How do they differ?
Which one should you choose?
What Is SATA?

Gavin Phillips/Unsplash
The SATA or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment connector uses the standard 15 power pins and seven data pins.
However, just because SATA drives focus on storage capacity doesn’t mean they’re slow.
Most consumer-based SATA drives start at 5400 RPM but can go as high as 7200 RPM.
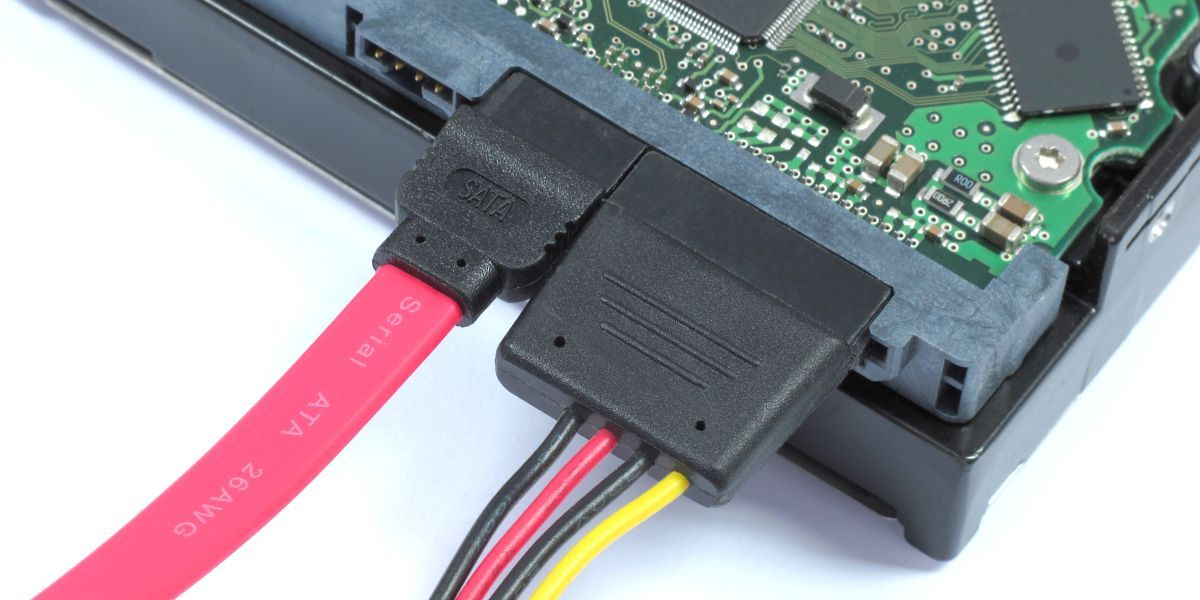
CyberVam/Shutterstock
Even withSSDs taking over, SATA HDDs are still popular for mass storage.
What Is SAS?
