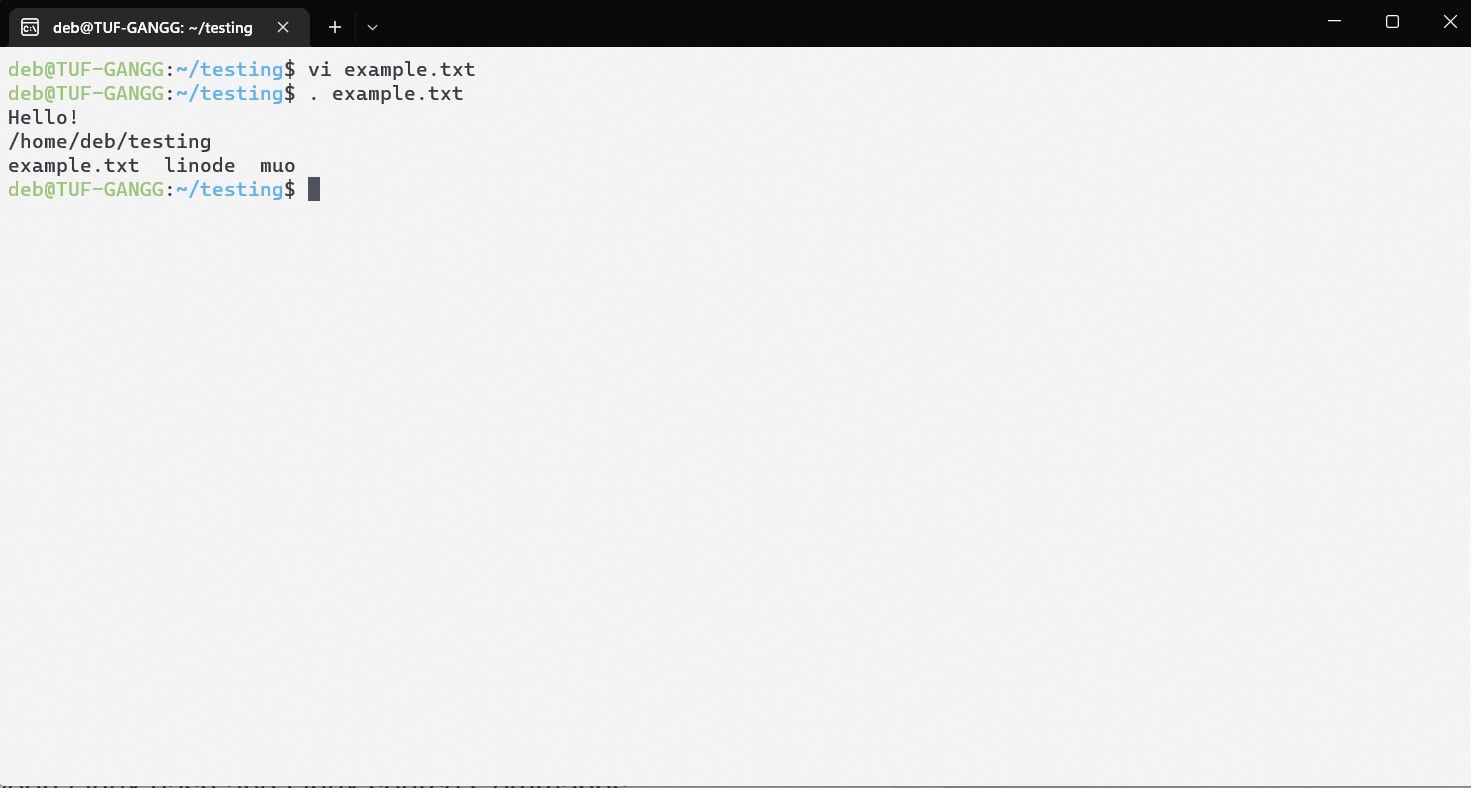
Start by creating a new file withthe touch command.
bring up the file in a text editor of your choice and write a few basic shell commands.
Write out the text file and proceed to pass it as an argument to the source command.
The system will execute the commands in the file and will return an output.
However, before you proceed, you must have a fundamental understanding ofenvironment variables in Linux.
The child process will not be able to modify the parent process’s environment.
It can only modify its own environment.
