Despite its dominance in the CPU market, the company struggled to adapt to key technology shifts.
The companies represent a sample of regions and industries that offer valuable insights into the factors behind these failures.
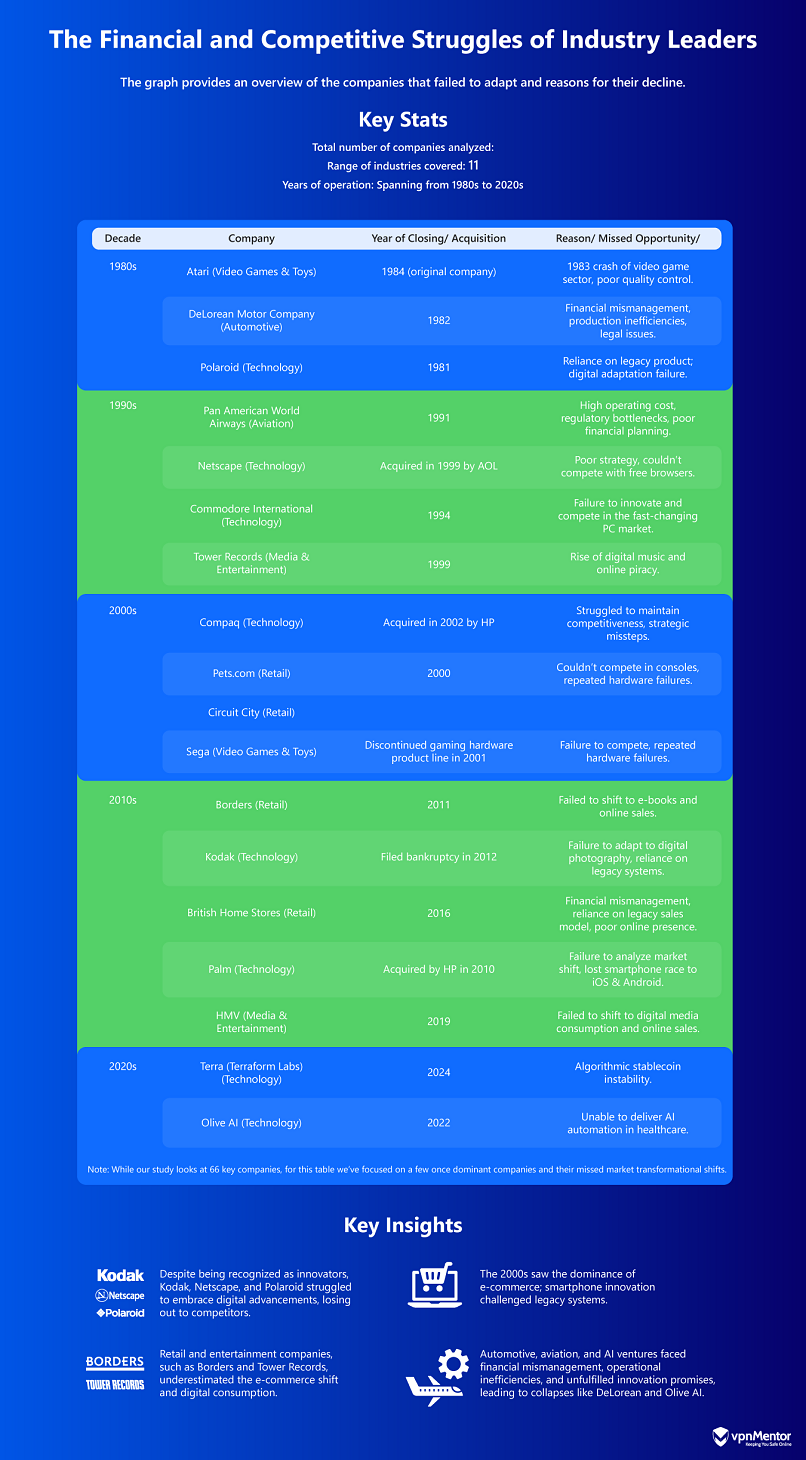
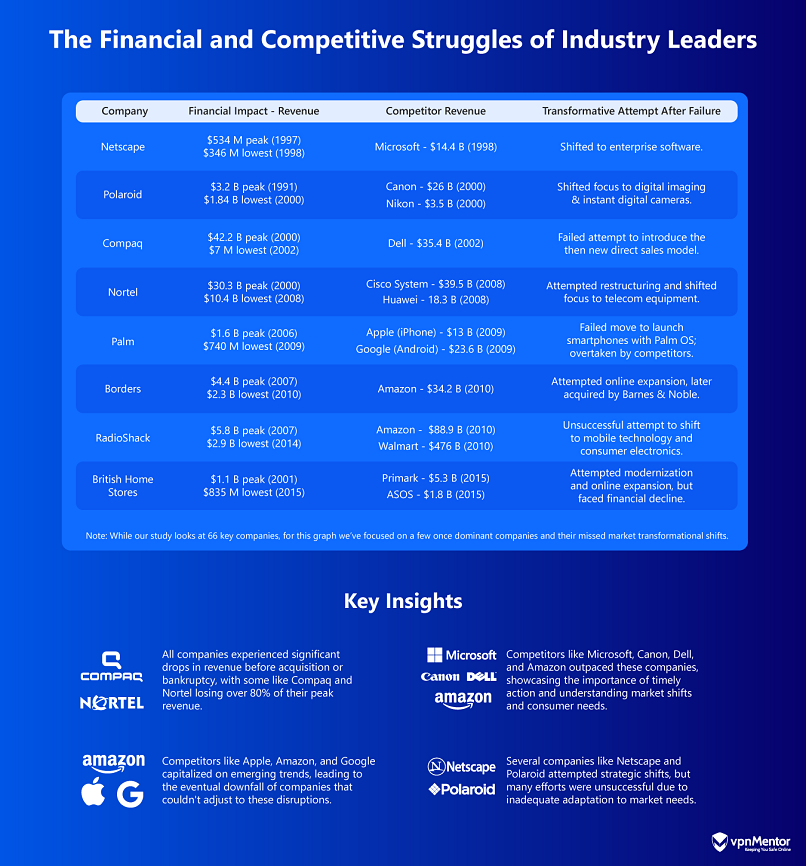
Table of Analyzed Companies
The table above provides a snapshot of the companies discussed in the analysis.

