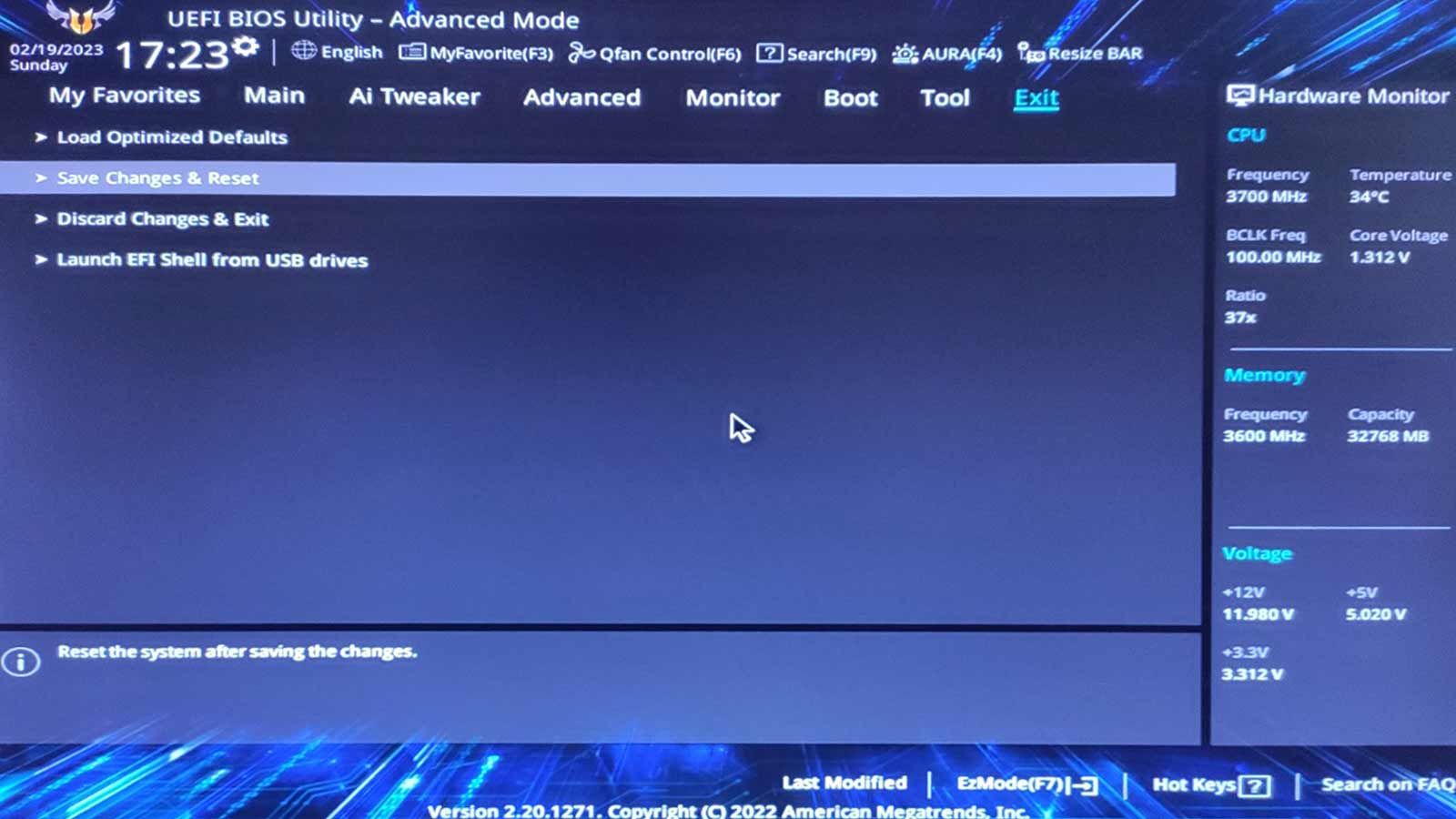
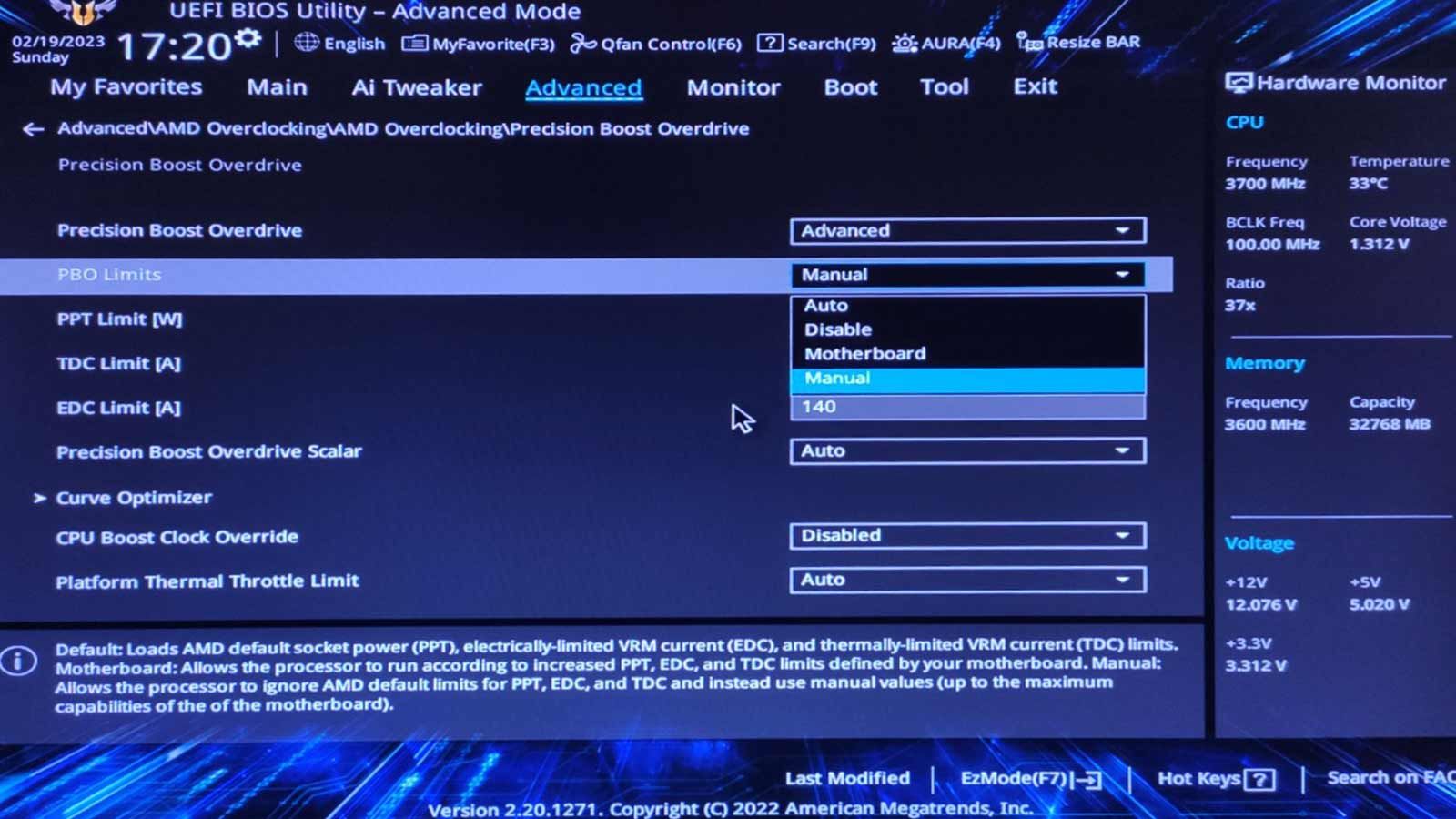
Rinse and repeat until you’re free to enter Windows as usual.
