As the popularity of the SMB protocol increases, so has the number of malicious attacks.
What Is the SMB Protocol?
SMB stands for Server Message Block.

The protocol allows local web connection computers to share resources such as files, printers, and other devices.
Imagine you are working with a team in which members work remotely from different locations.
In such cases, the SMB protocol is a great way toshare files quickly and easily.
It will allow each team member to reach the same data and collaborate on projects.
Multiple people can view or edit the same file remotely as if it is present on their own computer.
How Does the SMB Protocol Work?

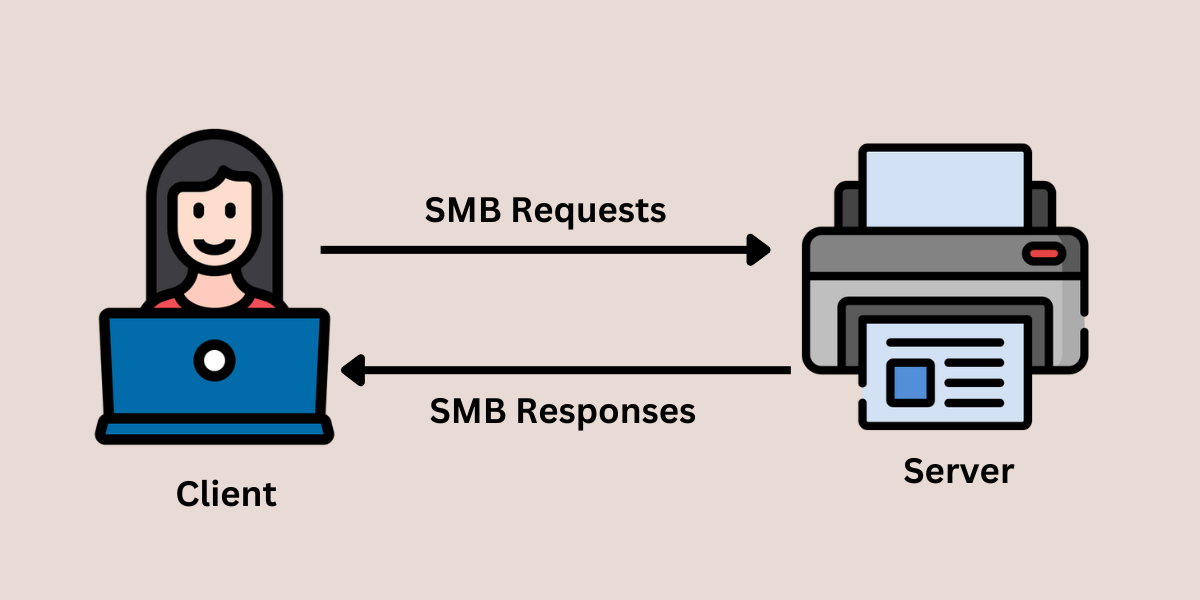
The SMB protocol follows the request and response method to create a connection between the client and server.
Here are the steps in which it works:
Step 1.
The packet contains the full path of the requested file or resource.
Process by Client: The client receives the response and then processes the data or resource accordingly.
Let us understand this with an example.
Hackers have targeted this protocol to gain access to corporate systems and networks.
This increases the chances of malicious actors exploiting these devices and gaining access to sensitive data.
Here are the most common SMB exploits.
In such attacks, hackers use automated tools to guess the correct username and password combinations.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Another attack vector used against SMB protocol is man-in-the-middle attacks.
They can then view and alter the data being exchanged.
Buffer Overflow Attacks
Hackers also use buffer overflow attacks against the SMB protocol.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks are also a major threat to SMB protocol.
If the ransom is not paid, they can delete all the encrypted data permanently.
Remote Code Execution
Remote code execution is another attack vector used against the SMB protocol.
Therefore, it is vital to ensure that all business systems and networks are secured against malicious attacks.
By following these measures, you might ensure that your business remains secure from malicious attacks.