SQLs versatility as a DBMS querying language has risen over the years.
Its expansive utility and versatility make it an all-time favorite for every data analyst.
There are quite a few advanced-level functions besides SQLs regular ones.

These functions are commonly known as window functions.
Window functions are beneficial when youre applying aggregate functions over a specific dataset, or collection of rows.
These functions go above and beyond the aggregation functions that GROUP BY provides.
it’s possible for you to’t use window functions within theWHERE,FROM,andGROUP BYstatements.
If you structure the command incorrectly, youll get an error and your code will fail to run.
Here’s the default syntax:
Where:
Window functions are different from some of themost basic SQL commands.
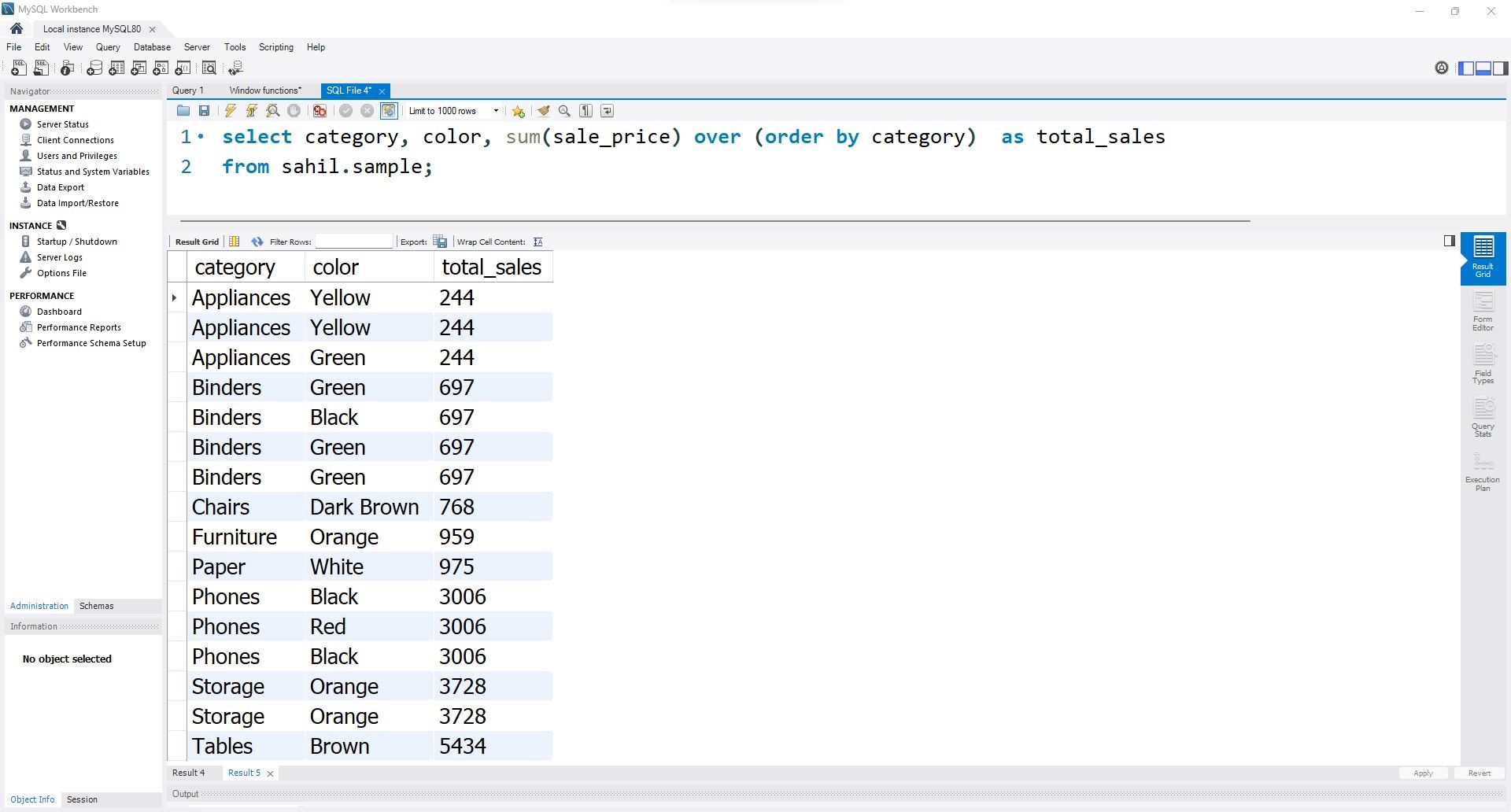
The sum function adds up the sale_price column.
