Page views are an important metric for tracking web performance.
Software tools like Google Analytics and Fathom provide a simple way of doing this with an external script.
But maybe you dont want to use a third-party library.
In such a case, you could use a database to keep track of your sites visitors.
Supabase is an open-source Firebase alternative that can help you keep track of page views in real time.
If you dont already have one, you cancreate a Markdown-based blog using react-markdown.
you’re able to also clone the official Next.js blog starter template from itsGitHubrepository.
You will use it to store the page views for each blog post.
Create a Supabase Database
Go to theSupabase websiteand sign in or sign up for an account.
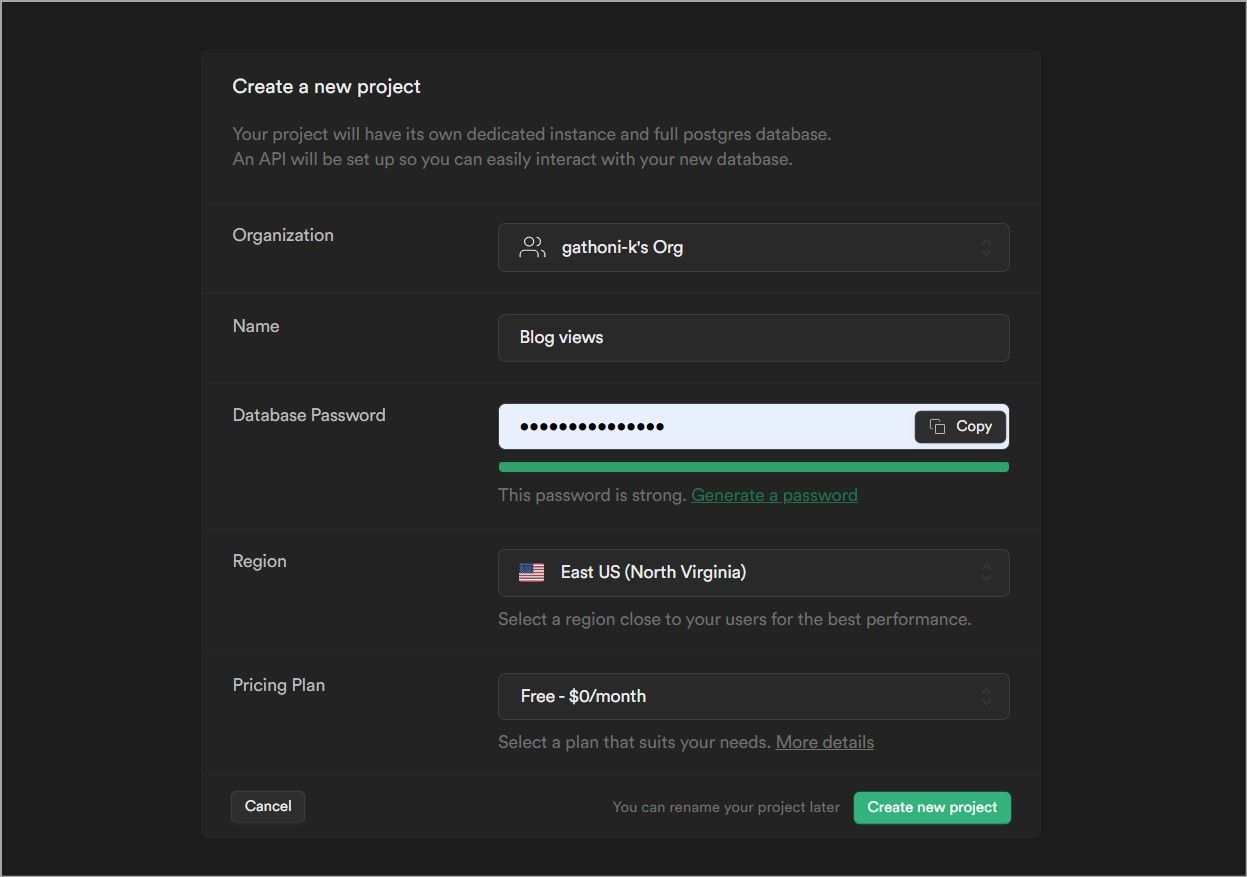
Fill in the project name and the password then clickCreate new project.
