Do you know when you should use one instead of the other?
Or which is best for storing your photos?
Here are the basics it’s crucial that you know.

Miha Creative/Shutterstock
RAW - The Uncompressed Image Data
You get RAW files straight from your DSLR.
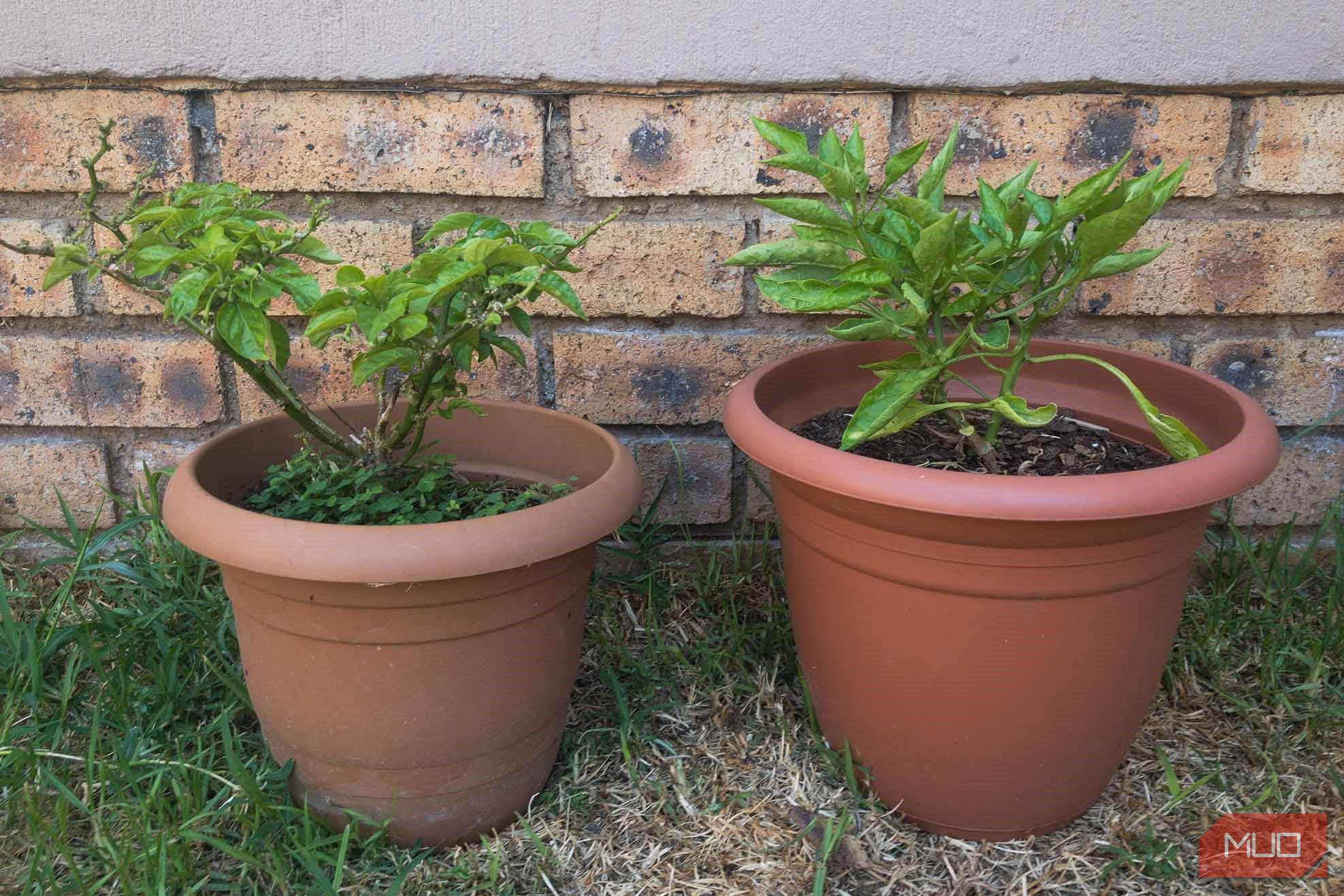
The RAW file is exactly what it sounds like… the raw picture file with no compression applied.
Every piece of information that your camera captured is contained in the RAW file.
