Plus, it’s not compatible with M3 Macs yet.
For everyone else, we’ll explain how to dual-boot Linux on Intel-based Macs below.
Use an Ethernet adapter to connect your Mac to the internet.

Raghav Sethi/MakeUseOf
This is important because your Wi-Fi may not work in Ubuntu without third-party drivers.
Finally,make a backup of your Mac.
You won’t lose data by installing Linux in a dual boot partition.
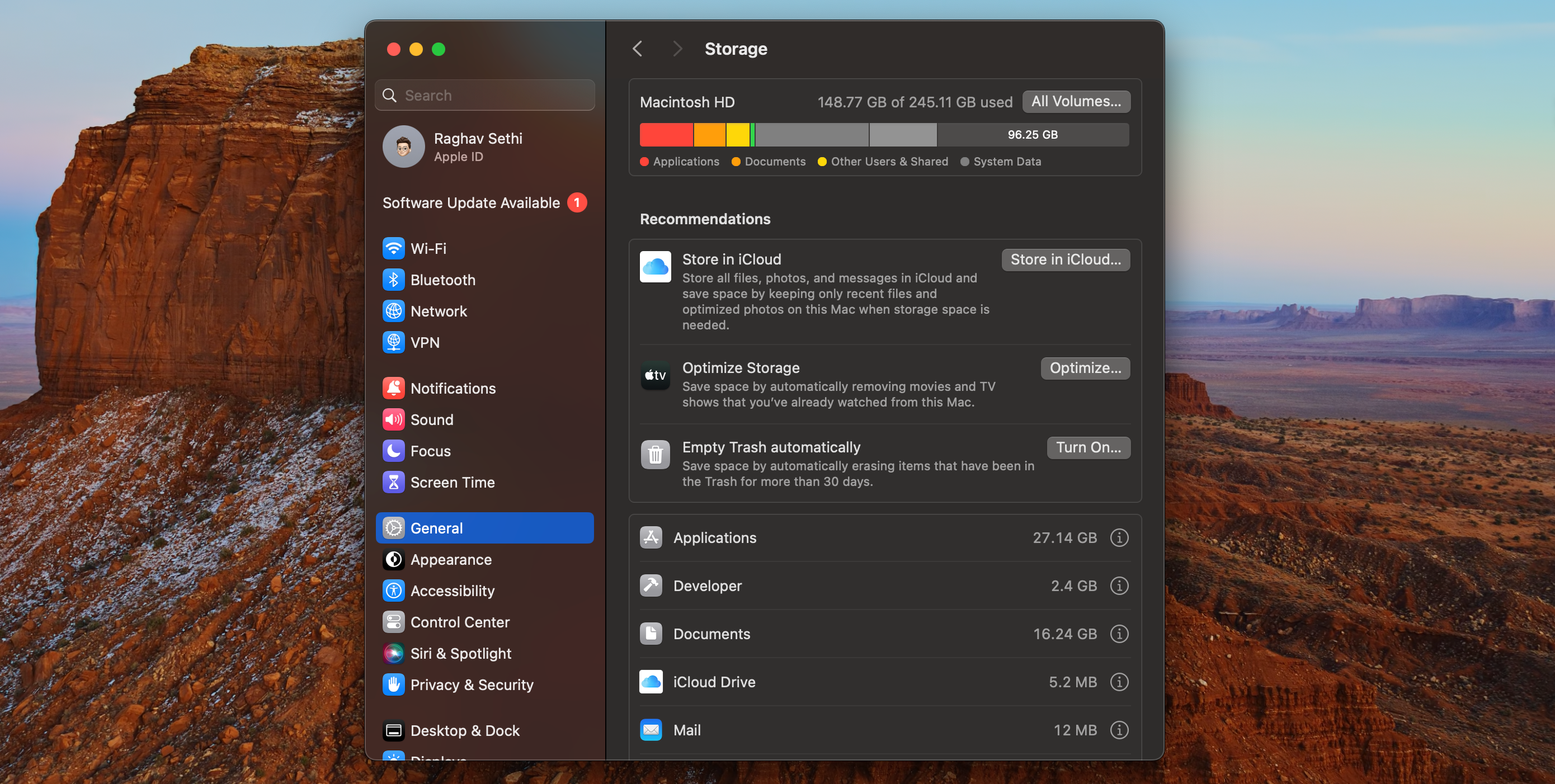
However, if something goes wrong, you may need to erase your entire Mac to fix it.
This will make it far easier to revert to macOS again in the future.
If you don’t want to create a dual boot system, skip to the next section.