CoreCycler Testing
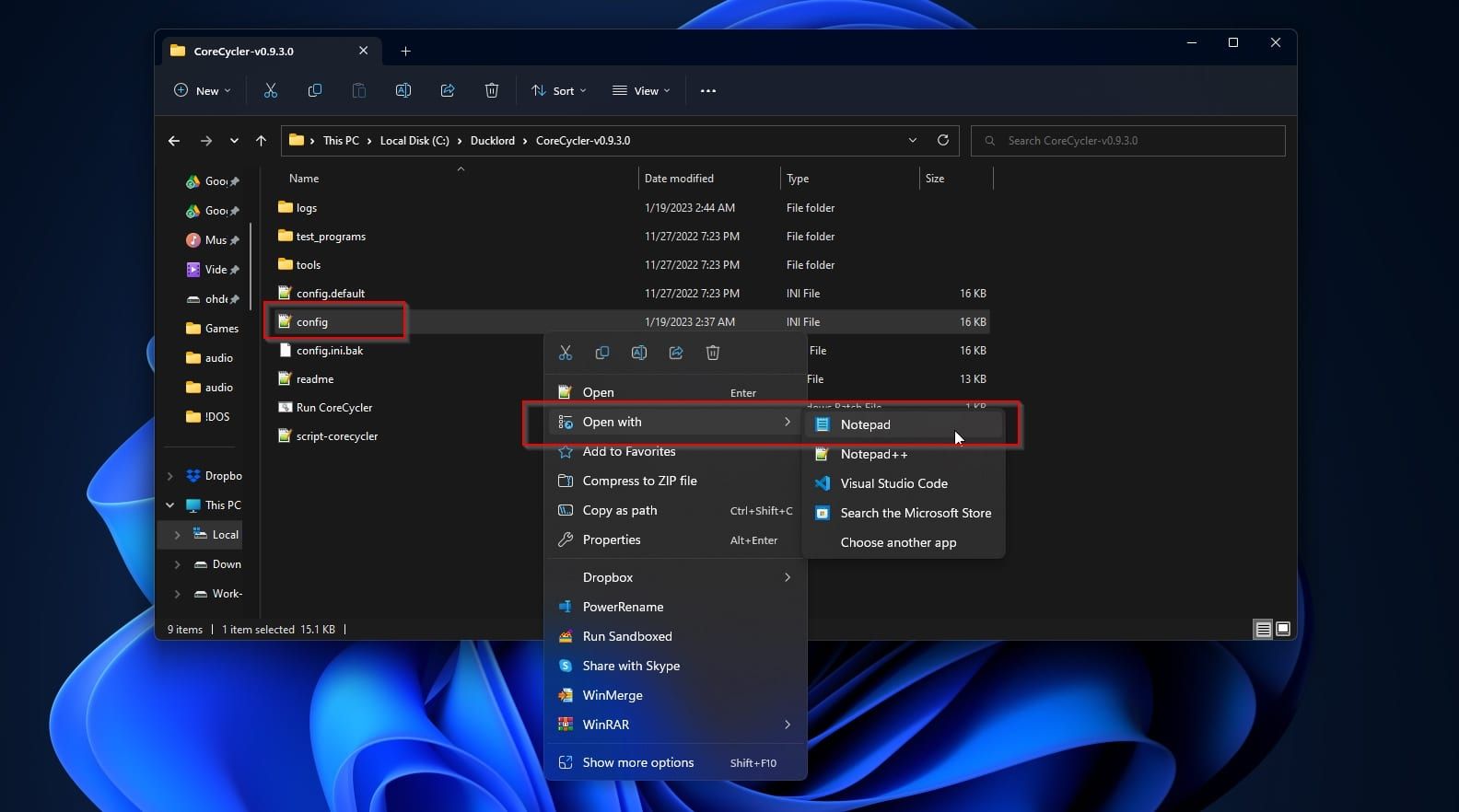
Enter the folder where you’ve extracted the CoreCycler archive’s content.