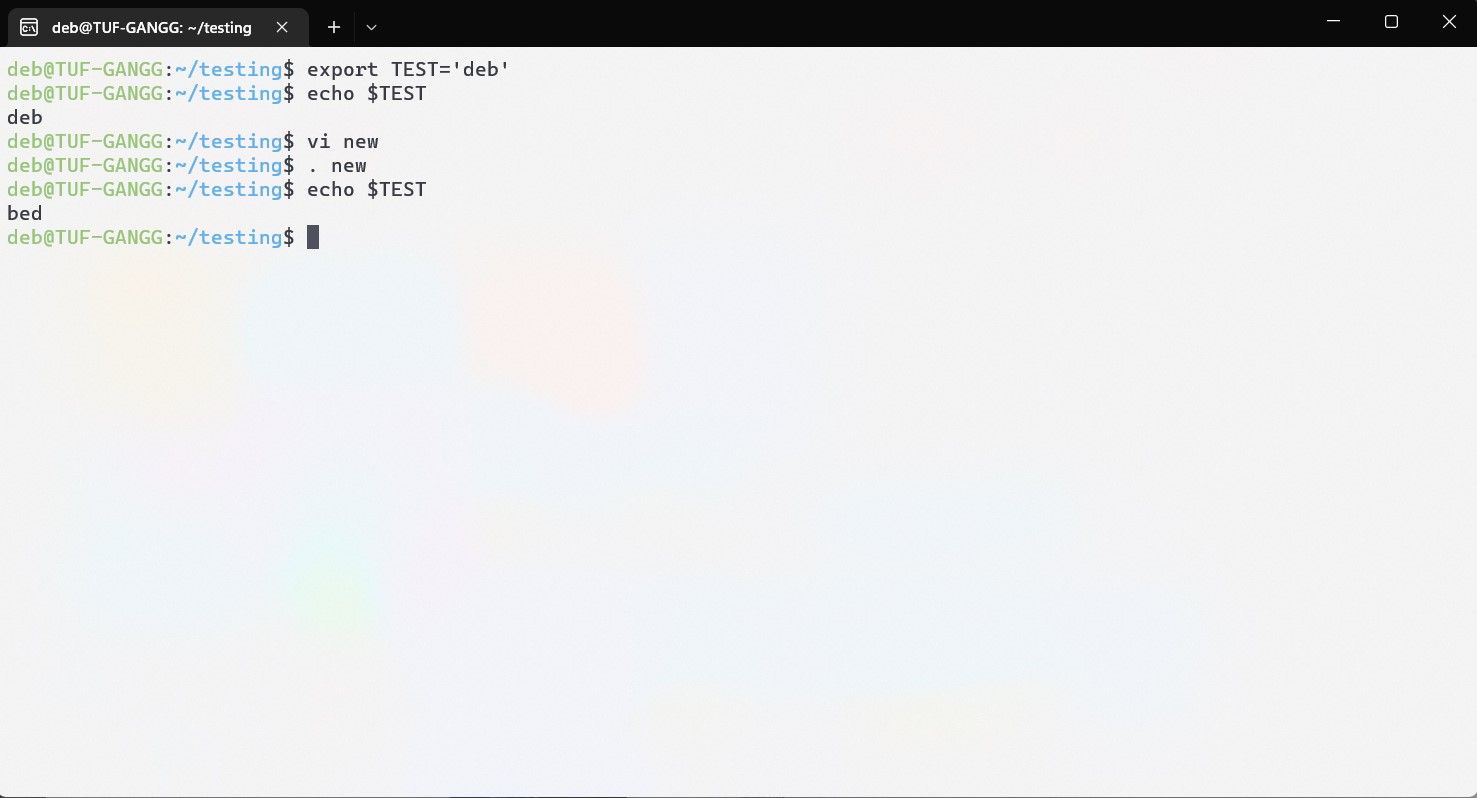
Let’s understand this with a practical example:
Here’s where the source command comes into play.
This is the primary use case of the source command, i.e., to modify the parent environment.
That’s all the steps you gotta update the Bash shell environment with the source command.
But the source command isa shell built-inthat reads and evaluates a file within the current shell process.
So, all changes made by the script will be retained in the Bash shell.
you’ve got the option to fix this error in two ways:
1.
Change the Shell
Some shells do not support the source command.
Fire up a new terminal afterchanging your shell, and try using the source command.
If the new shell supports sourcing, then it should work flawlessly.
Use the Dot/Period Syntax
Some shell environments do not support “source” syntax but the alternative “.”
The “source” syntax is a synonym for dot in Bash.
But this does not work in the POSIX shell, so for maximum compatibility, use the period syntax.
They are the very essence of using *NIX systems.