Nolen Jonker
For this reason, these files are huge; they can easily top 25MB each.
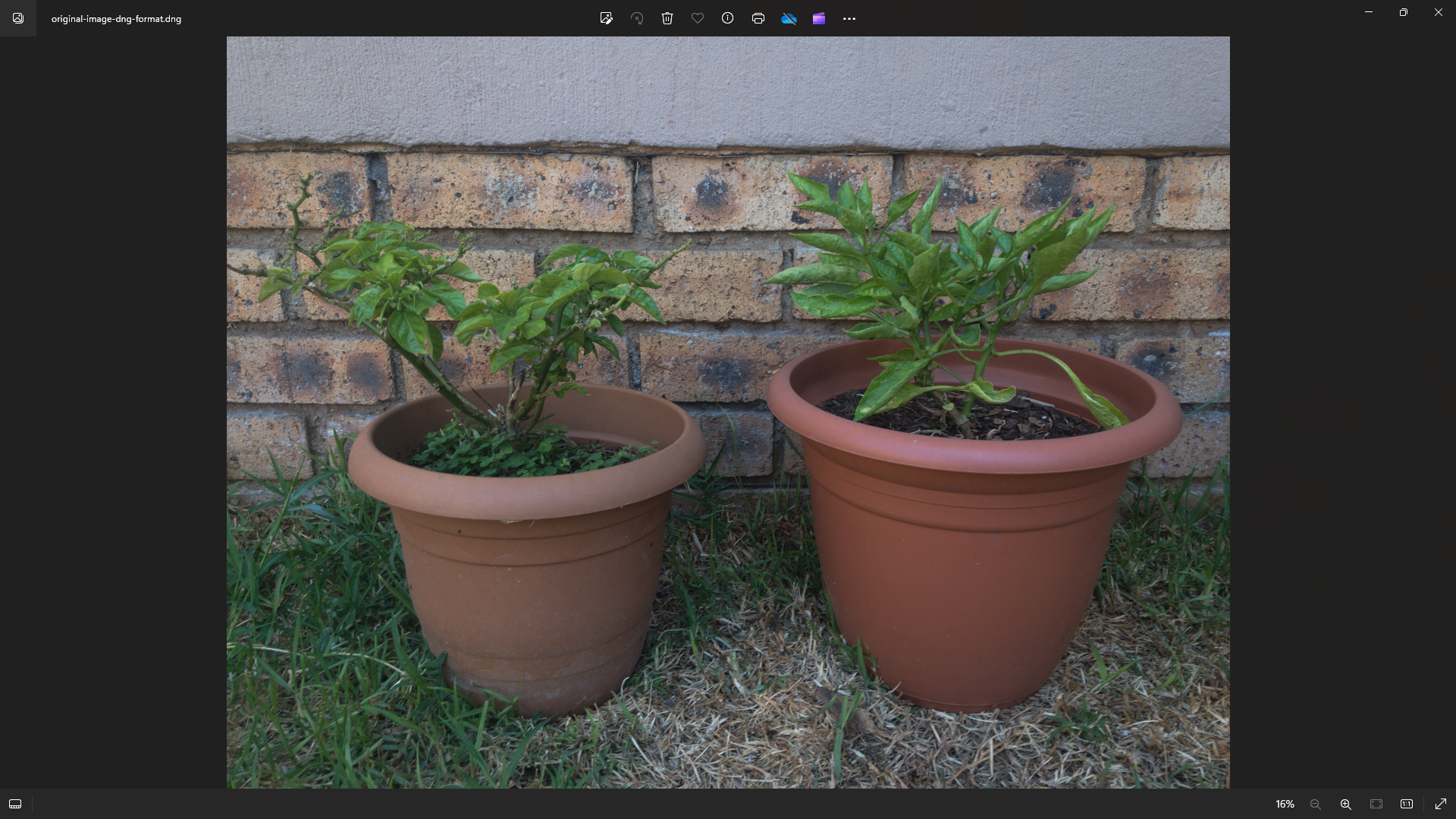
A RAW file is not actually an image and RAW is not a standardized image file format.
There’s also theDNG RAW image format(Digital Negative).

Nolen Jonker
However, not all camera manufacturers support this format.
