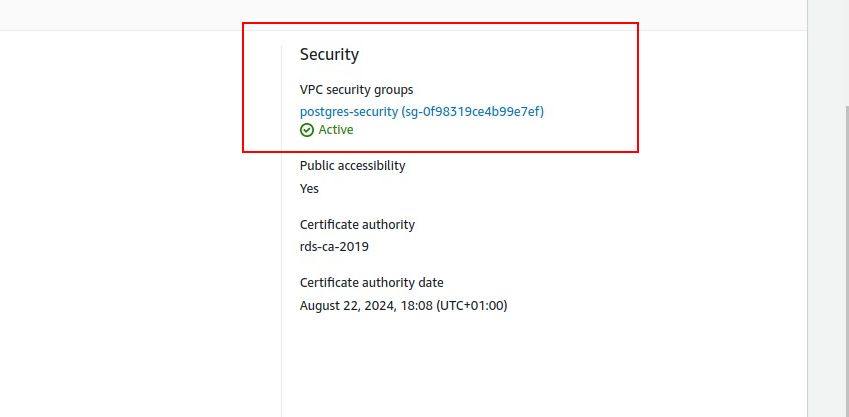
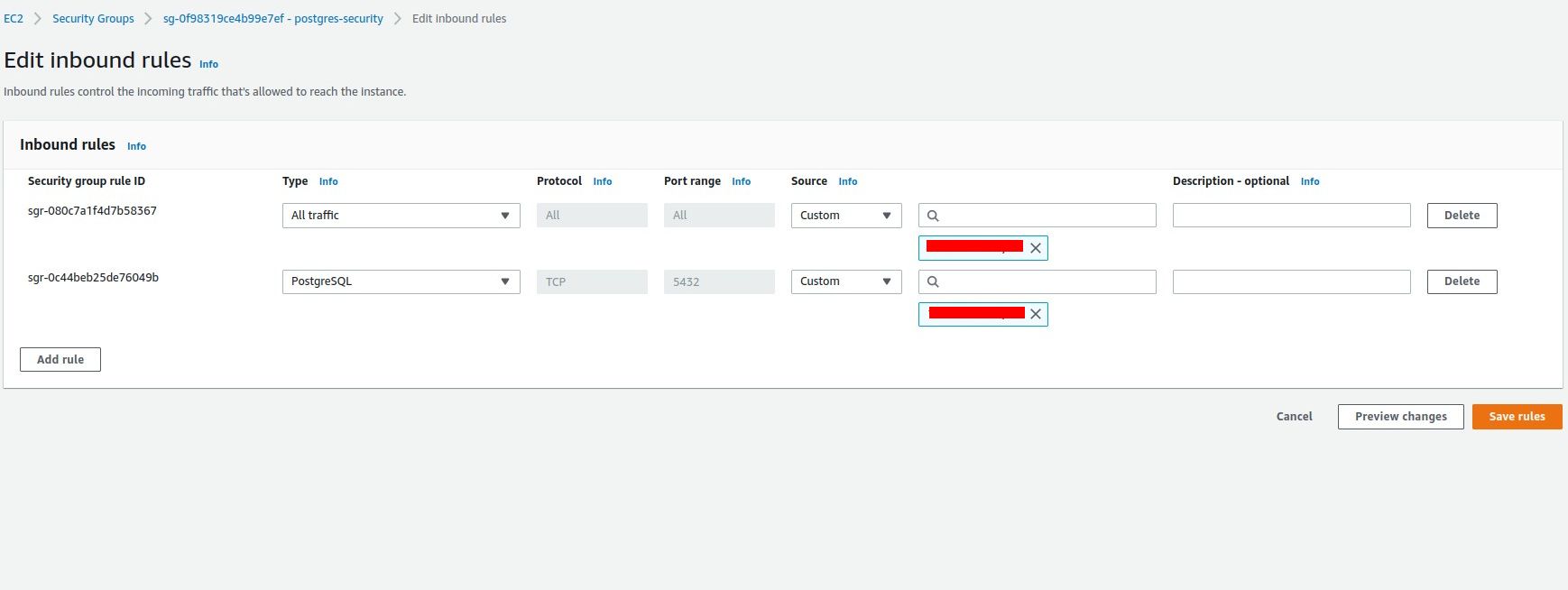
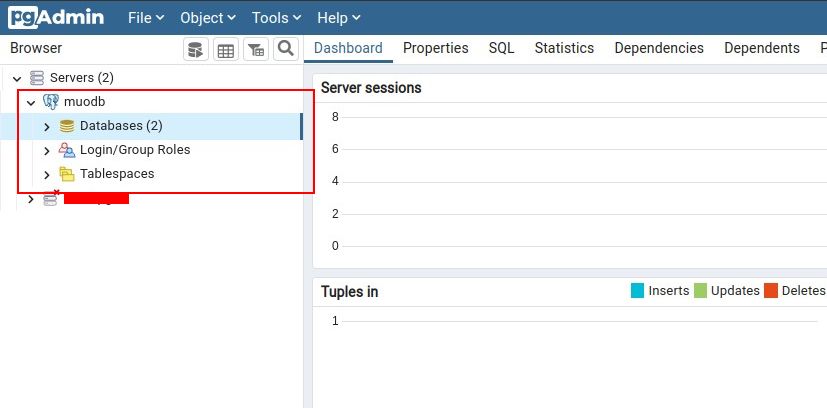
PostgreSQL (also known as Postgres) is one of the most widely-used database management systems.