It does so by category, since the OVER clause specifies ordering by the category column.
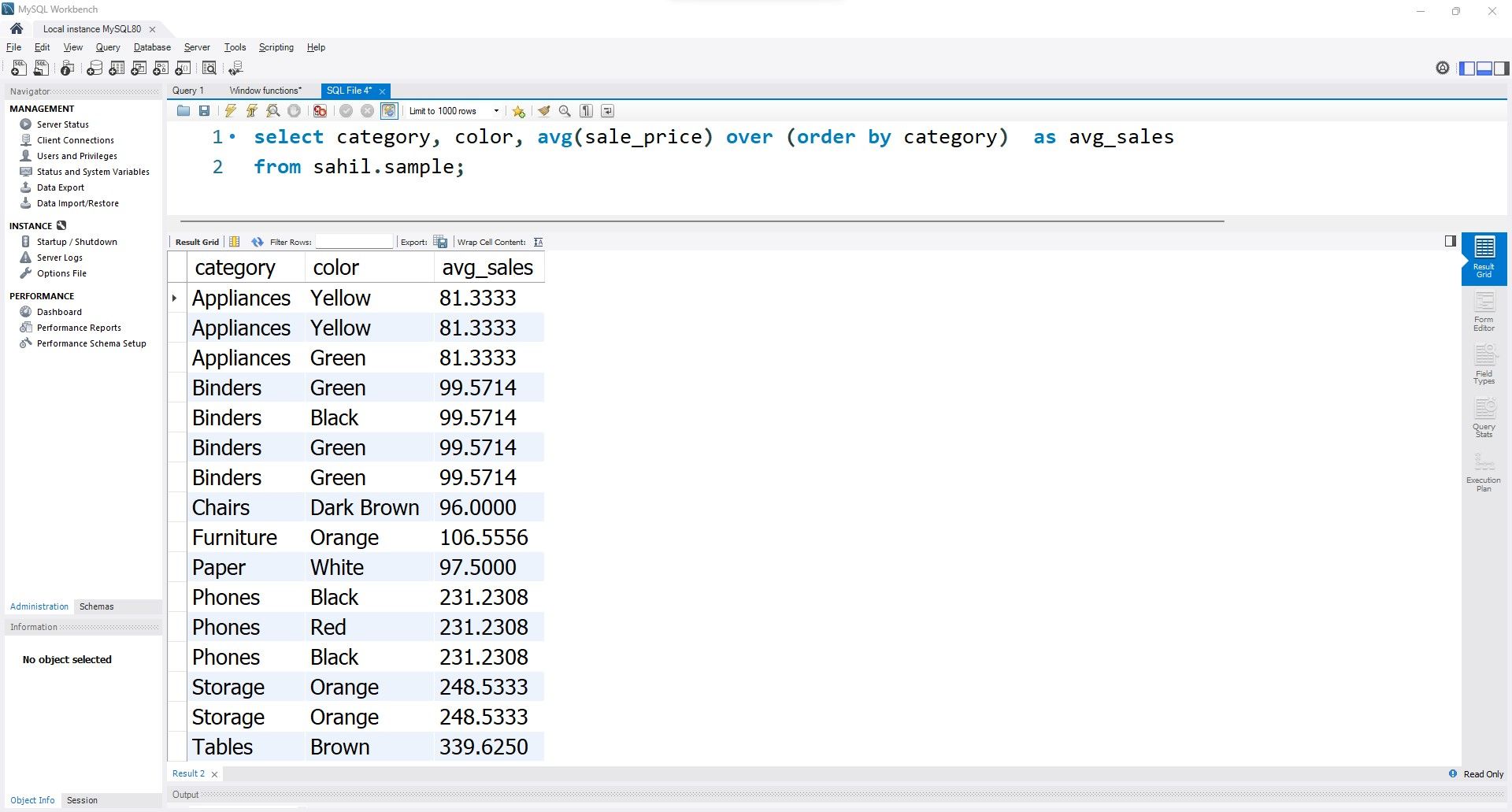
Instead of the sum, you will get a column with the average sales.