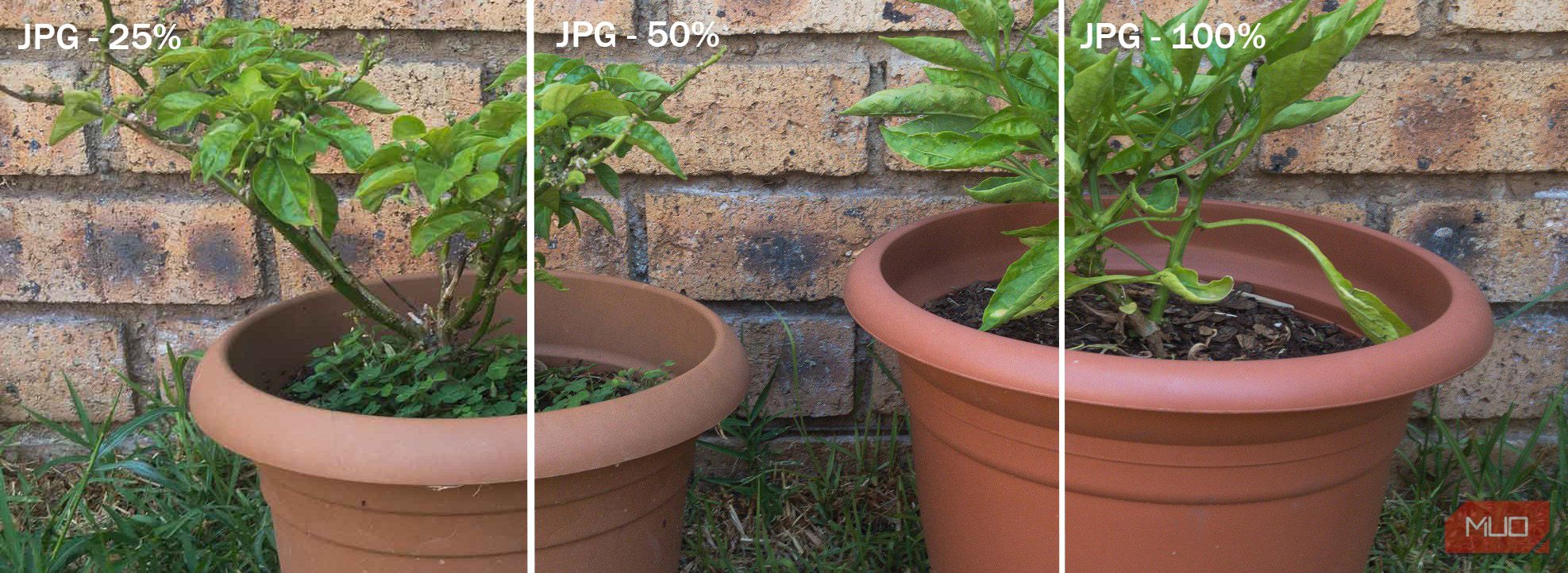
When more compression is applied, the quality of the photo decreases.
it’s possible for you to easily spot the pixelation in the low-quality version on the left.

Nolen Jonker
The high-quality version on the right has minimal visible pixelation.
In general, a high-quality and sometimes medium-quality JPEG is a good compromise between file size and quality.
Once you get to low-quality, however, the quality will suffer significantly.

Nolen Jonker
JPEGs tend to be best for photos or drawings, which have fewer sharp transitions than text.
This makes 256 colors available for GIFs.
Using lossless compression, GIFs can reproduce their limited color palettes perfectly over multiple decompressions and recompressions.

Nolen Jonker
Another important thing to know is thatGIFs can be animated, which has all sorts of cool uses.
However, it includes significantly more information than its predecessor, containing either 24 or 32 bits per pixel.
The 24-bit version contains RGB information, while the 32-bit version uses the RGBA color space.

Nolen Jonker
When you see a PNG image with a checkered background, as shown above, it usually indicates transparency.
Because it contains so much more information, a PNG file will be larger than a JPEG or GIF.
Below is a78.5MB PNG at 100% high-quality, converted from the RAW file.

Ed g2s via POV-Ray/Wikimedia Commons
It’s now a commonly used full-color file key in, accommodating both RGB and CMYK color models.
TIFFs can be saved either compressed or uncompressed, and the compression used can be either lossy or lossless.