Many development teams use it as their database of choice when planning the development of an program.
This is where Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) takes the burden off your shoulders.
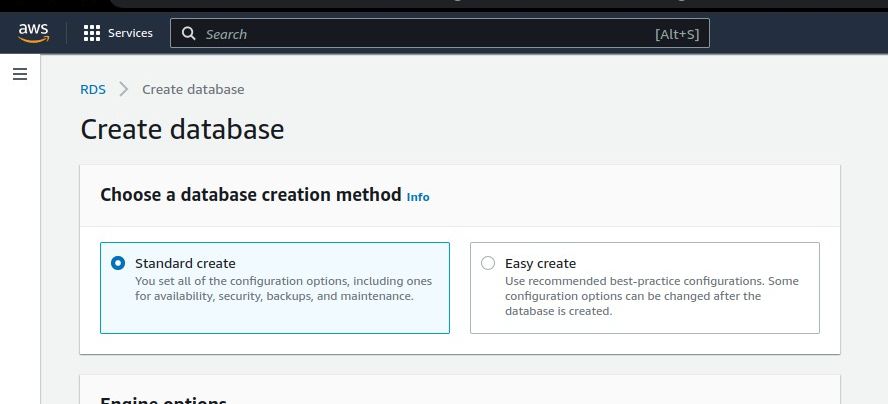
What Is Amazon RDS?
Relational Database Service (RDS) is a part of Amazon Web Services (AWS).
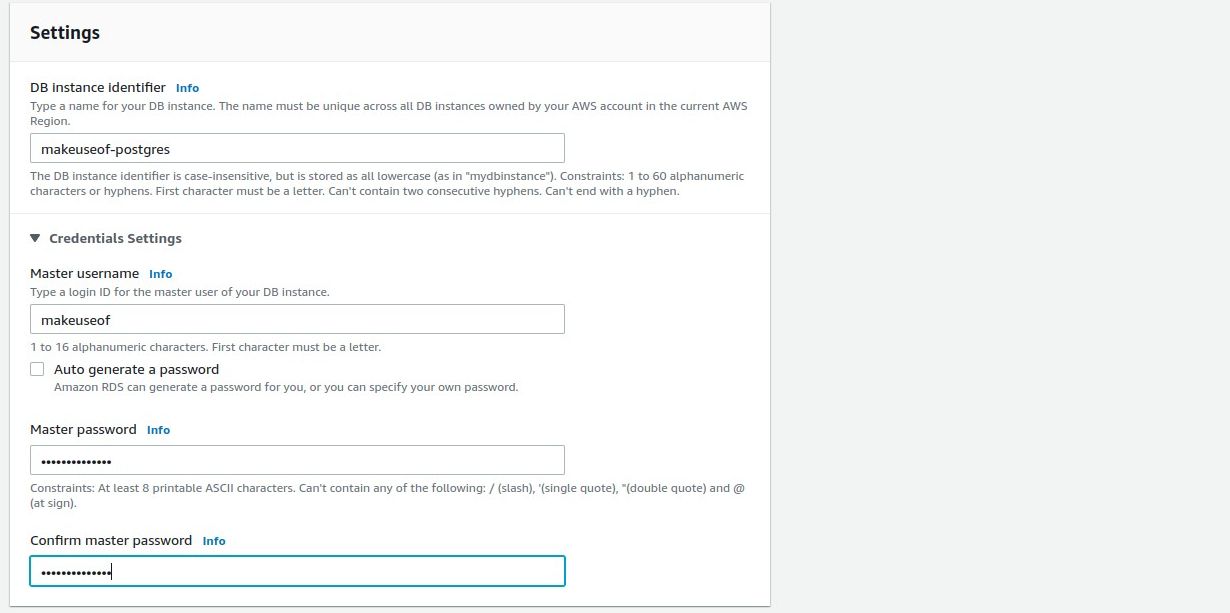
The only prerequisite you should probably create a database in RDS is an activeAWSaccount.