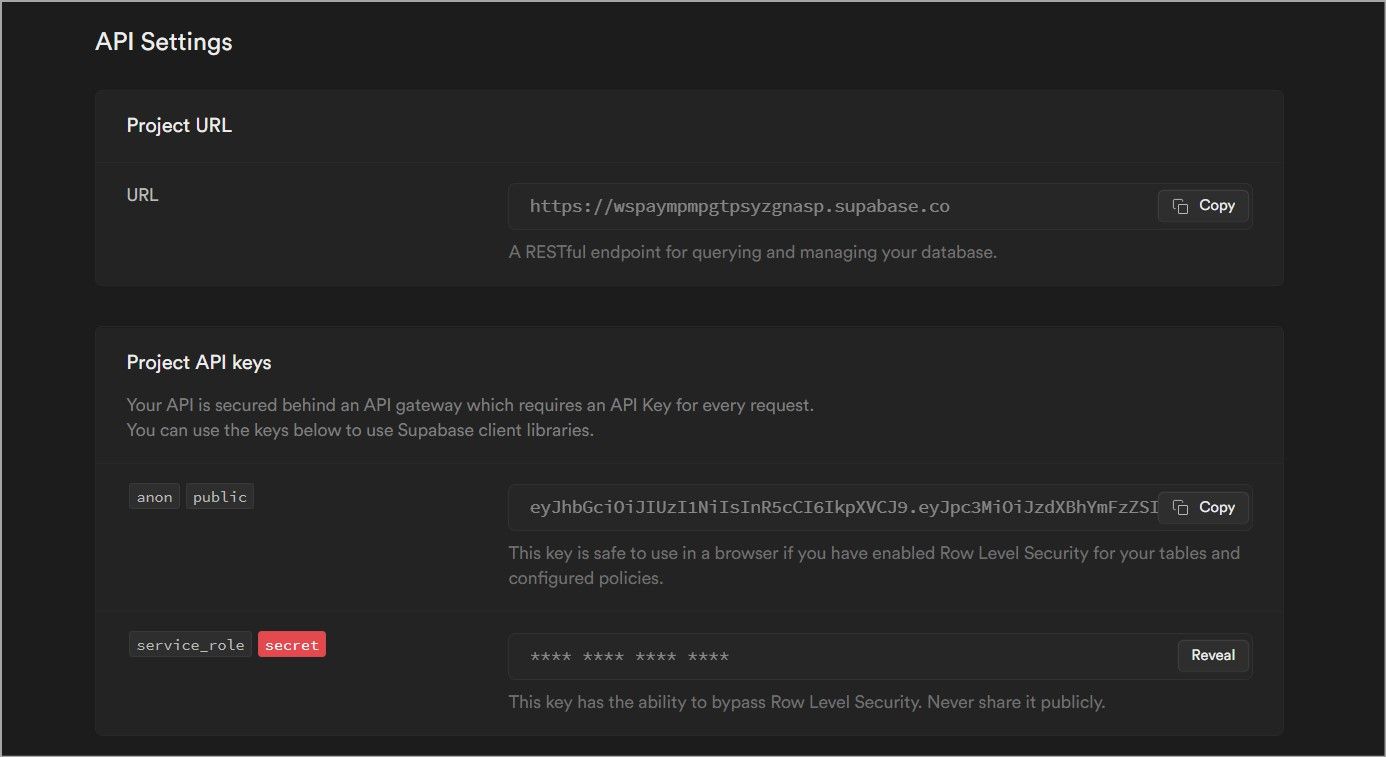
In the controls page under the API section, copy the project URL and the public and secret keys.
launch the.env.localfile in Next.js project and copy these API details.
Next, navigate to the SQL editor and click onNew query.
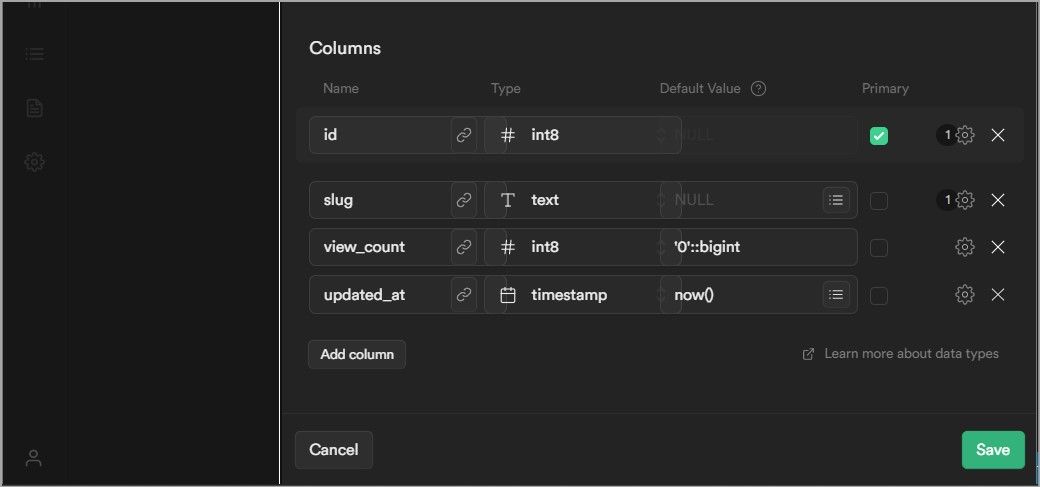
Use thestandard SQL command to create a tablecalledviews.
This function will be responsible for incrementing the view count in the views table.
If it doesnt, it creates a new entry for the post whose view count defaults to 1.
Next, create a/lib/supabase.tsfile in the root of your project and initialize the Supabase client.
Remember you saved the API credentials in .env.local when you created the database.
You will create this route in the/apifolder inside a file calledviews/[slug].ts.
Using brackets around the file name creates a dynamic route.
Matched parameters will be sent as a query parameter called slug.
The first if statement checks whether the request is a POST request.
If it is, it calls the update_views SQL function and passes in the slug as an argument.
The function will increment the view count or create a new entry for this post.
The second if statement checks if the request is a GET method.
If it is, it fetches the total view count for that post and returns it.
If the request is not a POST or GET request, the handler function returns an Invalid request message.
Start by installing the swr package.
You will use it to fetch the data from the API.
swr stands for stale while revalidate.
It allows you to display the views to the user while fetching up-to-date data in the background.
It accepts a posts slug as a prop and uses that value to make the request to the API.
If the API returns views, it displays that value otherwise it displays 0 views.
To register views, add the following code to the component that renders each post.
Check the Supabase database to see how the view count is updating.
It should increase by 1 every time you visit a post.
it’s possible for you to see which pages are performing well and which arent.
Remember you’ve got the option to always simplify things by using an analytics tool like Google Analytics.