TIFF functions as a file wrapper or container rather than a file pop in.

Nolen Jonker
Consequently, users have the option to achieve a broad spectrum of colors when working with TIFF files.
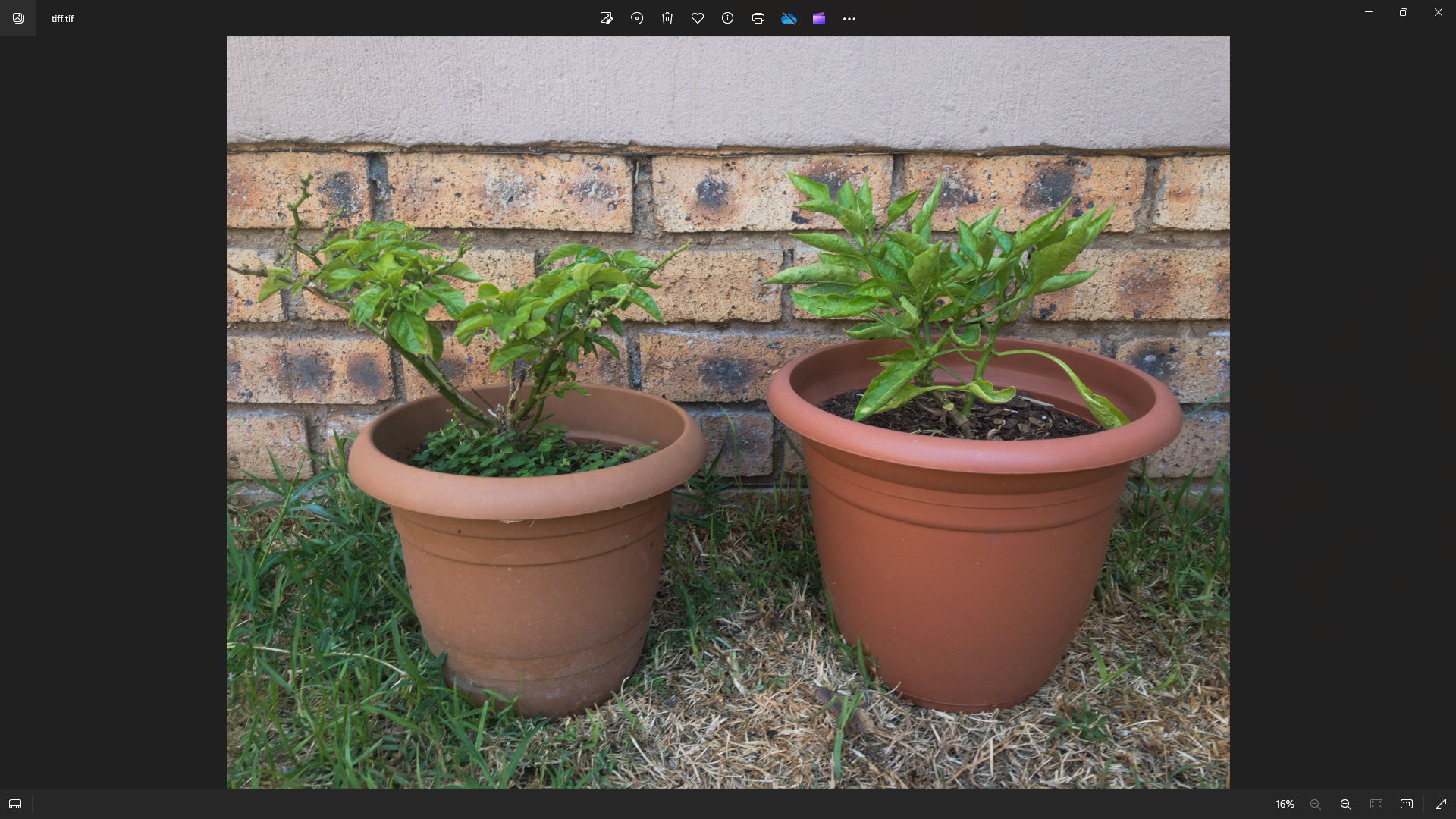
Because TIFF support isn’t universal in browsers, below are high-quality PNG screenshots of a TIFF file.
All the other formats above are raster-based.
