The processor is the brain of any computer, and it is constantly evolving to improve efficiency.
A processors design determines how many instructions it can do and how fast and efficiently it can do them.
Read on to learn more about them and their differences.
Image Credit:Thomas Schanz/Wikimedia Commons
An ISA is the part of the processor that contains all the basic instructions a processor can execute.
These instructions are the building blocks of a computer program.
They are usually not more complex than your basic addition and subtraction.
Image Credit:SiFive HiFive1/Wikimedia Commons
In general, there are two types of ISA circulating in the market.
They are the RISC and CISC architectures.
RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computer, while CISC stands for Complex Instruction Set Computer.

Basically, RISC is a computer architecture designed and optimized to use fewer instructions than its CISC counterparts.
What is ARM?
We have established that ARM processors are some of the top RISC architecture in the market.
Image Credit:SiFive HiFive1/Wikimedia Commons
So, what exactly is ARM, and why are they the most popular RISC processors?
They use their own closed-source ARM ISA to design highly efficient microprocessors and system-on-a-chip (SoC).
This close integration of multiple modules has allowed the ARM processors to be fast and efficient.

Image Credit: Codasip Group/Wikimedia Commons
What is RISC-V?
RISC-V is an open-standard ISA developed at the University of California, Berkeley.
So why is it?
This is because RISC-V is an open-standard ISA.
RISC-V only starts with a base instruction set of 47 instructions.
These instructions include all the basic functionalities a chip needs to work and do basic tasks.
ARM or RISC V?
ARM and RISC-V are ISAs that follow the RISC design philosophy, so which one is better?
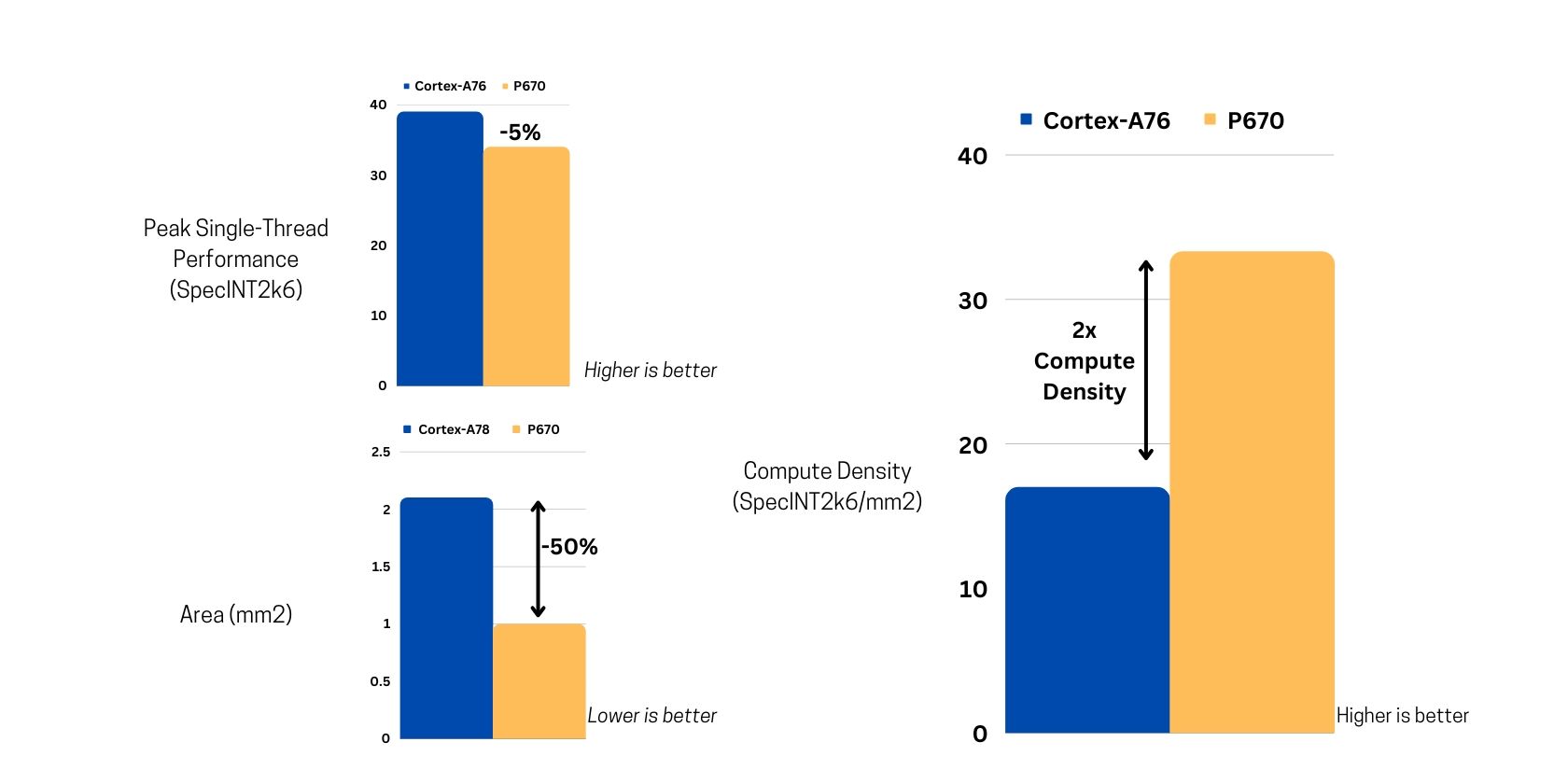
Although the Cortex-A78 wins in raw performance, the P670 doubles the compute density of the Cortex-A78.
Thats around a two-year difference in terms of research and development.
Arms latest processors now run on the ARMv9 ISA, significantly improving the ARMv8 that the Cortex-A78 uses.
So, in terms of raw performance, ARM processors are still in the lead.
Having shorter and fewer instructions allows RISC processors to be highly power efficient.
ARM is a closed-source ISA based on RISC that is licensed to companies for their processors and SoCs.
The ARM ISA allows Arm to design high-performance RISC processors like Apples M1 chips.