Adding a database to your app ensures data integrity and security.
Postgres supports most of the popular operating systems and is compatible with modern programming languages.
Postgres also handles various data and document types.

With SQL skills in high demand, learning to configure and use PostgreSQL is an advantage.
You’ll learn how to install, configure, and use Postgres in a Django software.
Install PostgreSQL on Your System
The following instructions explainhow to install Postgres on the Ubuntu operating system.
execute the commandpsql –version.
The output will show your Postgres version as shown below:
Exit the Postgres account by running theexitcommand.
Create a Database
you should probably create a database that you will connect to a Django app.
Navigate back to the Postgres shell and spin up the following commands consecutively.
Then use the client to create a database on the server.
The server returns the term CREATE DATABASE when it creates a database.
it’s possible for you to also check bylisting all the databasesin the system with the command\l.
Structure of PostgreSQL
Like a typical SQL database, PostgreSQL stores data in tables.
The tables represent different items/models in an software.
The tables have a fixed number of columns and rows.
A table might also have a foreign key connecting it to another table’s primary key.
The foreign keys define the relationships between two tables.
Next, you’re gonna wanna create a Django app and link the database.
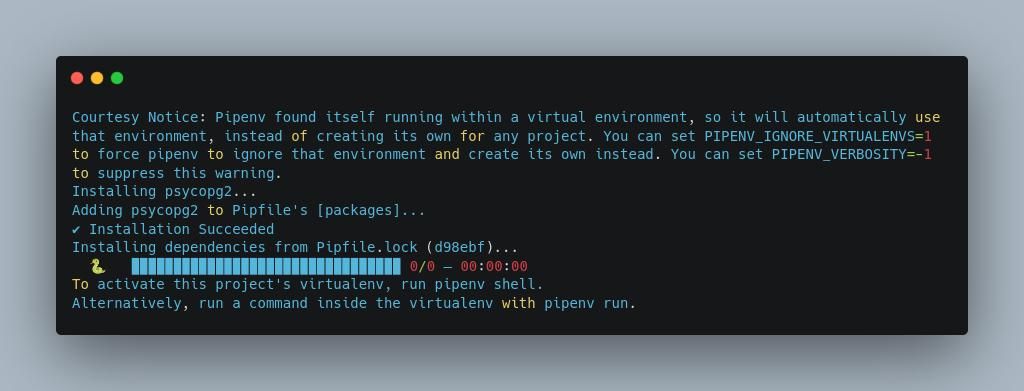
But first, installpsycopg2to help connect the app and database.
This is a Postgres dependency that helps to connect and communicate with Django.
fire off the following command to installpsycopg2andDjango:
4.
First, create a project calledmybomato support the app.
Django projects auto-generate dependencies and tool controls needed to trigger the app.
Then, change theDATABASESsettings to add your Postgres configurations.
Replace theUSERandPASSWORDwith yourpsqlusername and password.
Step 2: Update the Timezone
Next, in thesettings.pyfile, set theTimezoneto reflect your location.
Django projects are pre-configured with the UTC timezone.
Step 3: Create a Model
Create aProfilemodel in your app.
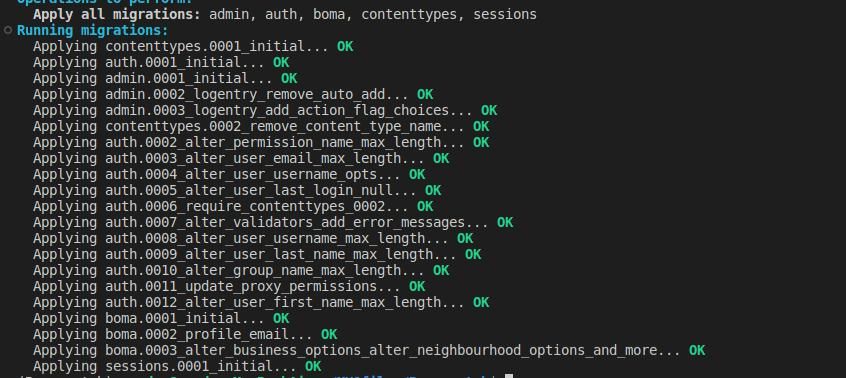
You have successfully connected Postgres to your program.
Test CRUD Commands on Your App
Django’s Python API will enable you to perform some CRUD database operations.
The API connects the functions with the models to allow you to manipulate the database.
Next, save the data in the database.
Use theProfile.objects.all()to retrieve all the data in theProfiletable in the database.
you’ve got the option to also retrieve a single object using aprimary keyorpk.
These are numbers assigned to each item saved in the database.
Why Use PostgreSQL?
Postgres is one of the most advanced SQL databases.
Its open-source builds ensure constant performance improvements.
Managing workloads is easier, and database sorting becomes better with each release.