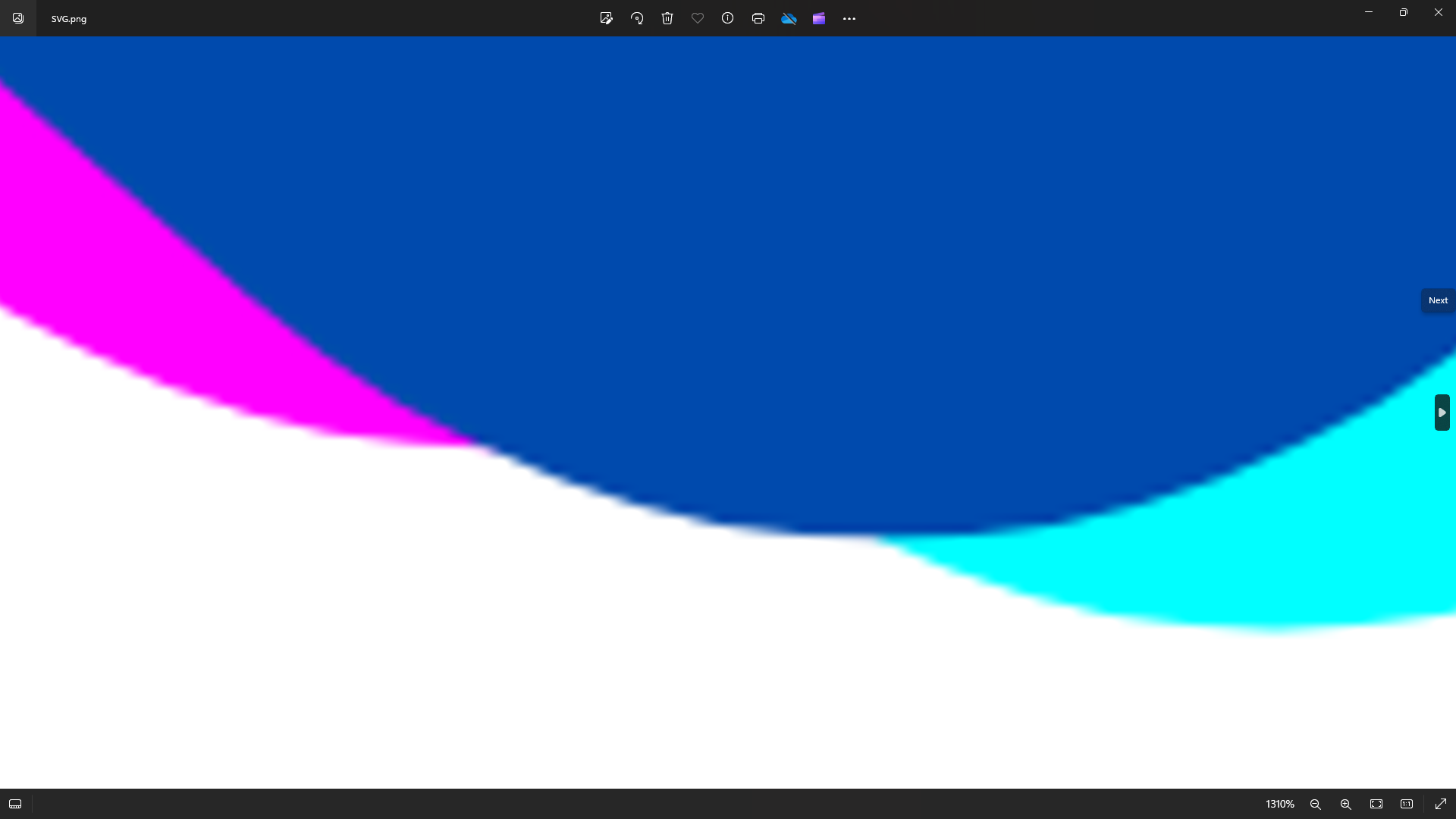
If you’re unsure about the differences, seeour guide to raster vs. vector images.
Below is a screenshot of a vector graphic, zoomed in to over 2,000%.
The edges of the graphic will remain smooth no matter how much you scale the image up or down.