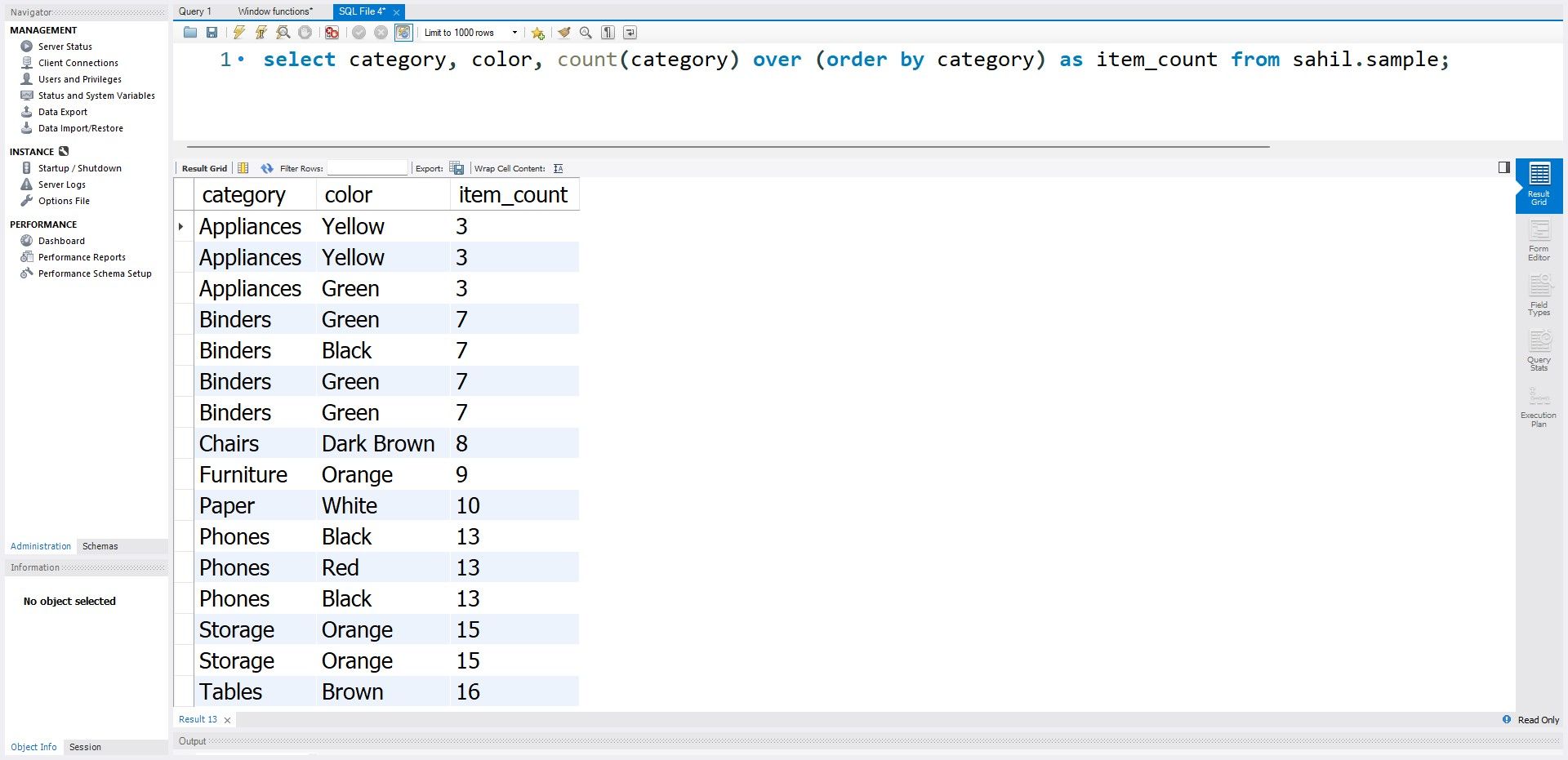
When you pass the count function, you get the total count of each value within the new column.