Expanding the graph to include these areas would require additional resources.
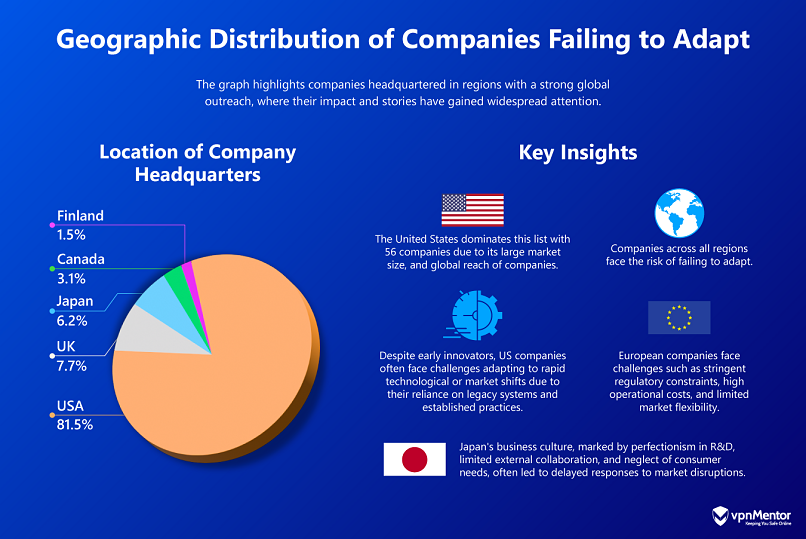
The findings reveal that 81.5% of the companies studied were headquartered in the United States.
Established in 1927, Pan Am was known for connecting continents with routes spanning Europe and Asia.

This started the airlines financial troubles.
The deregulation of the US airline industry in 1978 added to Pan Ams challenges.
The final blow were the acts of terrorism against its flights.

Despite efforts to restructure and sell assets, Pan Am ceased operations in 1991.
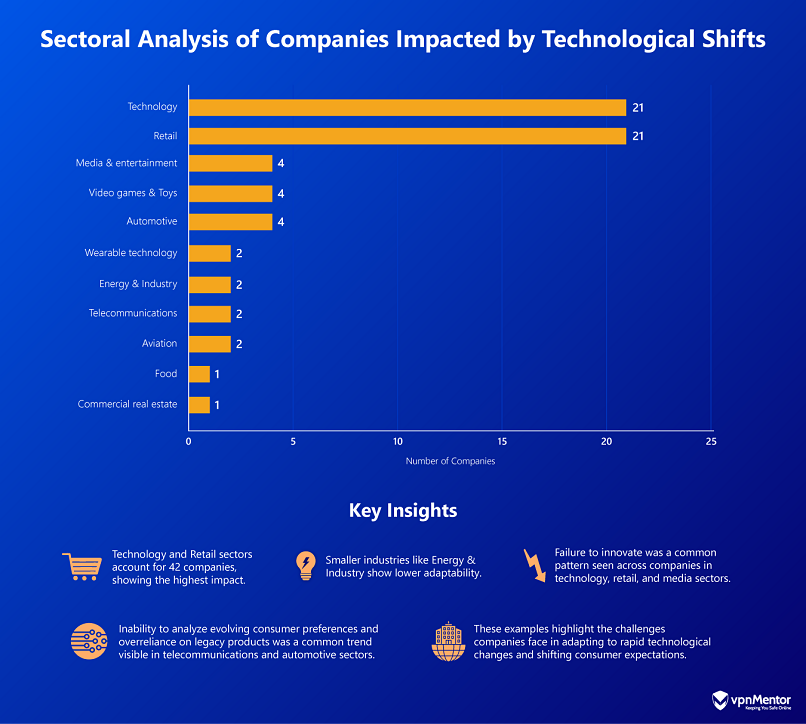
These are followed by the Media & Entertainment, Video Games & Toys, and Automotive sectors.