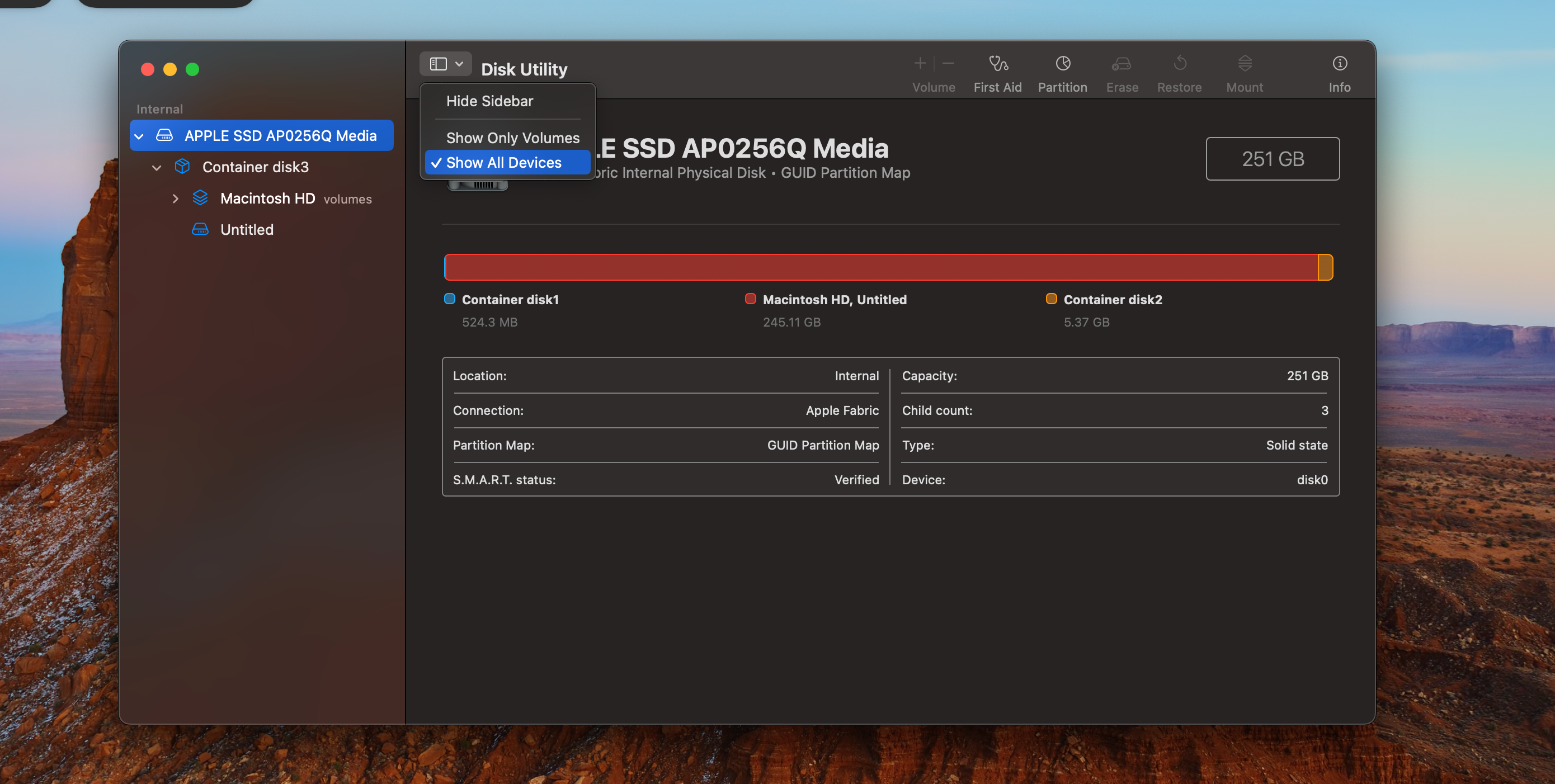
Ideally, you should set the swap partition to about half the RAM your Mac has.
Go toSystem configs > web link > FileVaultto turn it off.
Therefore, your next step is todownload rEFInd, which is the boot manager we recommend.