The row_number() function assigns a row number to each row, depending on the order by clause.
The starting row number is 1; the row_number assigns a corresponding value to each row until the end.
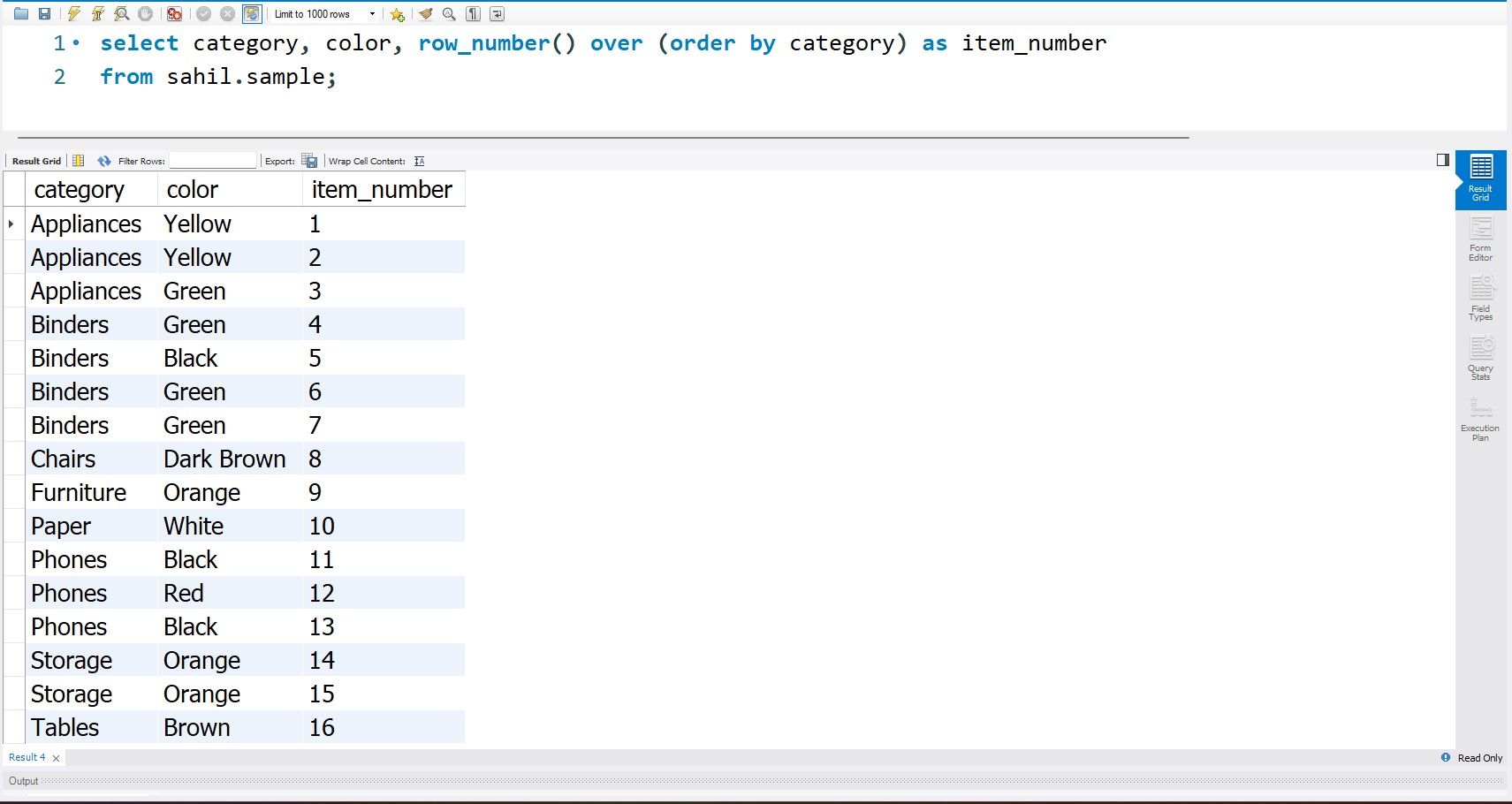
The above syntax sets a rolling serial number, irrespective of the items stored within the category.
you’re able to use thepartitionfunction to perform this simple, yet practical task.