Sectors like Wearable Technology and Energy & Industry also feature notable examples, with fewer companies experiencing setbacks.
The dominance of technology and retail companies highlights their reliance on consumer preferences and innovation cycles.
The success of Atari inspired several copycat companies that flooded the market with consoles and low-quality games.
This oversaturation frustrated consumers and damaged the industrys reputation.
A critical misstep was the rushed release of the poorly designed E.T.
game, which flopped and left Atari with millions of unsold cartridges.
This sector-focused analysis provides valuable insights into how companies in these industries are impacted by fast-changing market dynamics.
Their inability to innovate and align with emerging trends can often bring down even established companies.
BlackBerry failed to anticipate that everyday consumers, not just business users, would drive the smartphone revolution.
The company also underestimated the transformation of smartphones into comprehensive mobile entertainment units.
Competitors prioritized convenience and accessibility, creating devices that appealed to both everyday and business users.
While B&N launched its internet store, Borders focused on expanding brick-and-mortar stores both domestically and internationally.
It also outsourced online sales to Amazon, losing customers to a rival.

Moreover, Borders overlooked the rise of e-books and digital readers.
The fall of Borders underscores the necessity of adapting to technological and market shifts to sustain business success.
These failures demonstrate the vital importance of innovation and the ability to adapt to new market demands.
Understanding these failures provides valuable insights for businesses trying to thrive in todays evolving market.
Established in 1937, Polaroid became synonymous with instant photography, renowned for its innovative instant cameras.
This resistance to change, combined with delayed market entry for new products, eroded its market share.
By 2001, declining sales and strategic missteps led Polaroid to file for bankruptcy.
These cases highlight the importance of agility and foresight in todays competitive market.
Lessons from Failure: What Can Businesses Learn?
The failures of once-successful companies offer important lessons for businesses today.
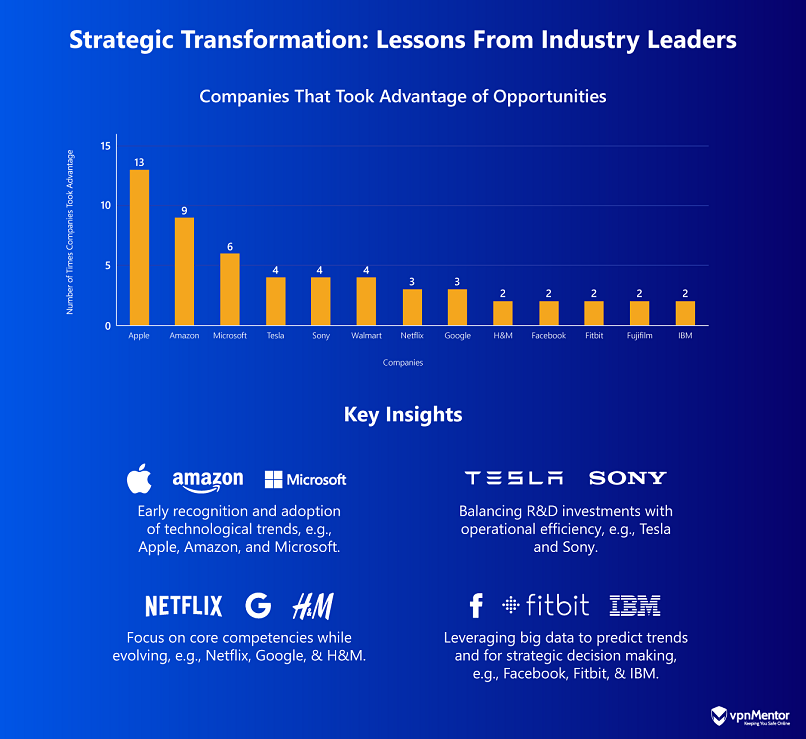
Their continuous investment in customer-centric innovation has allowed them to dominate their respective markets.
Balancing innovation with operational efficiency is another key lesson.
Companies like Ford and Sears faltered because they failed to combine bold innovations with efficient execution.
Another key factor is keeping pace with customer expectations and industry trends.
Companies like JCPenney and HMV failed to adapt to the rise of e-commerce, leading to their decline.
This enabled a thorough examination of how these companies failed to adapt to technology shifts and trends.
Visualizations and graphs were created to highlight common patterns and trends that these companies encountered.
The inability to recognize and respond to emerging trends often leads to missed opportunities and decline.
By learning from past mistakes, businesses can navigate the rapidly changing markets and avoid falling behind their competitors.
kindly, comment on how to improve this article.