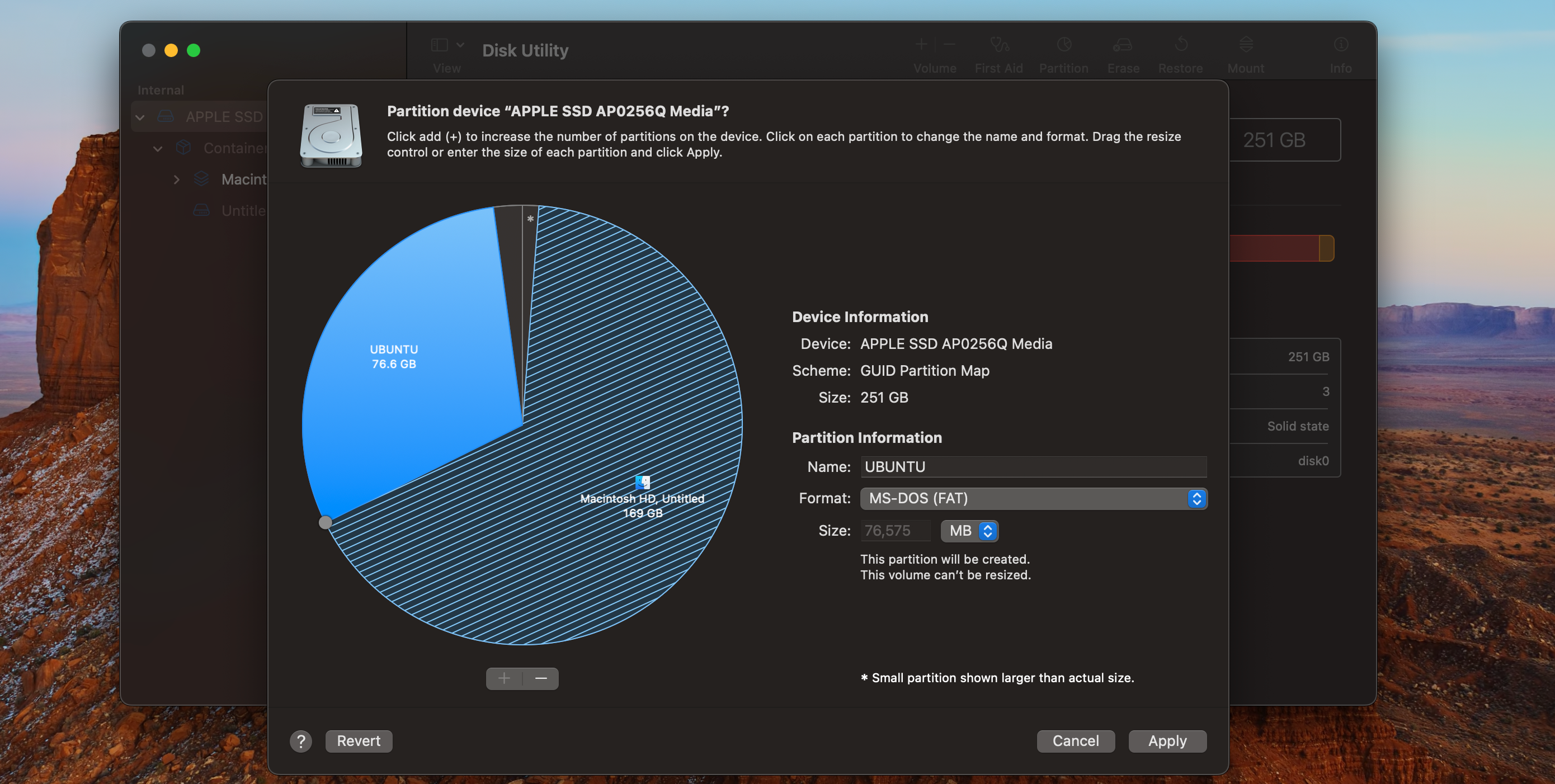
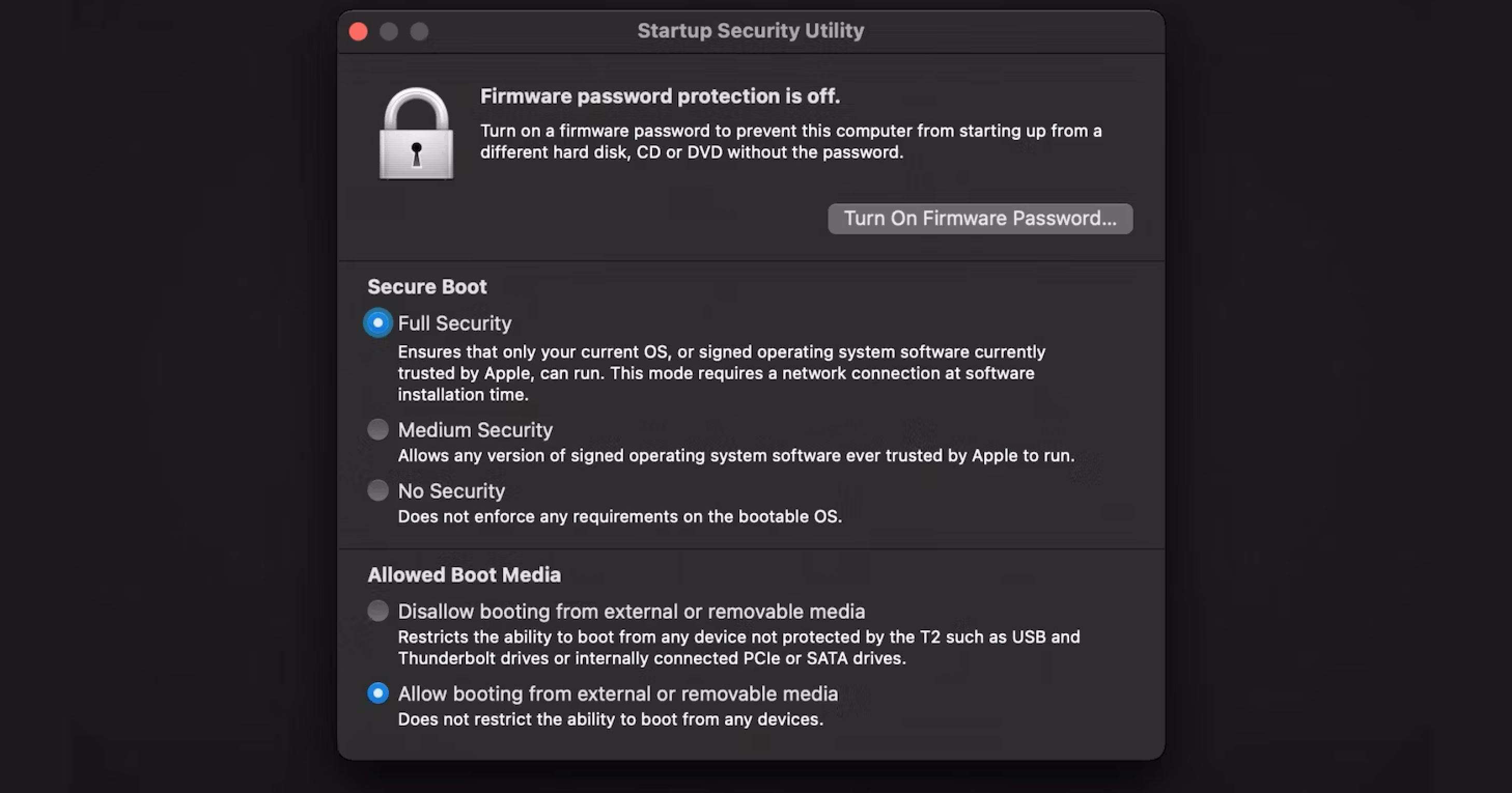
To install rEFInd, it’s crucial that you temporarilydisable System Integrity Protection in macOS.
This is an important security feature, so verify you re-enable it after.
But if it doesn’t, holdOptionwhile booting up to load your boot manager.
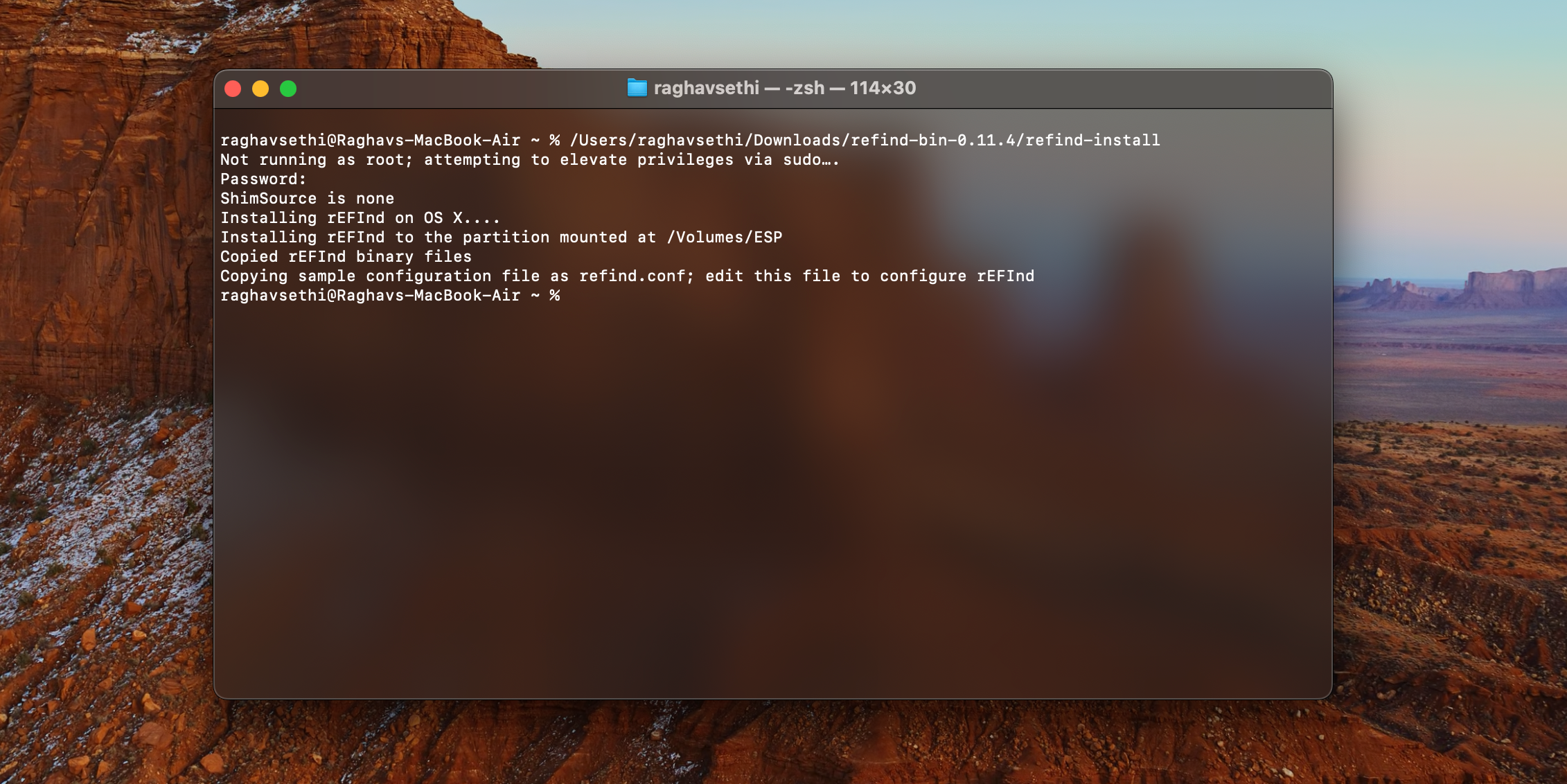
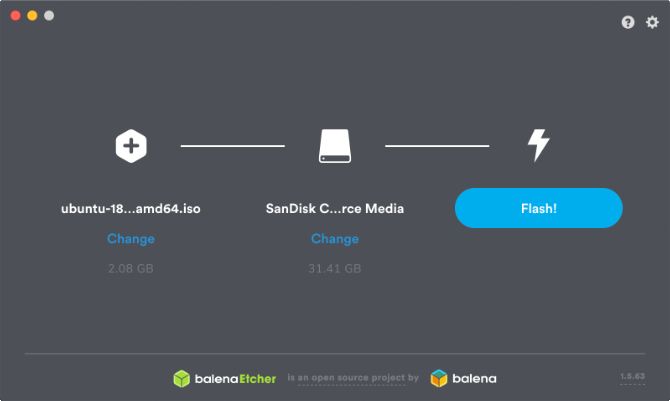