The partition keyword assigns designated row numbers basis each category item.
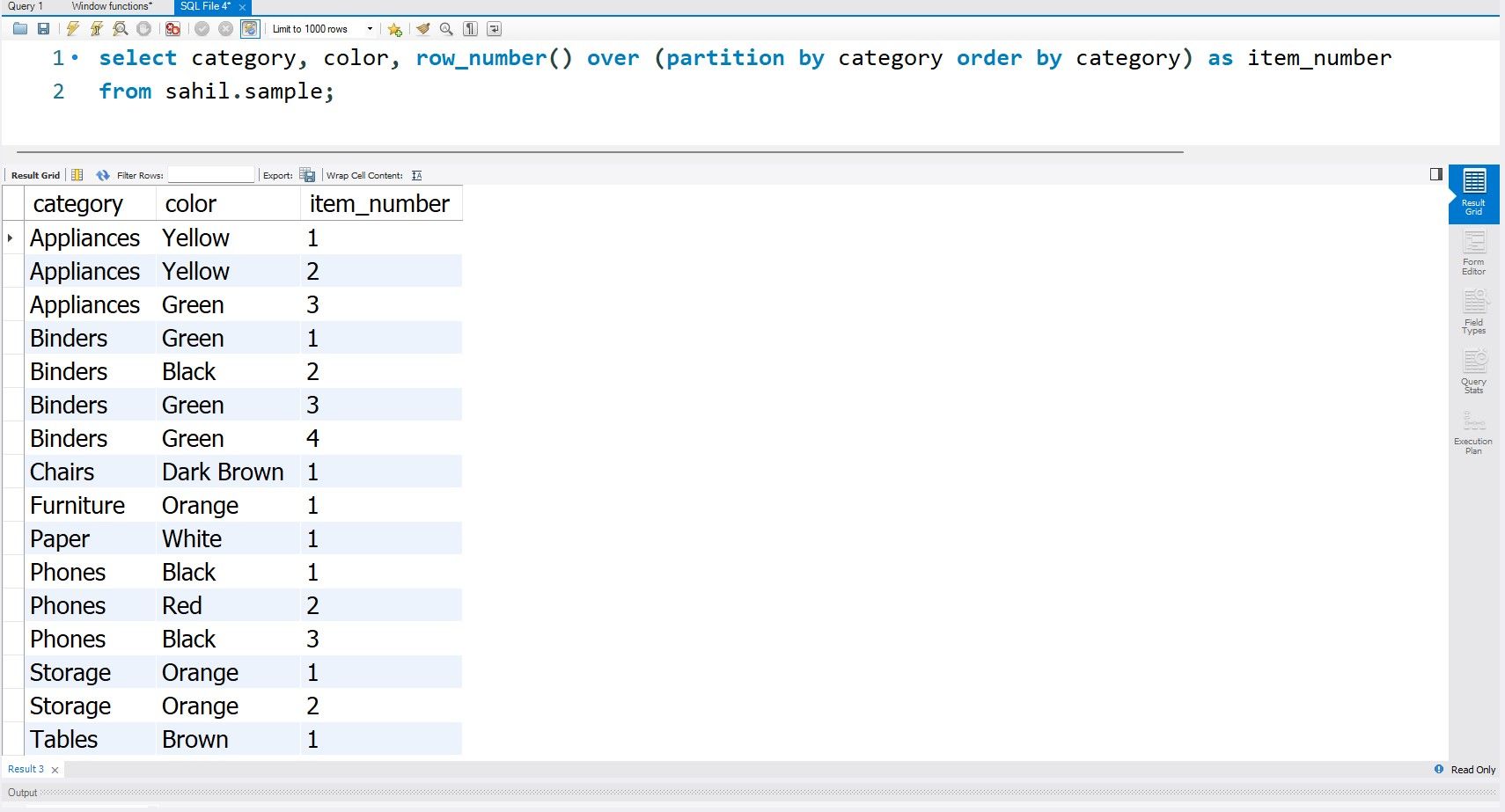
The query will then use that order to assign a rank value to each row.