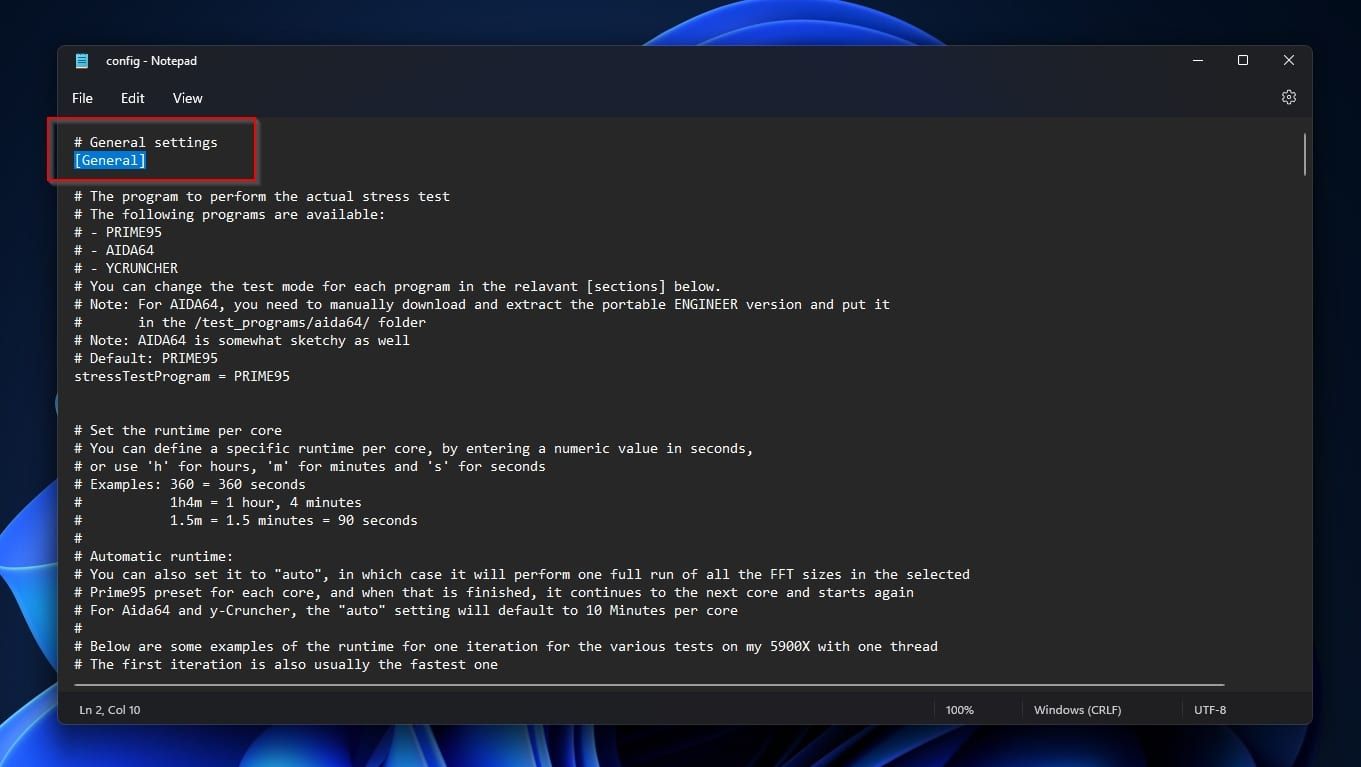
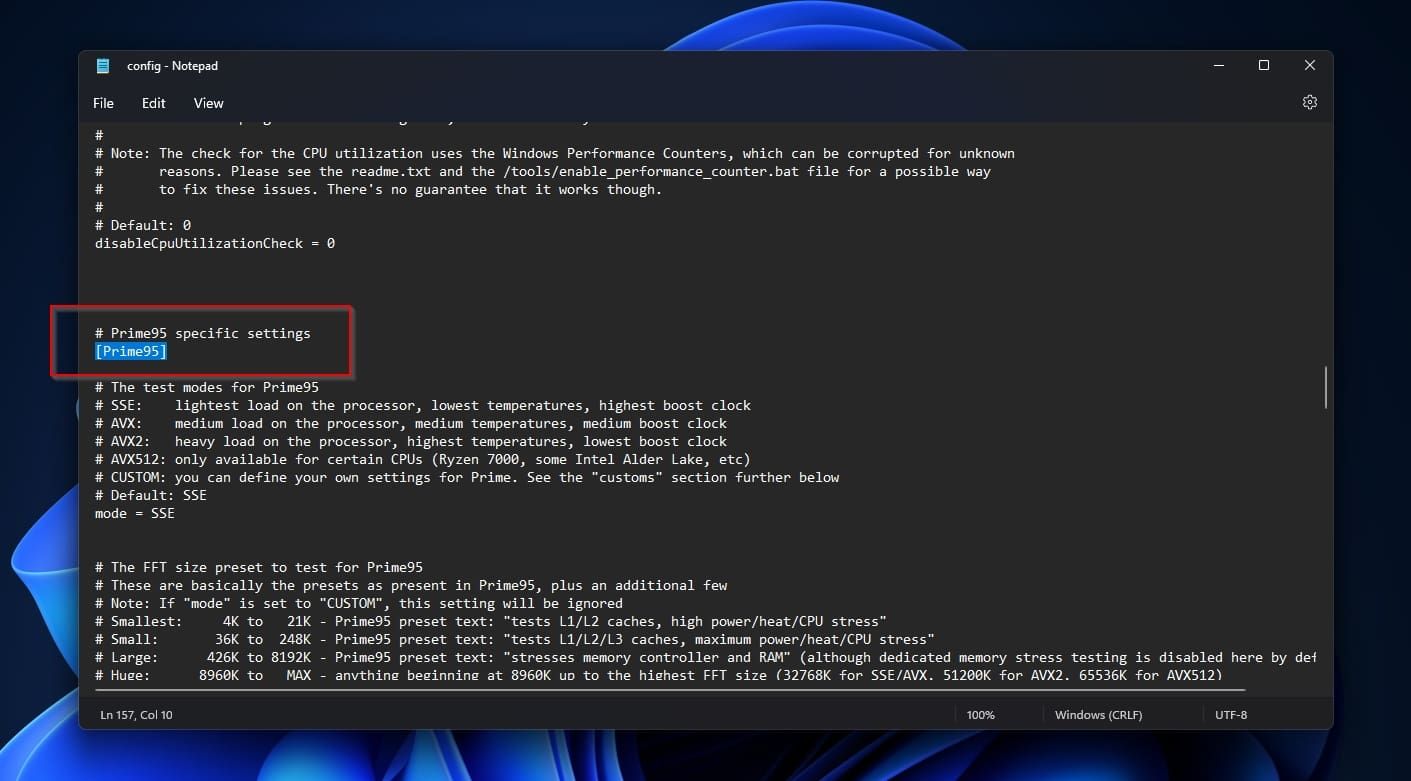
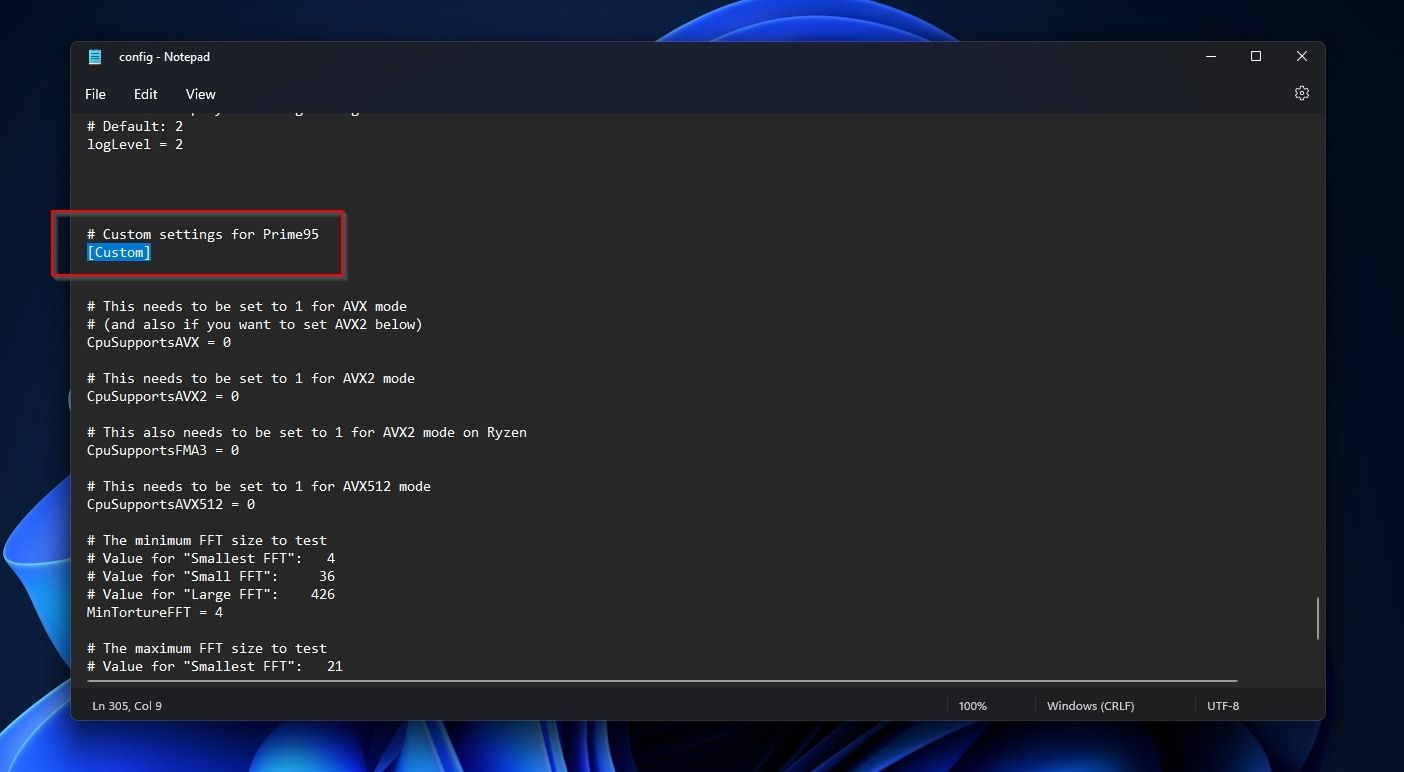
Right-click onconfig.iniand edit it with your favorite text editor (Windows Notepad will do).