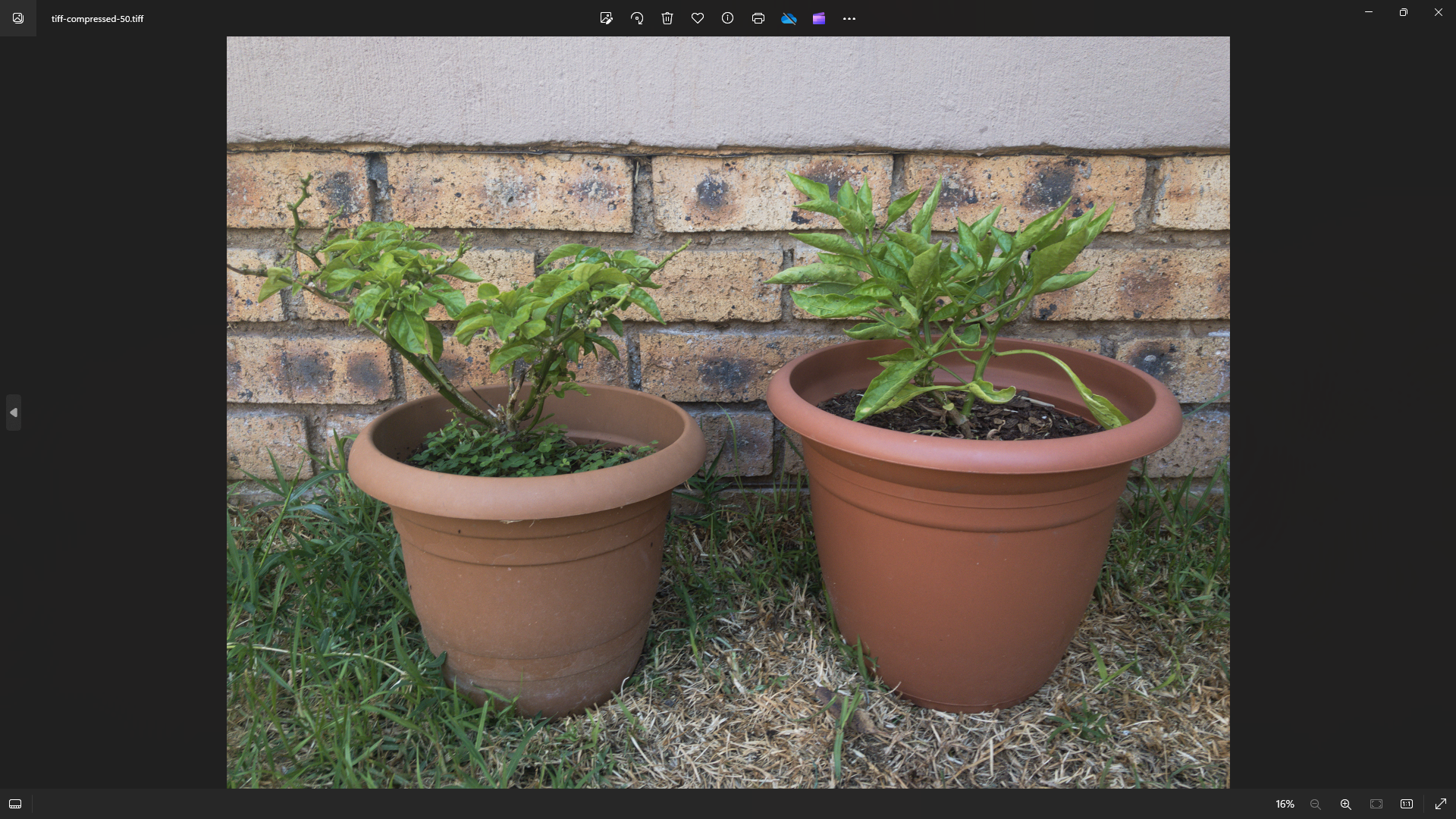
Here is a PNG version of the same graphic.
When zoomed in at the same point, it becomes very pixelated.
SVG files are usually very small in comparison to raster formats like JPEG and PNG.
It is not optimized for handling the complexity and richness of photographic content of real-world scenes.
After all of these details, you still might be asking which file pop in is the best.
Opt for high or mid-quality JPEG for more compression.
![]()
TIFF is ideal if you’re after lossless compression, high color depth, and versatility.
GIF is suitable for simple graphics and animations, while SVG offers infinite scalability.