you gotta use a third-party app to create a USB installer from the Ubuntu disk image.
One of the simplest apps for this isEtcher, but you’re able to use anything you like.
This can cause problems when booting from a USB drive.
To solve this, you’ll need to take some extra steps.
you’re able to ignore this part if your Mac doesn’t have a T2 chip.
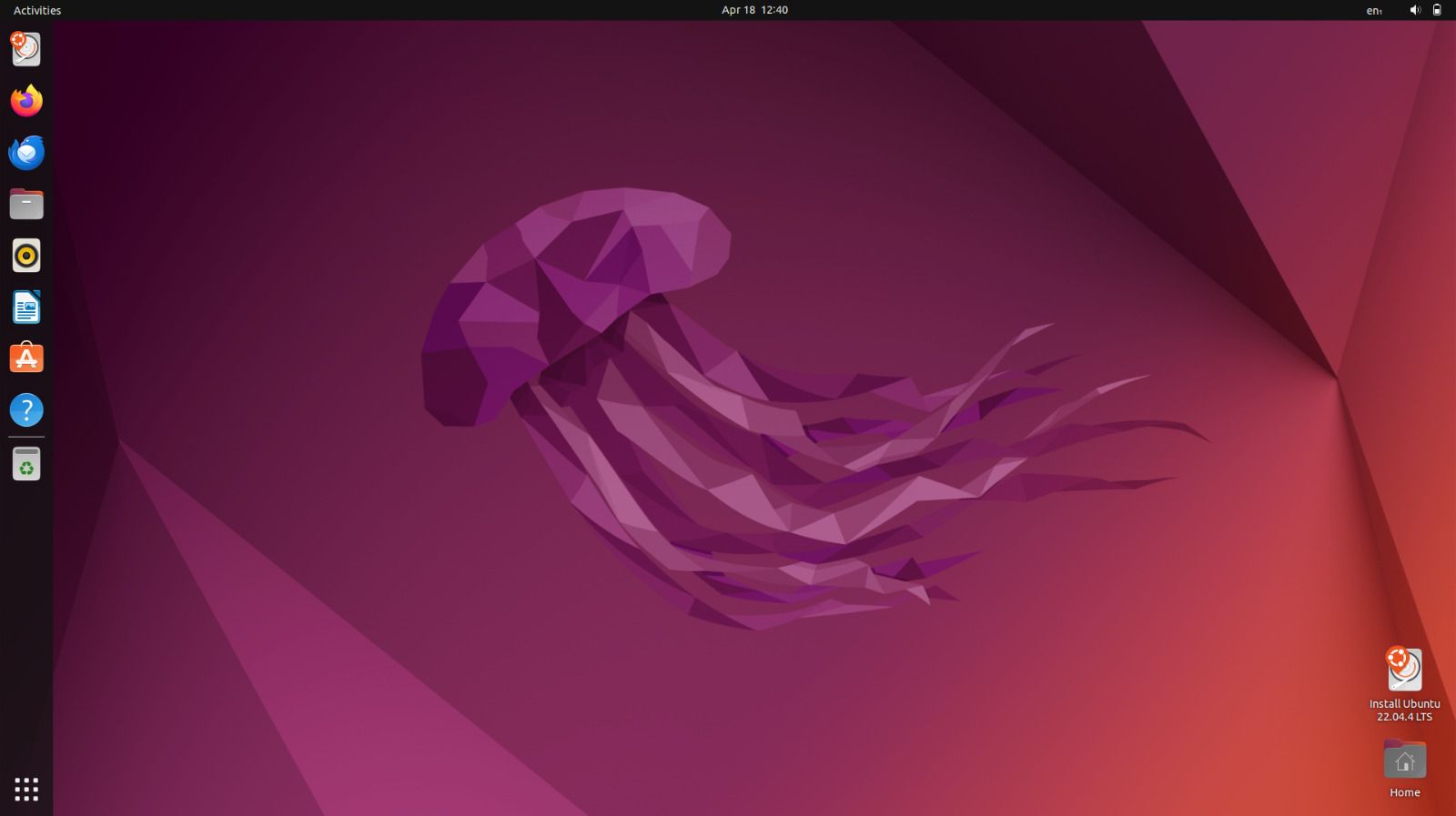
An Ubuntu loading screen appears, followed by the Ubuntu desktop.