Find and change the following values if yours are different.
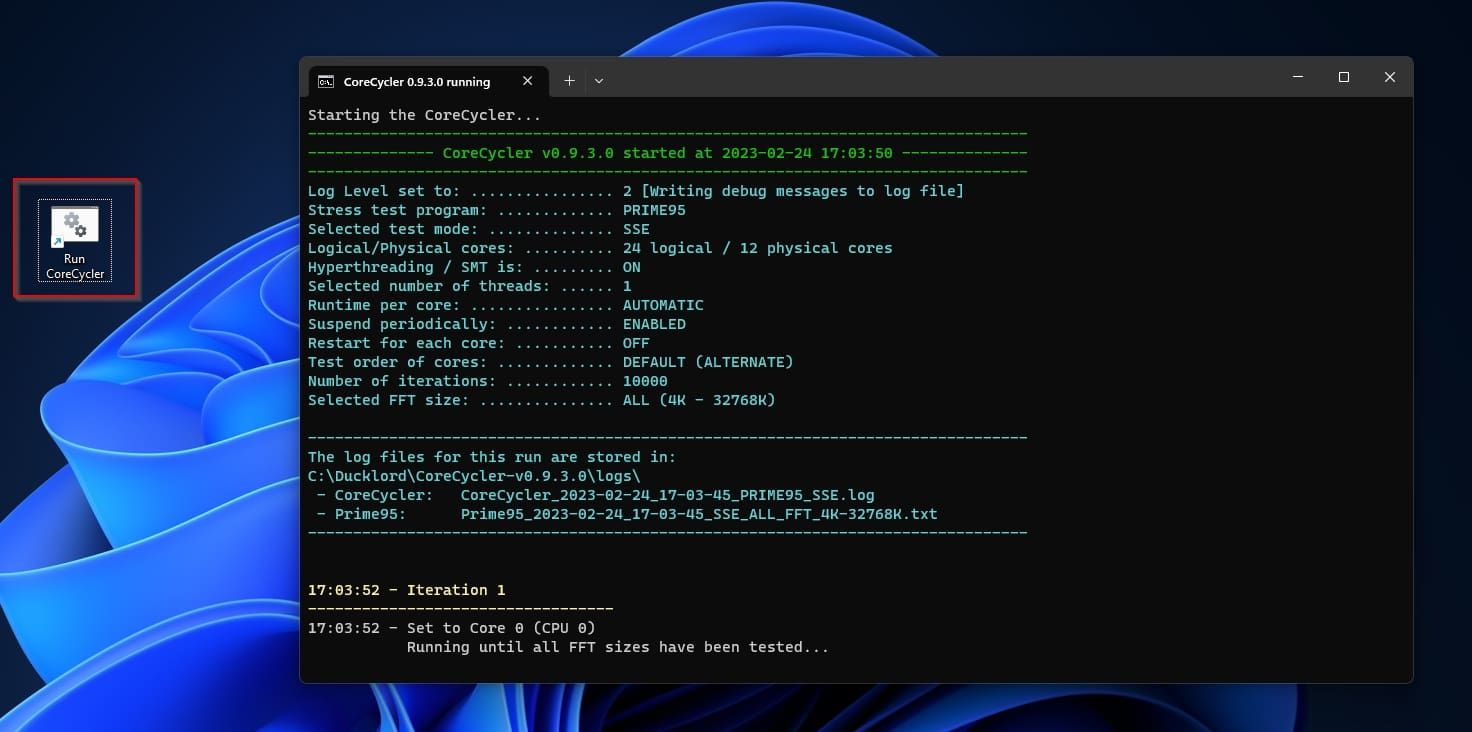
Then, double-click onRun CoreCycler.batto start stress-testing your CPU.
If, after around twelve hours, your PC’s still going, you’re more or less OK.