The following steps are all you better spin up a PostgreSQL database in RDS.
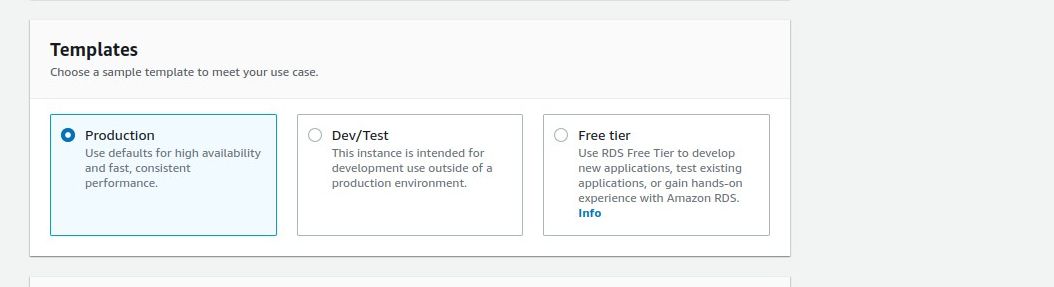
Always choose a template that best meets your needs at a particular time.
This will ensure you dont incur unnecessary AWS charges.
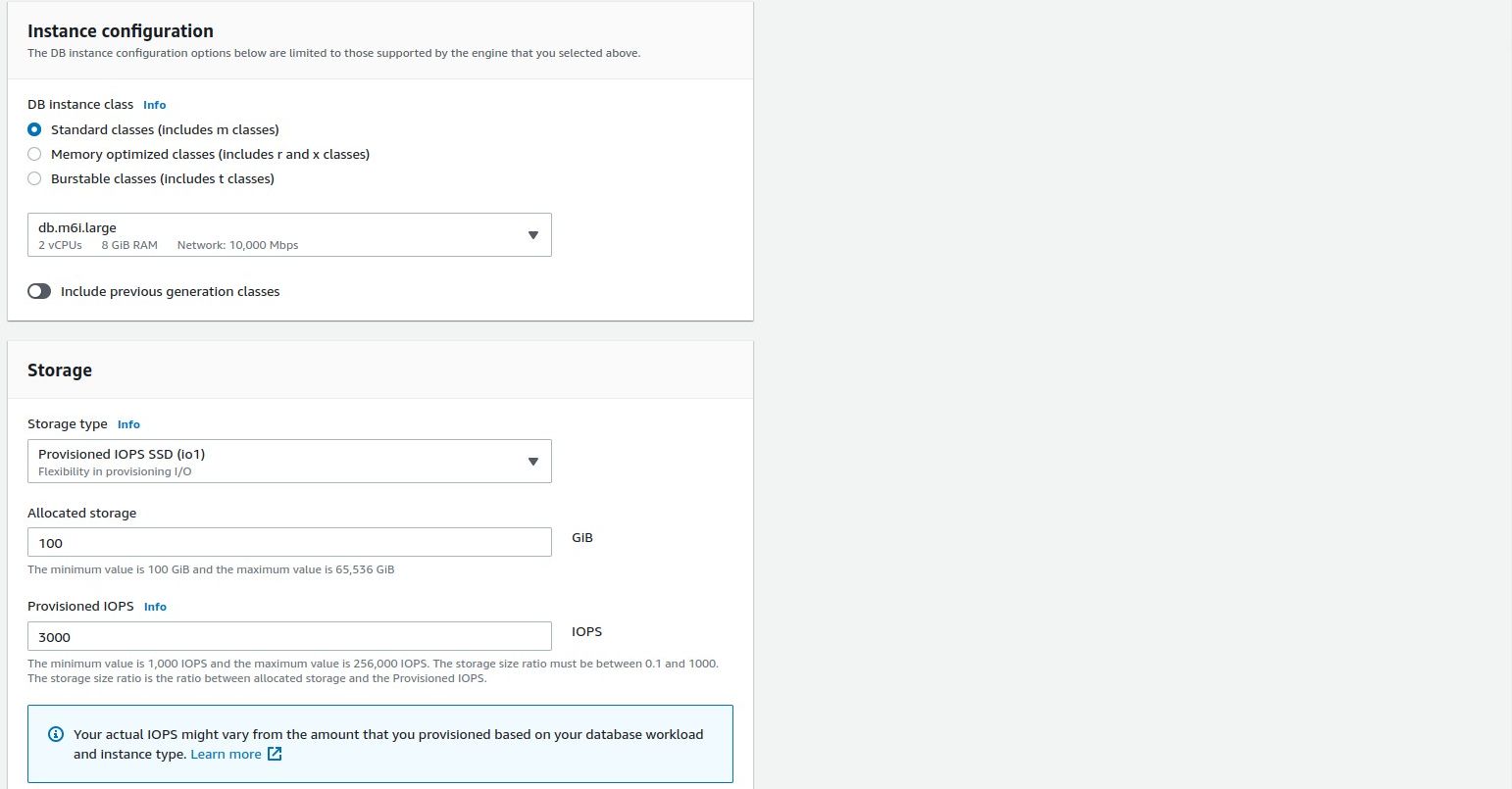
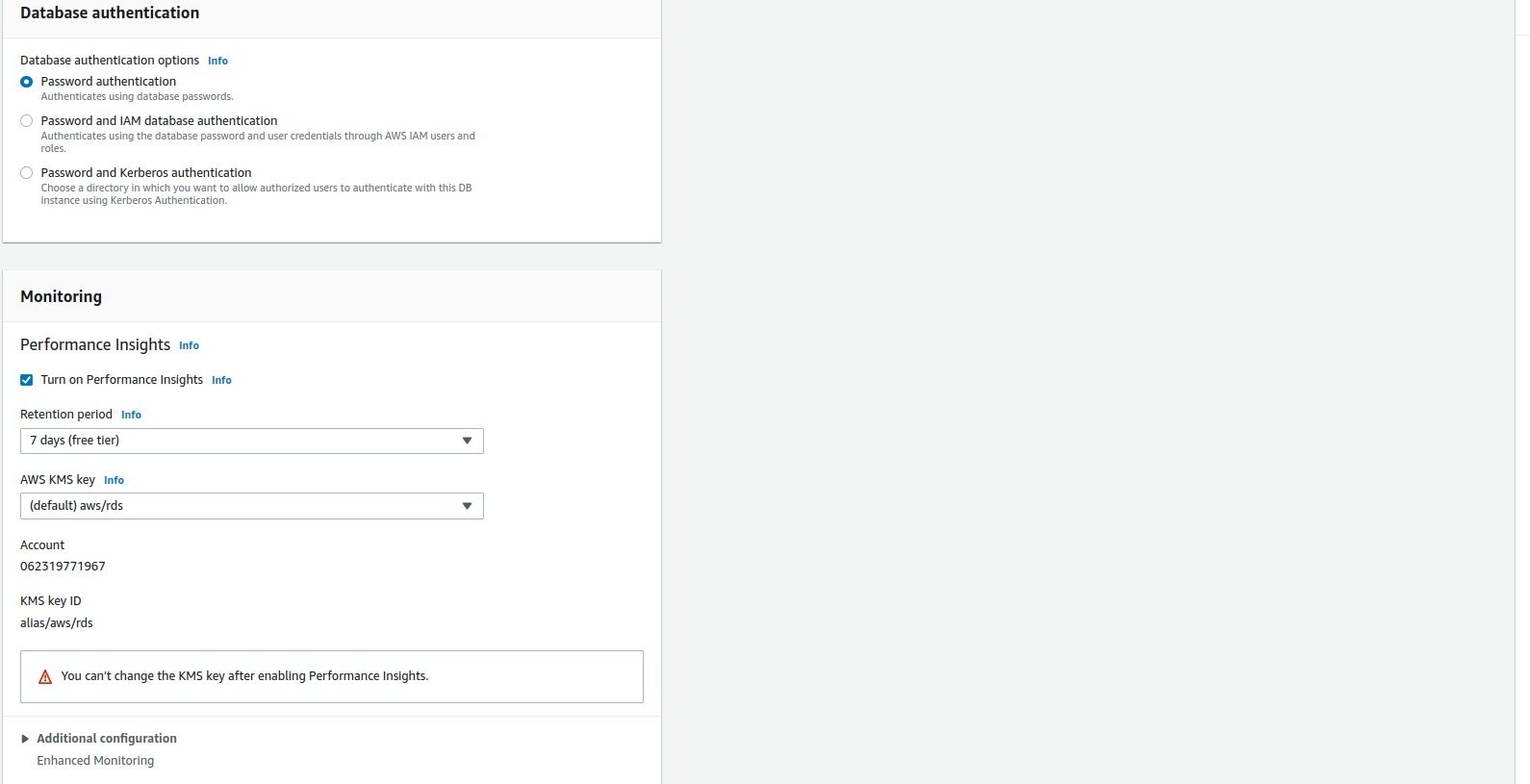
If you enable theStorage autoscalingoption, RDS will increase your storage when it reaches the threshold.