The order by function sorts the color category, while the rank function assigns a rank to each color.
However, all the same color values have the same rank, while the different colors have separate ranks.
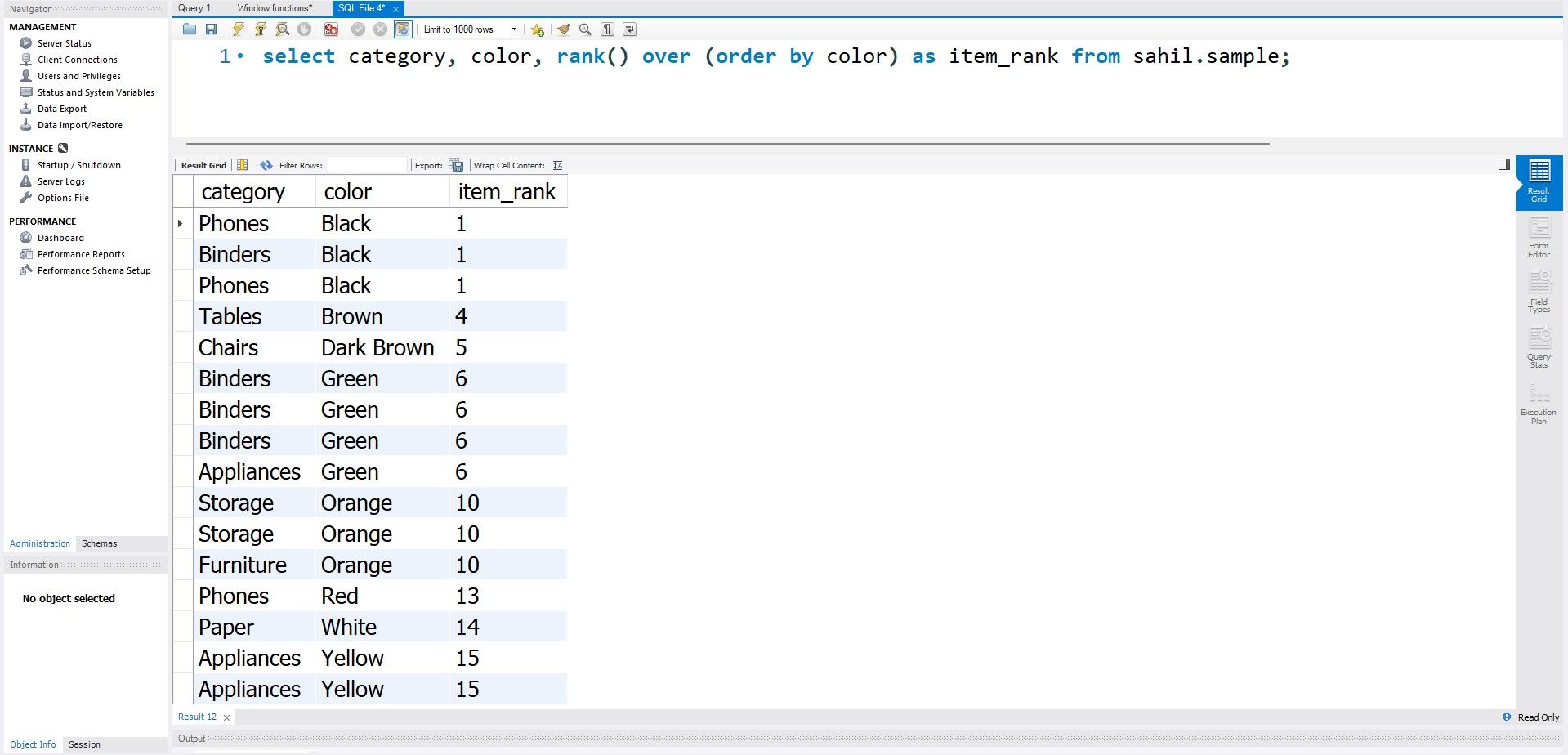
However, the next color Brown gets a rank 4 instead of rank 2.