However, it’s more probable your PC will crash and reboot.
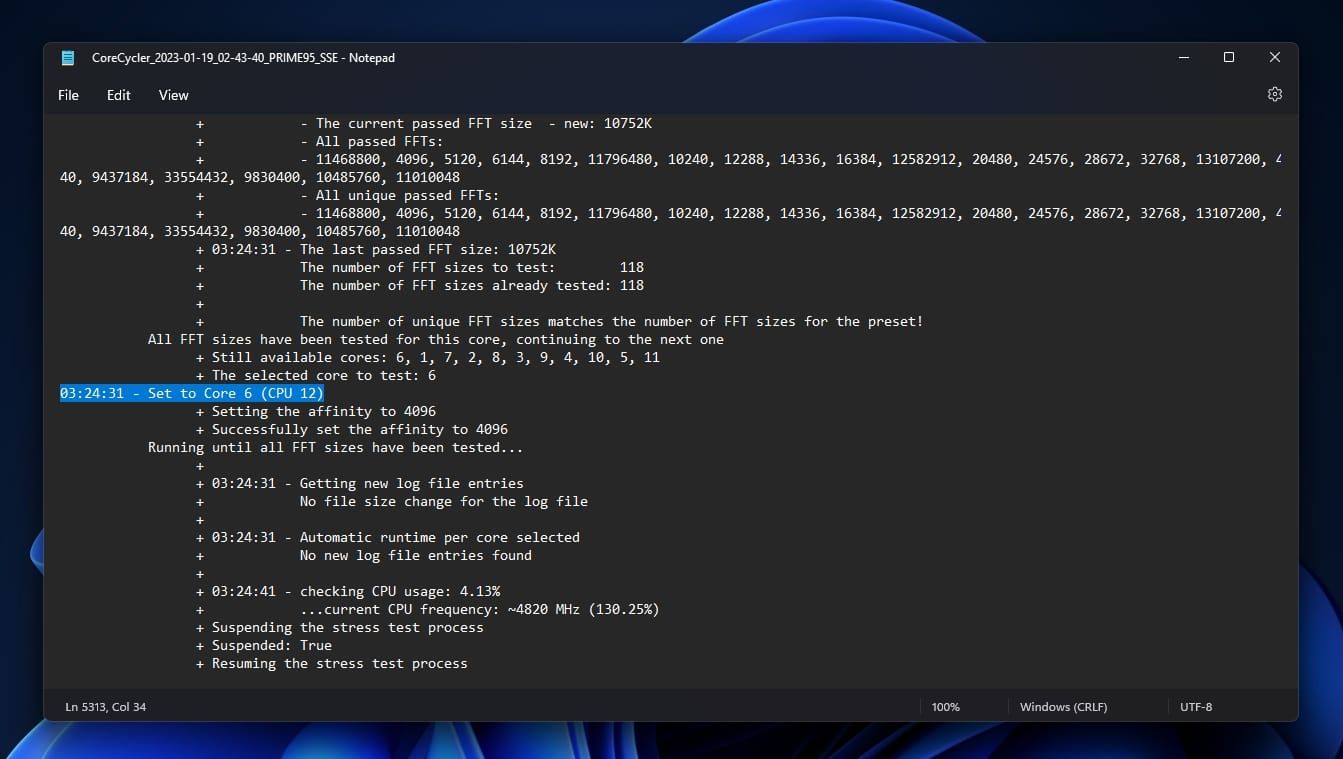
If that happens, when back on your Windows desktop, revisit CoreCycler’s folder.
Enter thelogssub-folder, and pop swing open the latest log.
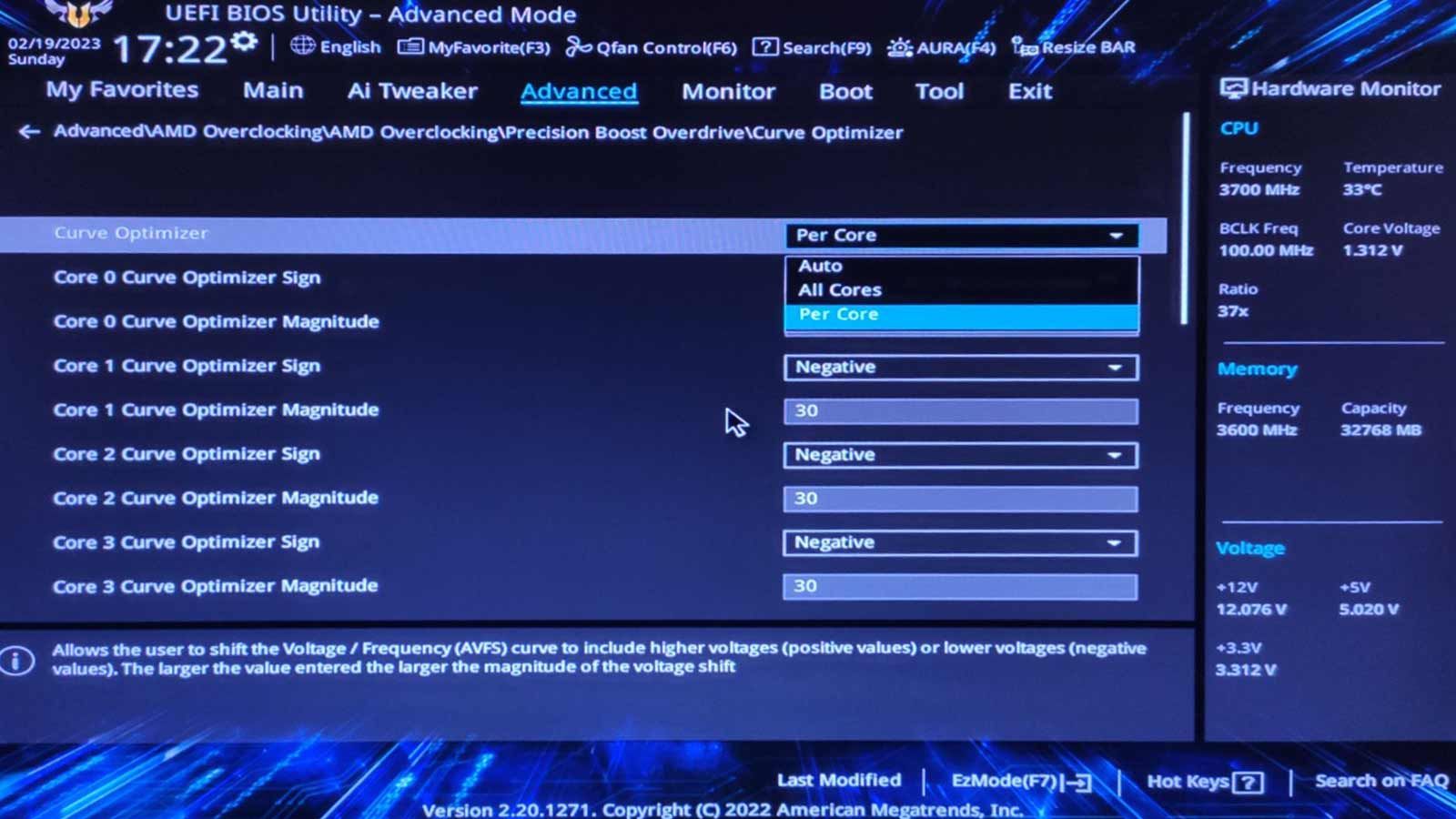
