Execution time is one of the common measures of the efficiency of a program.
The faster the execution time the better the program.
Threading is a technique that allows a program to perform multiple tasks or processes simultaneously.

You will learn how to use the Python built-inthreadingmodule and theconcurrent.featuresmodule.
For example, a program that downloads multiple image files from the internet.
This program can utilize threading to download the files in parallel rather than one at a time.
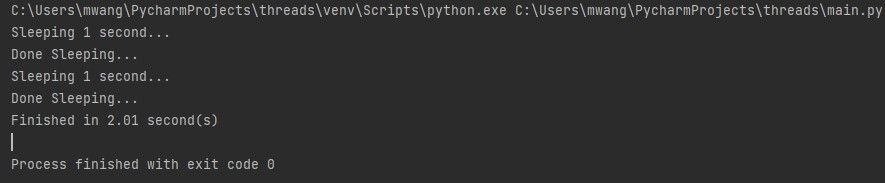
Initial Program Before Threading
The function in the following program represents a task.
The task is to pause the execution of the program for one second.
The program calls the function twice hence creating two tasks.
The output shows the program took 2.01 seconds to execute.
Each task took one second and the rest of the code took 0.01 seconds to execute.
you’re able to use threading to concurrently execute both tasks.

This will take both tasks one second to execute.
Implementing Threading Using the threading Module
To modify the initial code to implement threading, import thethreadingmodule.
Create two threads,thread_1andthread_2using theThreadclass.

Call thestartmethod on each thread to start its execution.
Call thejoinmethod on each thread to wait for their execution to complete before the rest of the program executes.
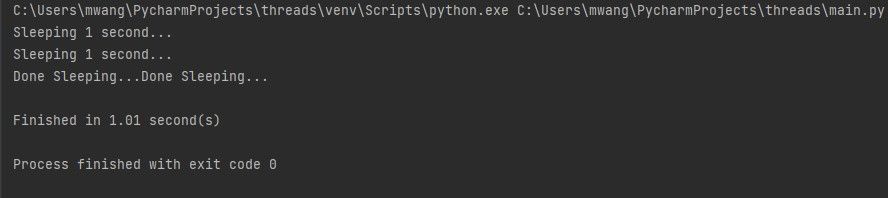
The program will run both threads concurrently.
This will reduce the amount of time it takes to accomplish both tasks.
The output shows the time taken to spin up the same tasks is around a second.
This is half the time the initial program took.
Implementing Threading Using the concurrent.futures Module
Python 3.2 saw the introduction of theconcurrent.futuresmodule.
This module provides a high-level interface for executing asynchronous tasks using threads.
It provides a simpler way of executing tasks in parallel.
To modify the initial program to use threading, import the concurrent.features module.
Use theThreadPoolExecutorclass from the concurrent.futures module to create a pool of threads.
Submit thepausefunction to the pool twice.
Thesubmitmethod returns afutureobject that represents the result of the function call.
Iterate over thefuturesand print their results using theresultmethod.
The concurrent.features module takes care of starting and joining the threads for you.
This makes your code cleaner.
The output is identical to that of the threading module.
The threading module is useful for simple cases where you better run a few threads in parallel.
In the real world, threads save more time.
Create a program that downloads images from the internet.
Start bycreating a new virtual environment.
Import the requests library and the time library.
Create a list of URLs of the images you would like to download.
Loop over the listof URLs downloading each image into the same folder that contains your project.
Display the time taken to download the images by subtracting the finish time from the start time.
The program takes around 22 seconds to download the 12 images.
Modify the program to use threading using the concurrent.features module.
Instead of a loop, use a function.
This is the function you will pass to theexecutorinstance.
The time reduces significantly.
It took only 4 seconds to complete the execution of the program.
Most programming languages support some form of threading.
It is important to familiarize yourself with the implementation of threads in other languages.
This equips you with the necessary skills to tackle different scenarios where threading may apply.