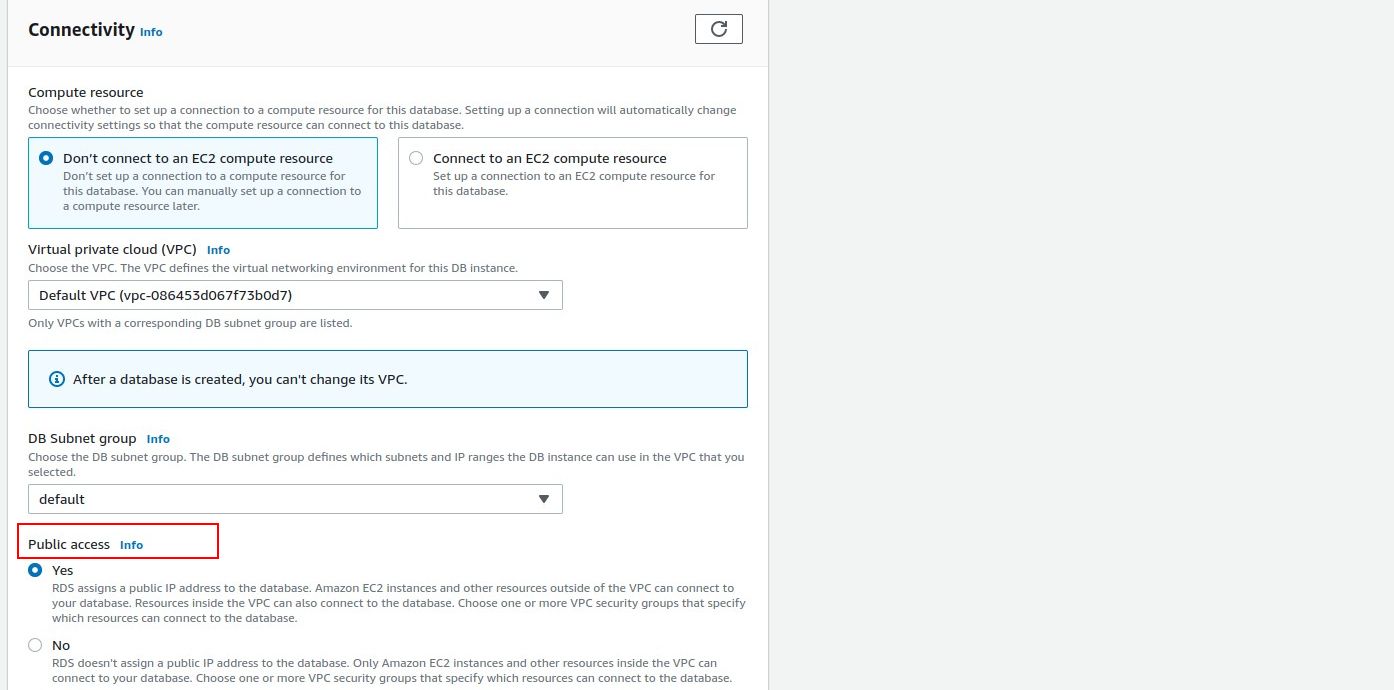
Your app server may not be running on any of AWSs services like EC2 or Elastic BeanStalk.
PostgreSQL is an excellent first choice, but RDS lets you create and manage databases using many other engines.