Use this opportunity to test Ubuntu on your Mac.
Note that because Ubuntu is running from your USB flash drive, it may be slow.
If prompted, choose to keep your partitions mounted.

Option 1: Dual Boot Ubuntu With macOS
From theInstallation typescreen, selectSomething Elseand clickContinue.
On the next screen, you’re gonna wanna identify and select theUBUNTUpartition you created.
Double-click to select it and chooseUse as: Ext4 journaling file system.
Set theMount pointto/and check the box toFormat the partition.
In the popup alert, clickContinueto write previous changes to the disk.
Now, identify your SWAP partition, which should also havefat32in the name.
Double-click it and choose toUse as: swap area, then clickOK.
Open theDevice for boot loader installationdropdown menu and select your UBUNTU partition again.
The name should match what you selected for it from the table above.
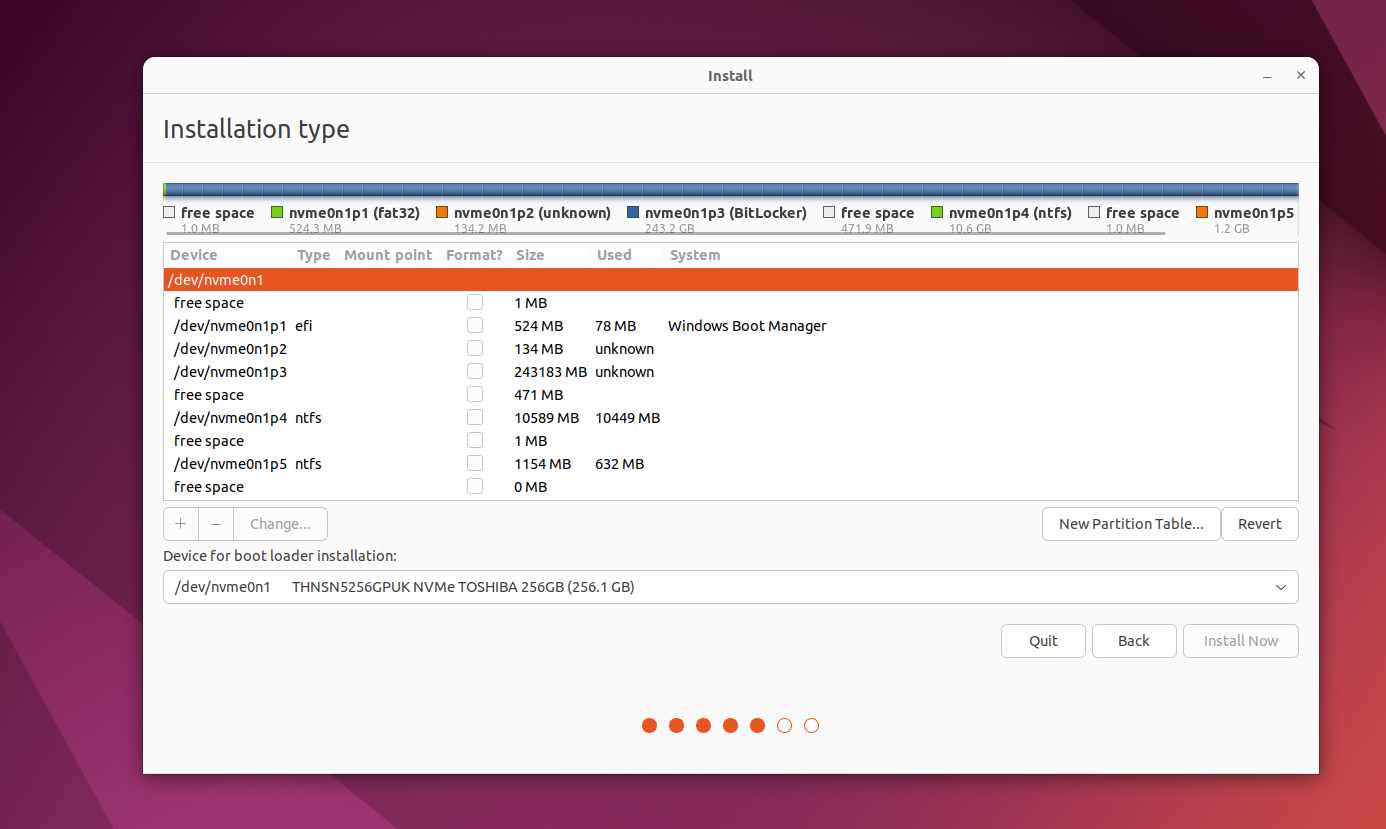
Take a moment to ensure you selected the correct partitions, then clickInstall Now.
ClickContinuein the popup alert to confirm you want to write changes to those disks.
Option 2: Replace macOS With Ubuntu
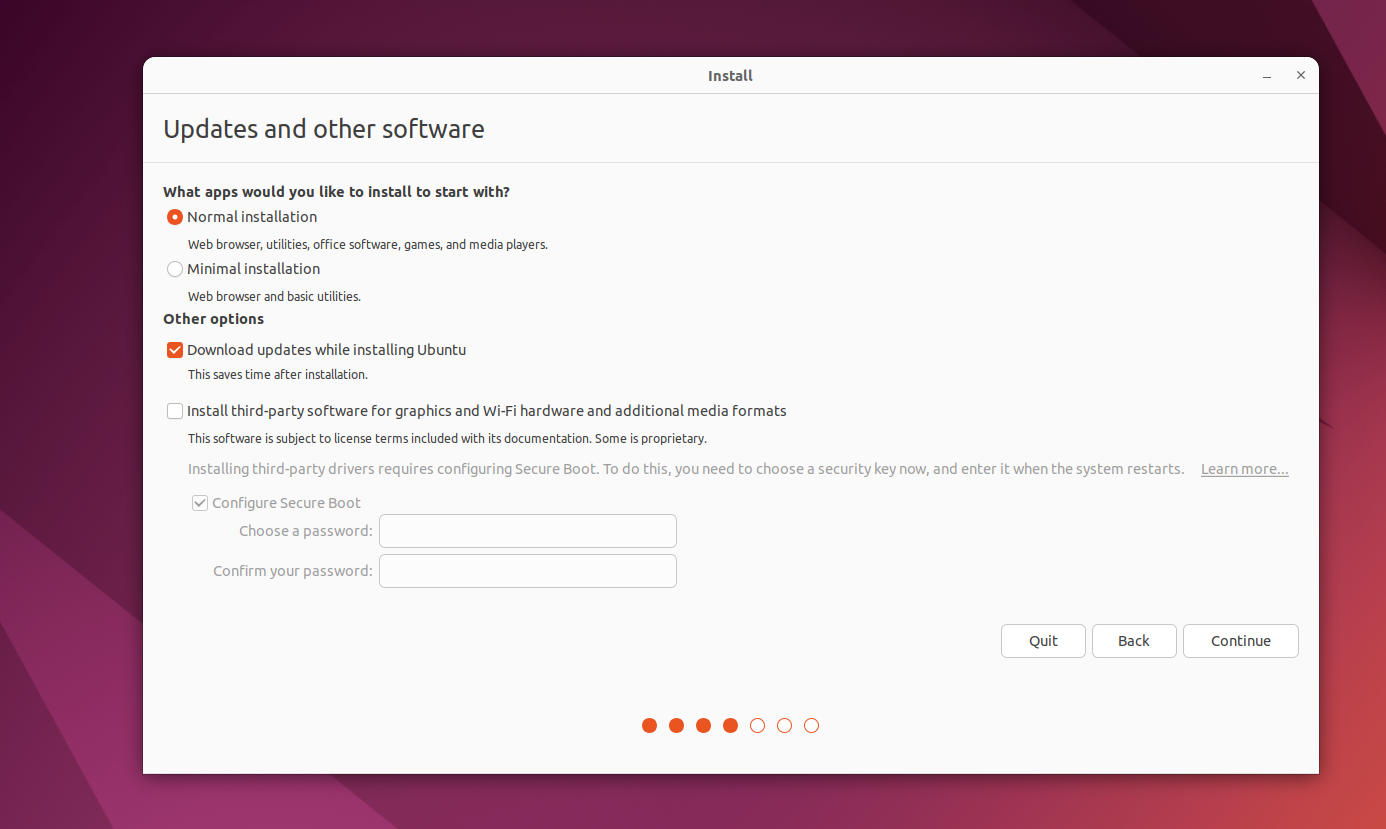
From theInstallation typescreen, selectErase disk and install Ubuntu.
