NVIDIA is known to release a new-generation graphics card architecture every two years.
In 2018, it released the Turing chip for the GTX 16-series and RTX 20-series GPUs.
Then, in 2020, it introduced the Ampere chips for the RTX 3000 GPU.

NVIDIA
So, what improvements does the Ada Lovelace microarchitecture bring to the RTX 4000 GPU?
Thissmaller nm brought by improvement in the node processallows the RTX 4000 series to deliver more power efficiently.
However, ray tracing is completely different from rendering scenes.
Image Credit:NVIDIA
This means GPUs are less efficient when it’s processing many different shaders.
This allows the streaming multiprocessors to work more efficiently, as they simultaneously work on the same data.
That’s why NVIDIA developed DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling).
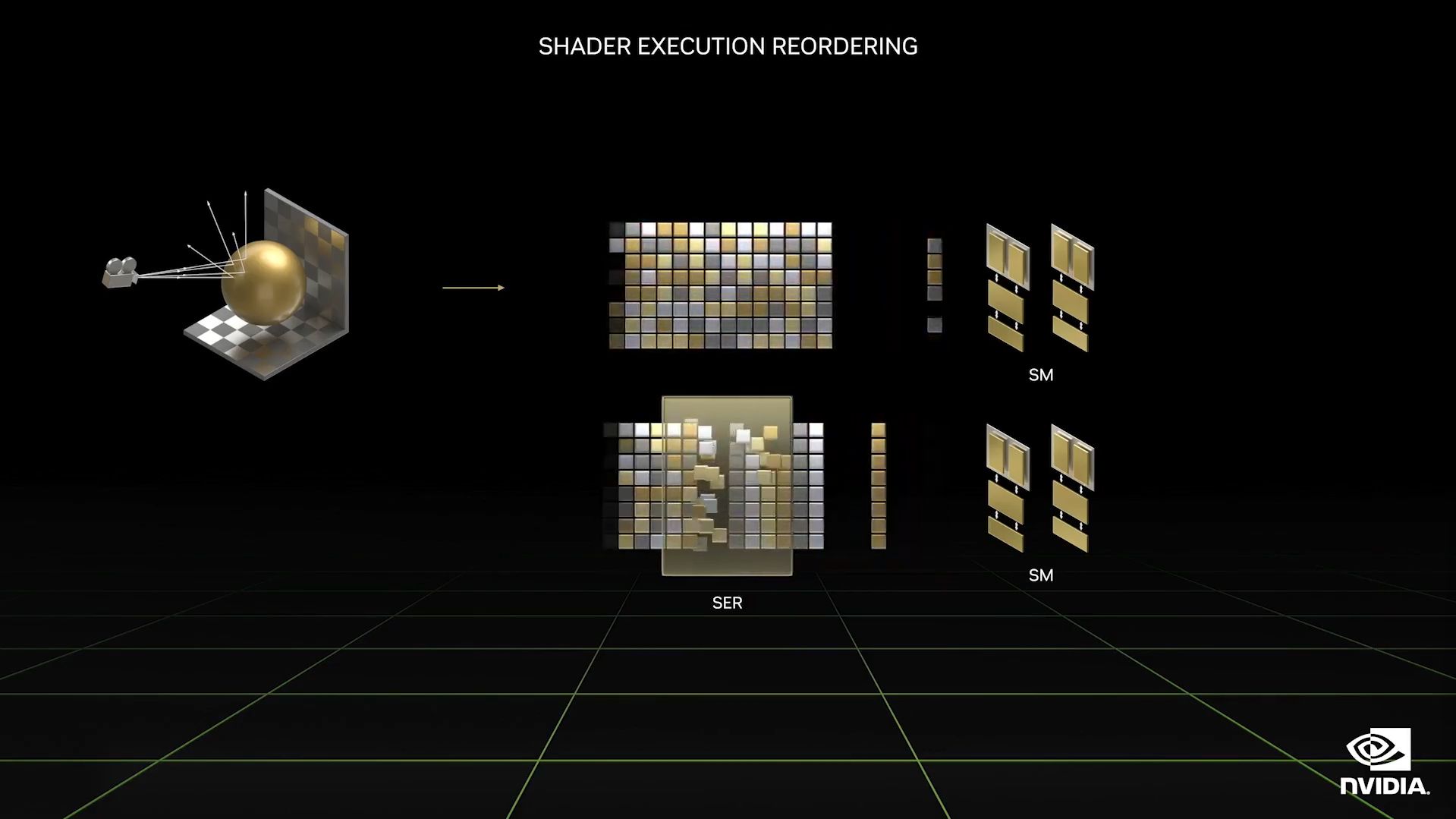
Image Credit:NVIDIA
DLSS technology uses AI to predict the next pixel, helping reduce the workload on the GPU.