Each physical core on a multicore CPU appears as two cores in the OS and most UEFI setups.
Core 1 appears as Cores 1+2; Core 2 is Cores 3+4, etc.
However, to complicate things further, the core count usually starts at 0.
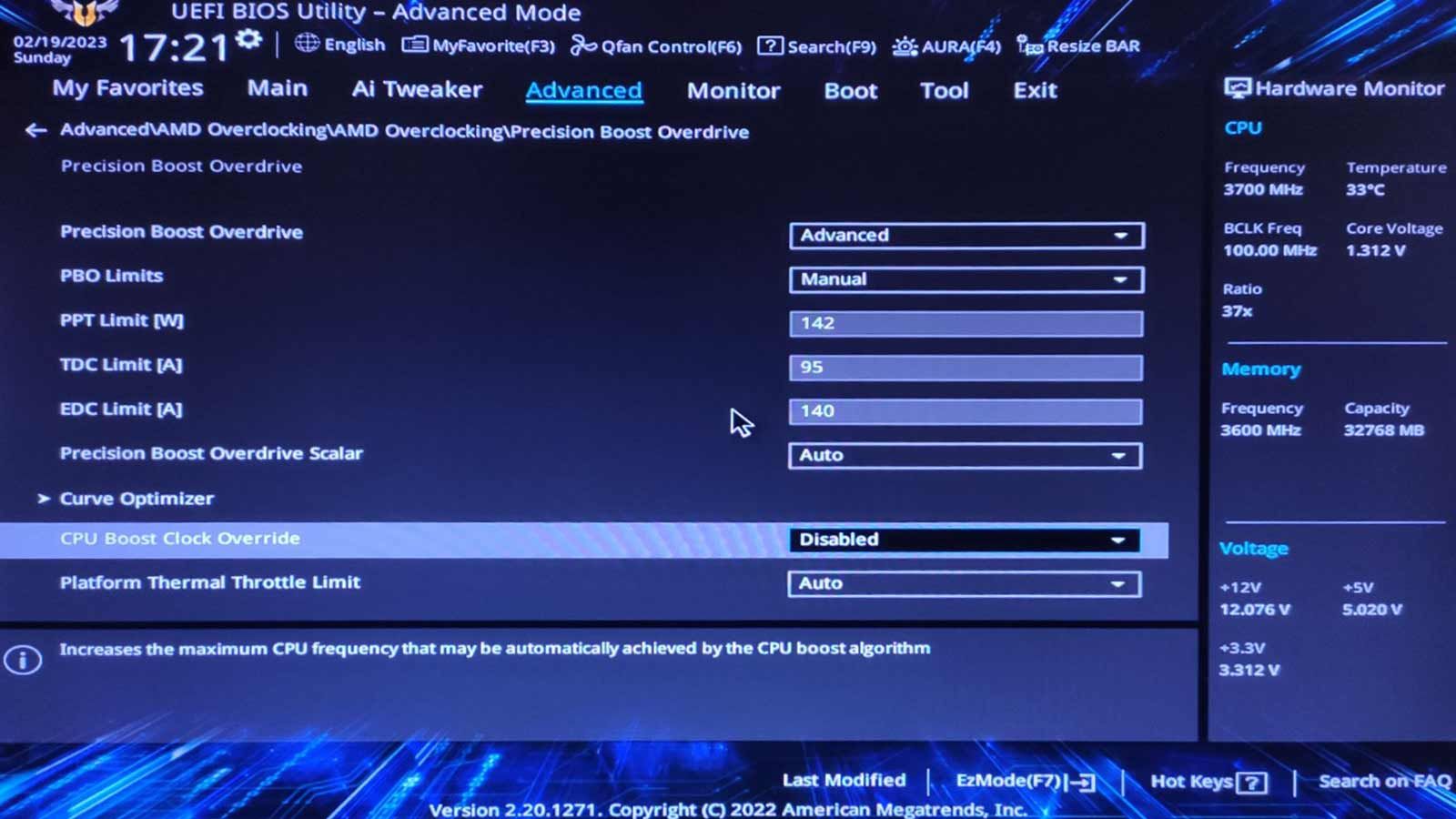
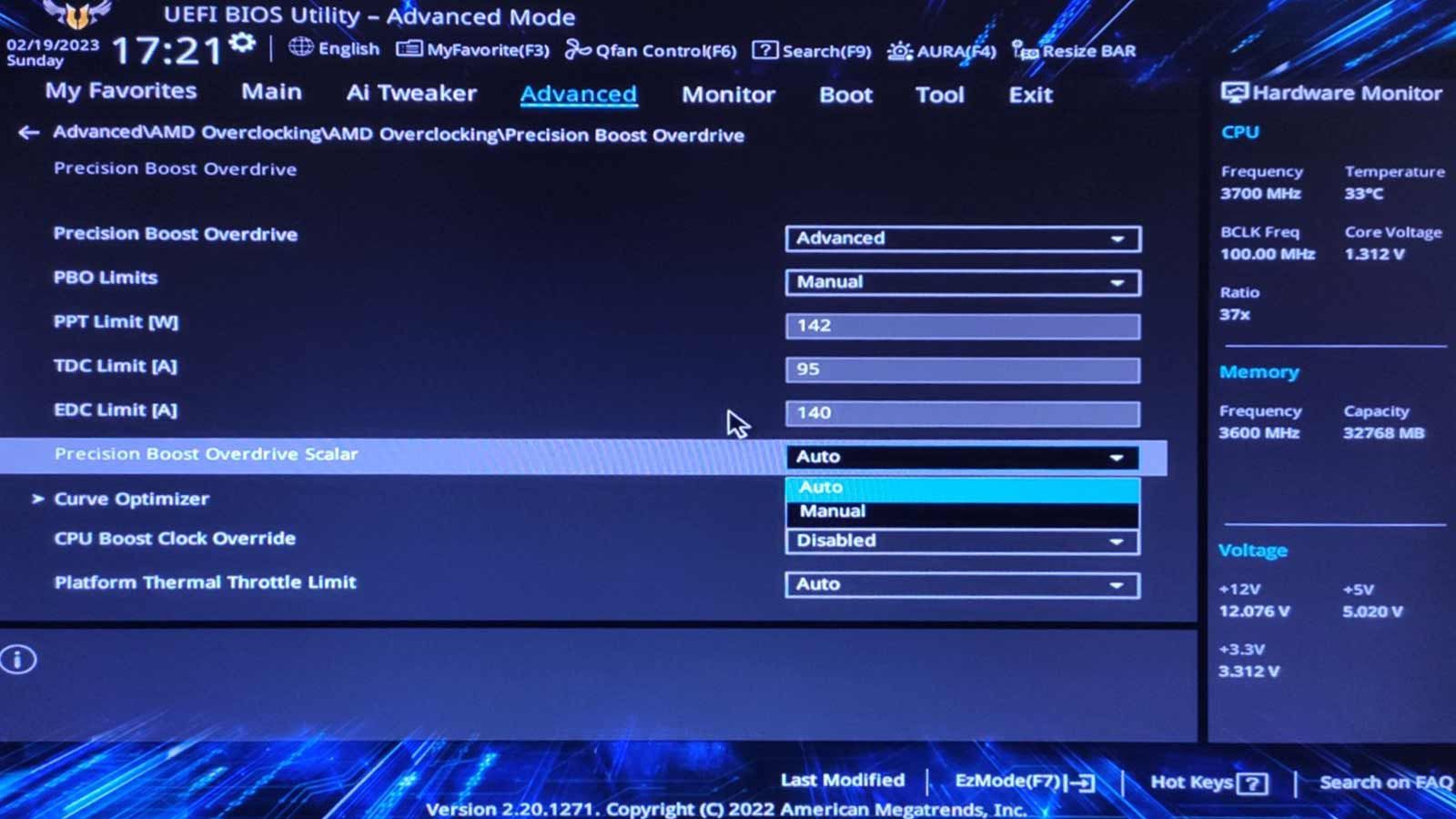
Locate the core that caused the crash according to CoreCycler’s log and reduce itsCore Optimizer Magnitudevalue by two.
Is My PC Now Free of Blue Screens?
You’ll still meet the occasional crash.
Keep saving frequently, and have a full OS backup handy.
You never know if and when your PC will crash again.