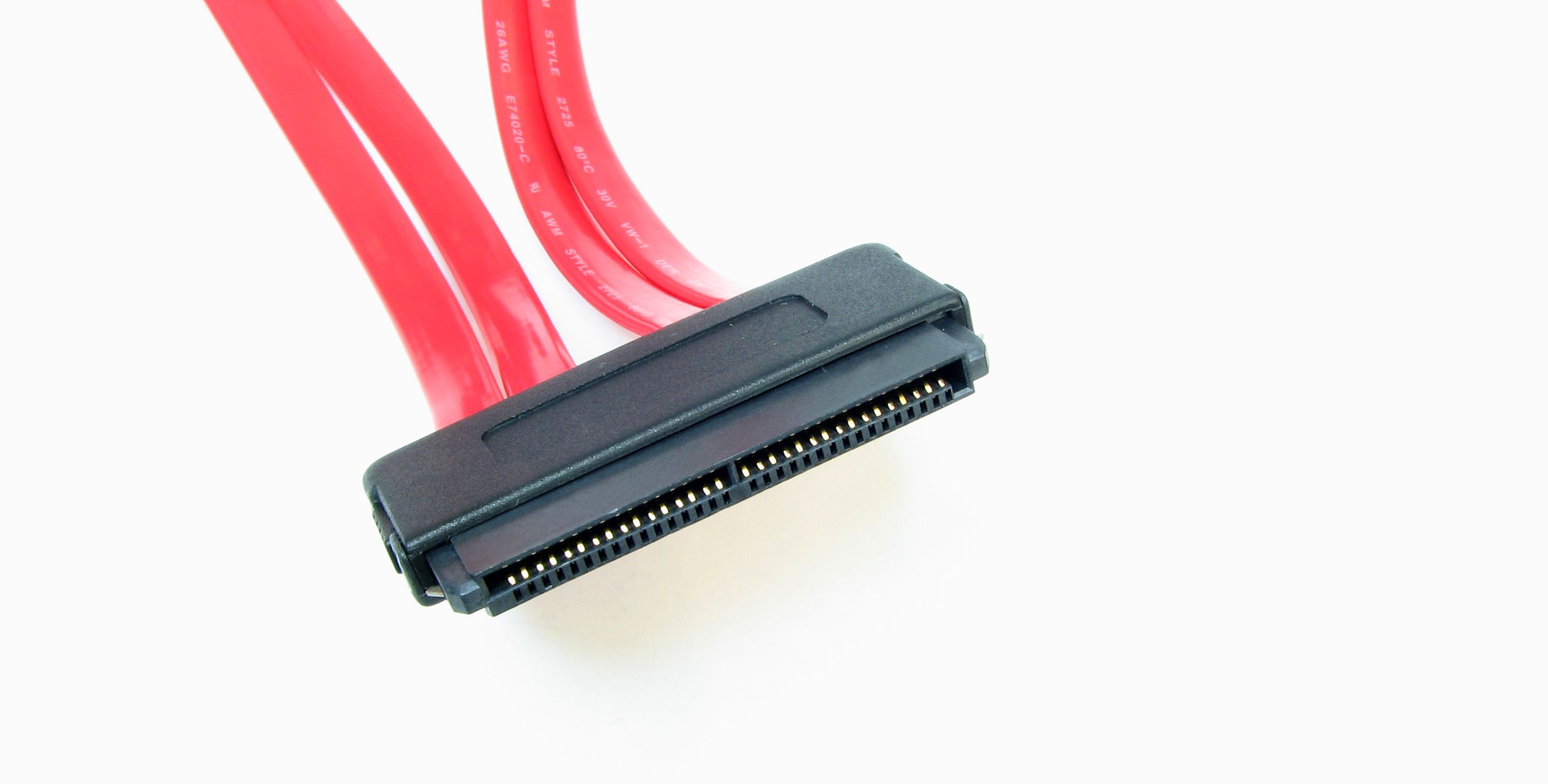
SAS stands for Serial Attached Small Computer System Interface.

Adamantios/Wikimedia
It uses a similar connector to SATA, also using 15 pins for power and seven for data transfer.
However, the split in the SATA connector between the power and data transfer pins isn’t as prominent.
SAS drives are faster and more reliable than SATA drives in terms of data transfer.
A SATA connector is fast at storing data, but outbound data isn’t transferred at the same speed.
SAS remedies this issue by transferring data out as fast as it goes in.
They’re commonly used in enterprise-level applications and servers designed to run 24/7.
SATA vs. SAS: What’s the Difference?
SATA and SAS drives have pros and cons, so here’s a handy table to compare the two.
1TB drives start at $35-$40.
Use Cases
Consumer PCs, laptops, and storage solutions
Enterprise environments such as servers and data centers.
EvenPCIe SSDs can be a good alternative compared to SATA.
Should You Use SATA or SAS?
As you’ve got the option to probably guess, both technologies have specific uses.
You get faster, more reliable storage designed to run constantly without failure.
That said, it does come at a slight premium: cost.
Overall, the choice comes down to what you’ll be using your drive for.