But with the Ada Lovelace architecture’s DLSS 3.0, NVIDIA expands the prediction from pixels to frames.
This new generation of Tensor Cores is probably why DLSS 3.0 performs much better than its previous iterations.
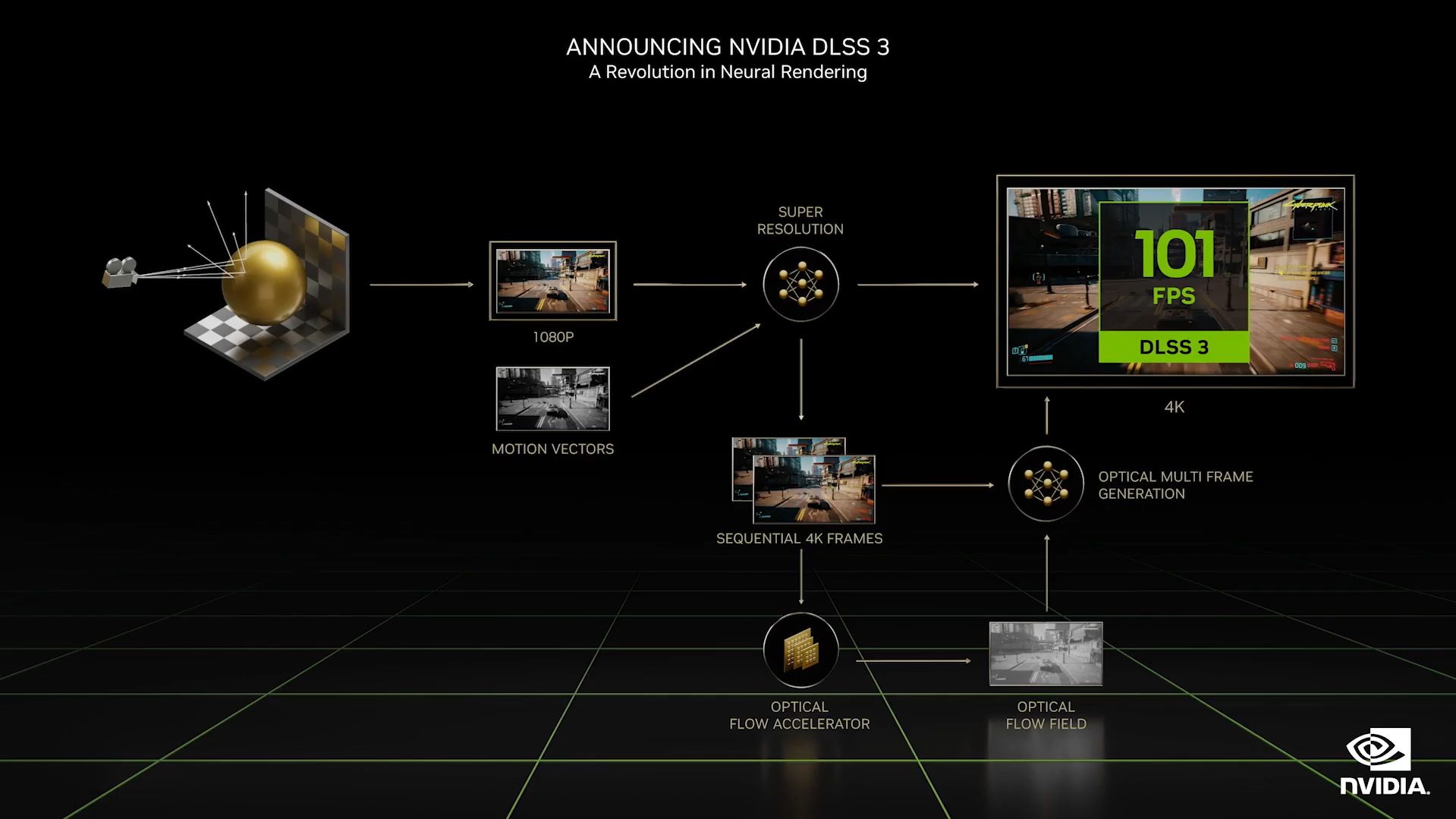
Image Credit:NVIDIA
It could also be why comparatively lower-model 4000-series chips outperform the top-tier models of the 3000-series GPUs.