The rank function skips values and assigns the next chronological value to the different entries.
The dense_rank function doesn’t skip any rank values during the order by function.
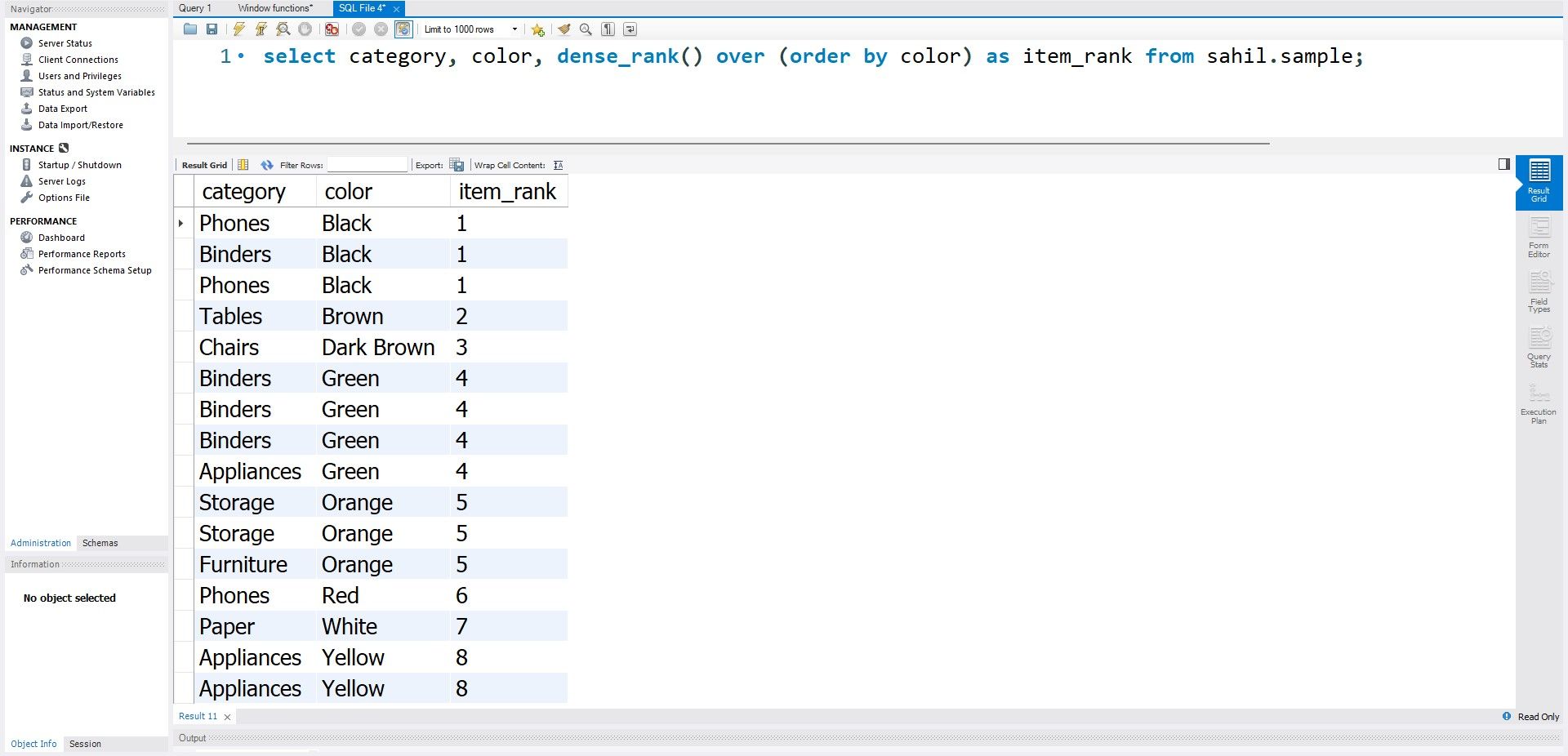
For example, the first three color items (Black) will have rank 1.
Sub queries are an excellent tool to perform advanced functions, enhancing your results' quality.