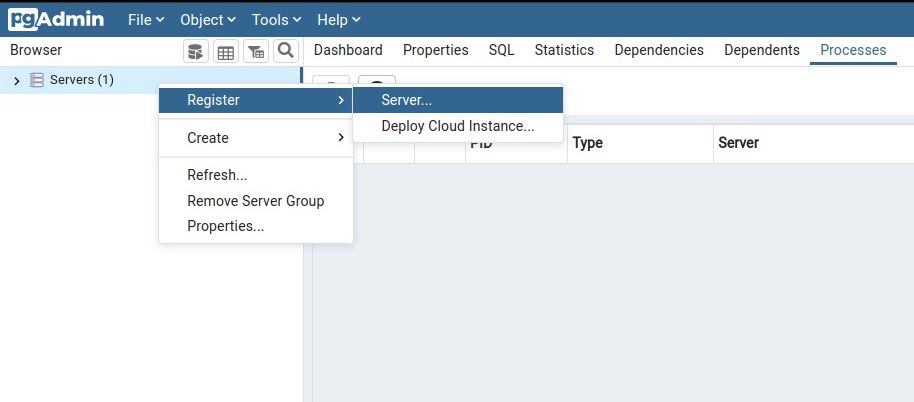
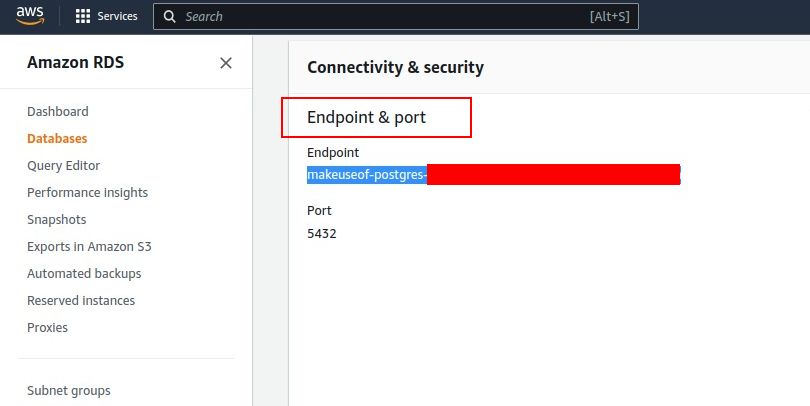
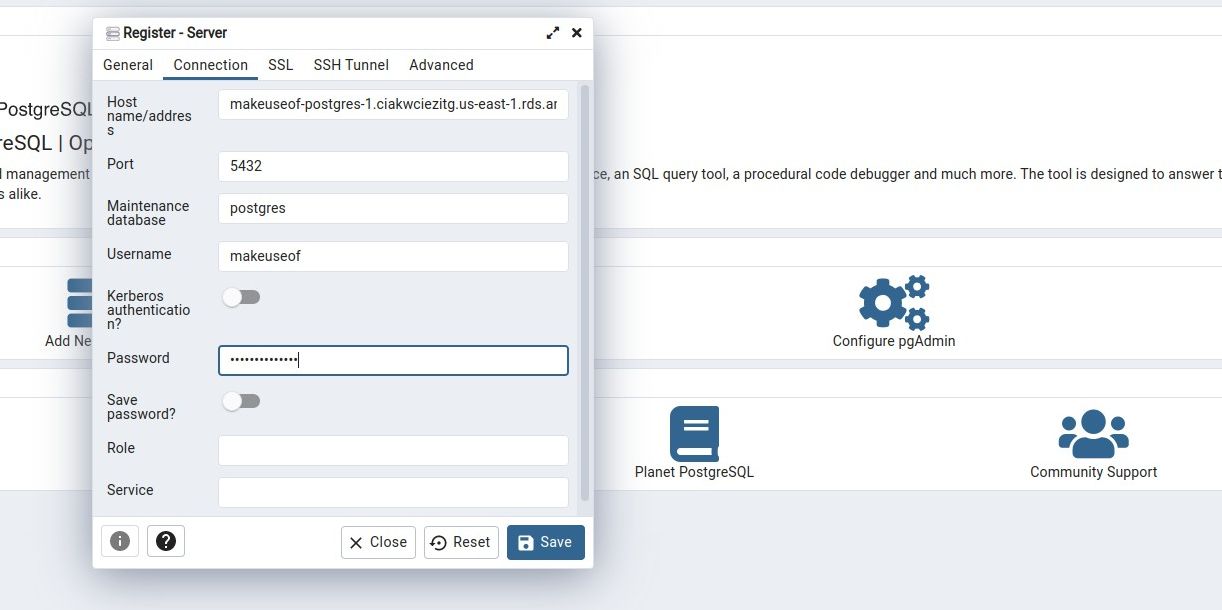
you might use PgAdmin4 to connect and manage your databases.