Furthermore, they say that its latest chips offer more than twice the performance for the same power rating.
So, we’re holding our breath and waiting to see actual benchmarks when retail units hit store shelves.
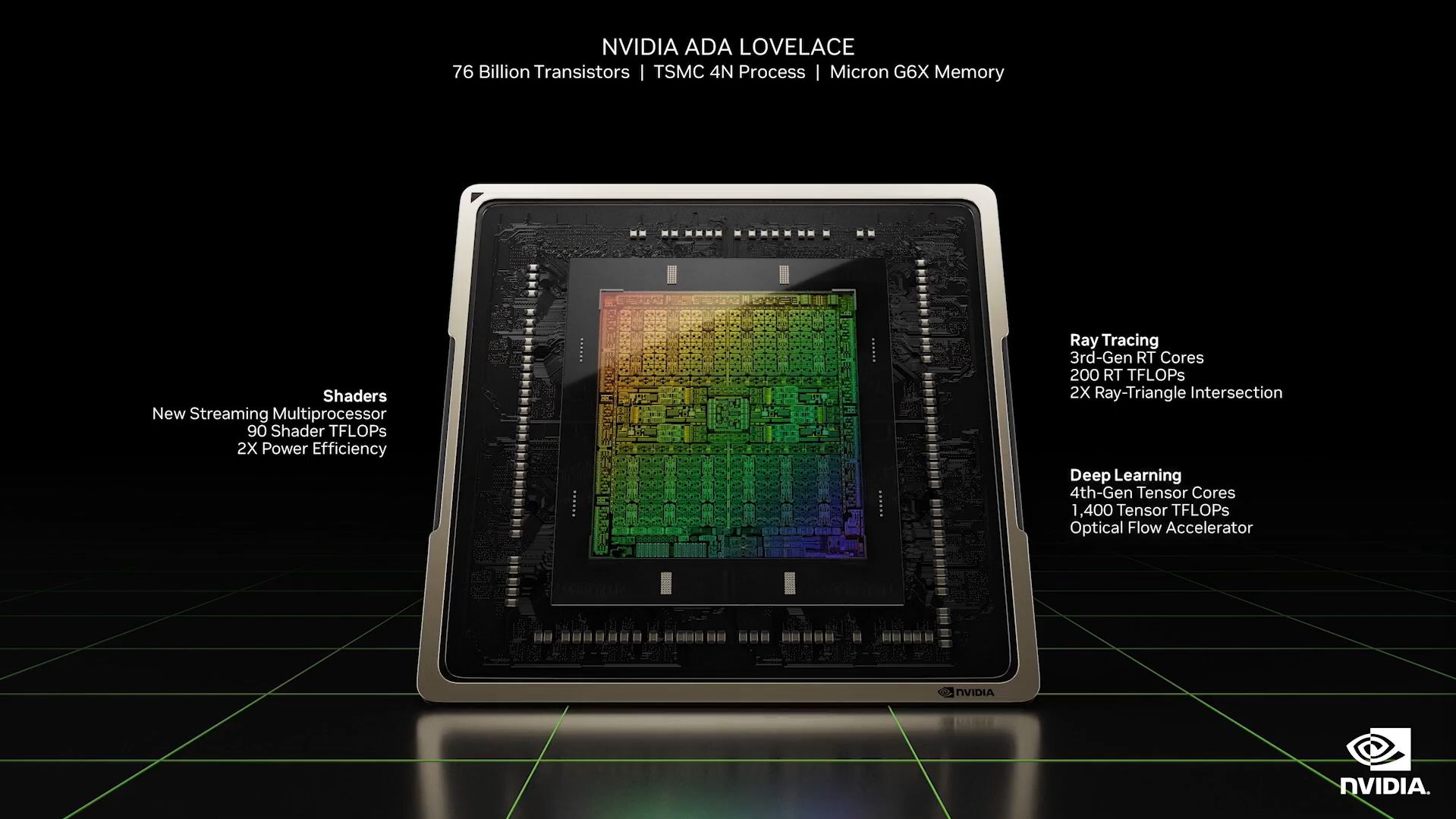
Image Credit:NVIDIA
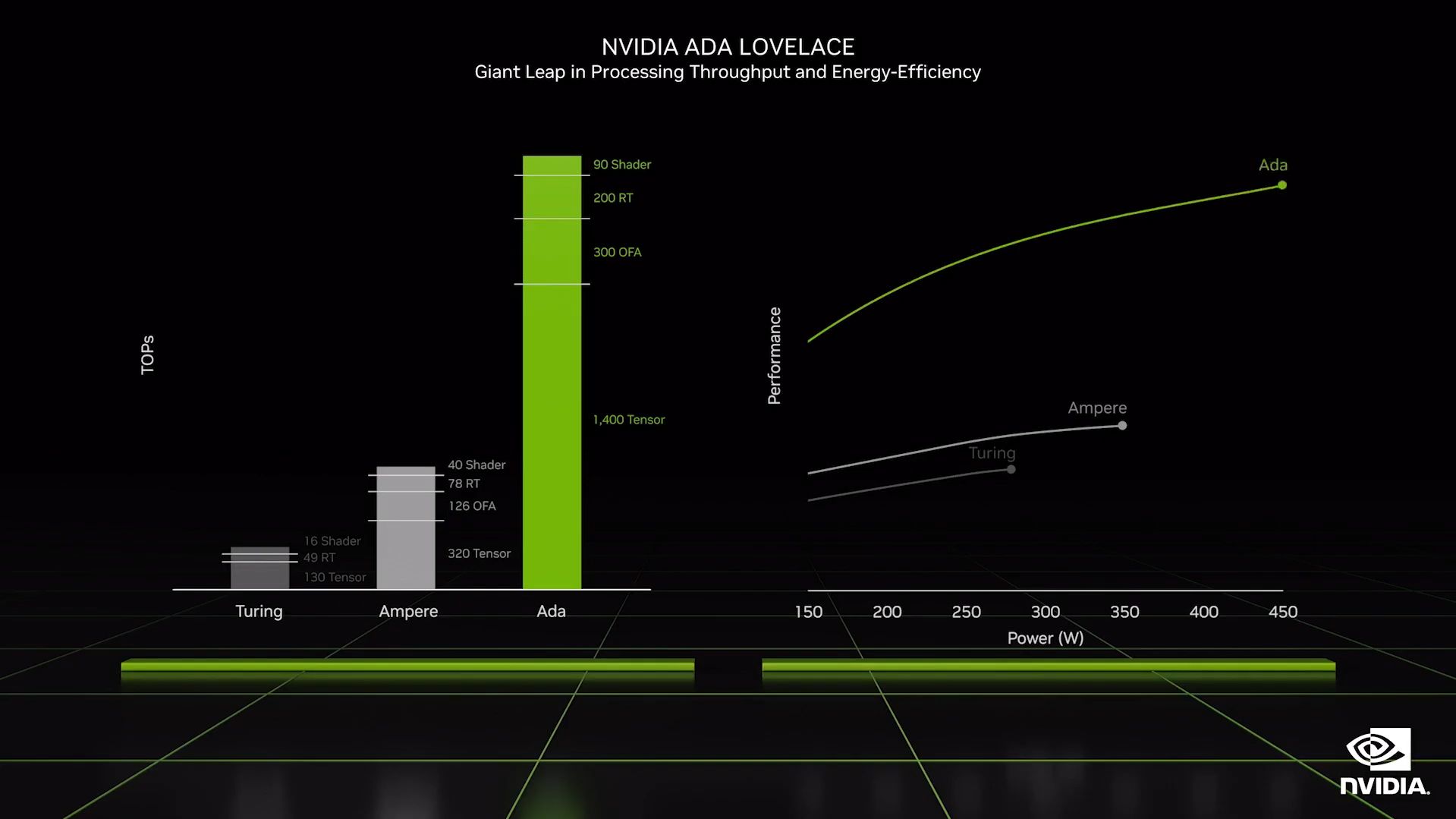
Image Credit:NVIDIA