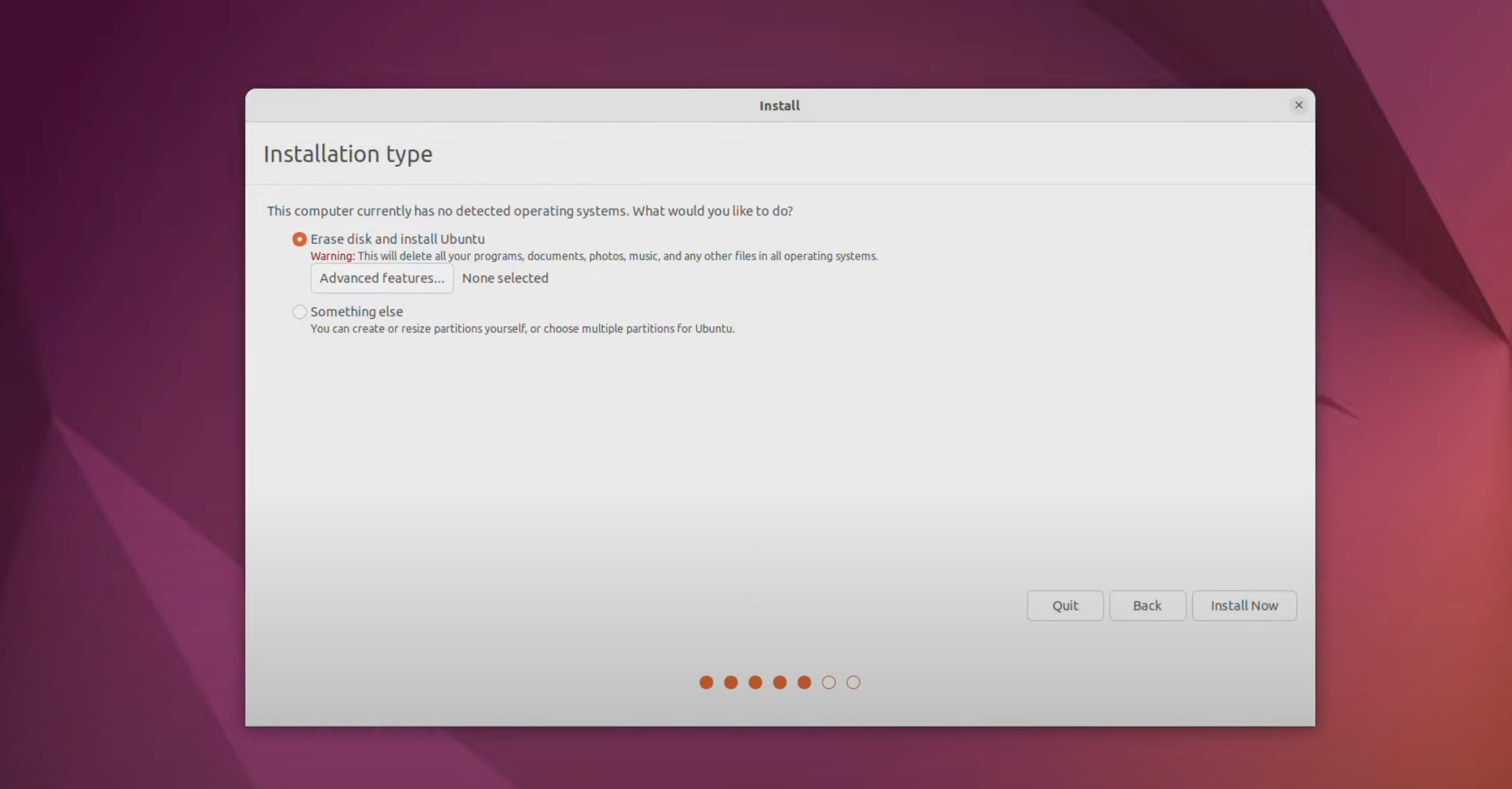
This erases everything from your Mac, including the operating system and the recovery partition!
You’ve now installed Linux on your Mac successfully!