A Docker registry is a system that stores and distributes Docker images.
There are many images hosted on a registry hub.
One image can have multiple versions, each identified by a different tag.

A registry lets users pull Docker images from it and push new images to it for hosting.
This allows you to have a copy of your program online.
It also enables you to share the images with others.
Find out everything you gotta push an image of an utility to the Docker registry.
Why Use Docker Registry?
Although there are many public registries online, DockerHub is very popular.
The Docker registry is a product of Docker Inc, the company responsible forthe Docker platformitself.
It hosts both public and private repositories.
you’re free to use public repositories or pay for restricted private repositories.
The Docker registry provides automated builds, corporate accounts, and source control integration.
The setup is much likeGitHub, the collaborative open-source platform.
The Docker engine interacts with the Docker registry by default.
you might also run your CI/CD processes.
it’s possible for you to learn more about the Docker registry by deploying a demo app.
Create a Docker Registry Account
Start by navigating to theDocker Hub websiteand registering an account there.
Once you’ve signed up and logged in you will have access to your Docker account.
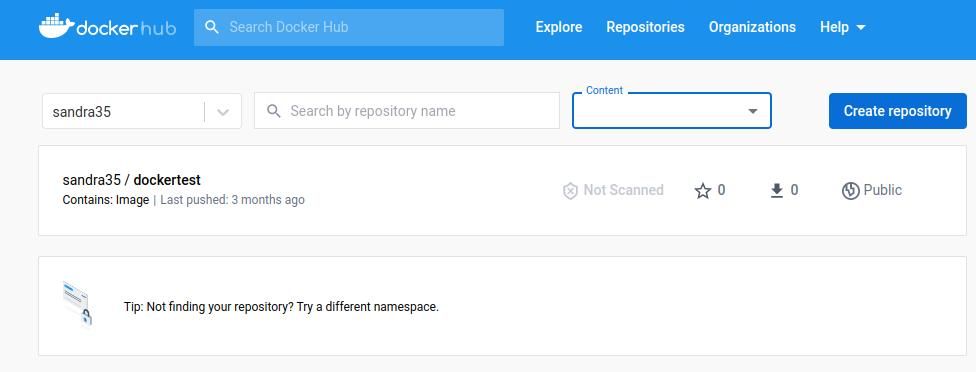
it’s crucial that you create a repository to push a demo app image to.
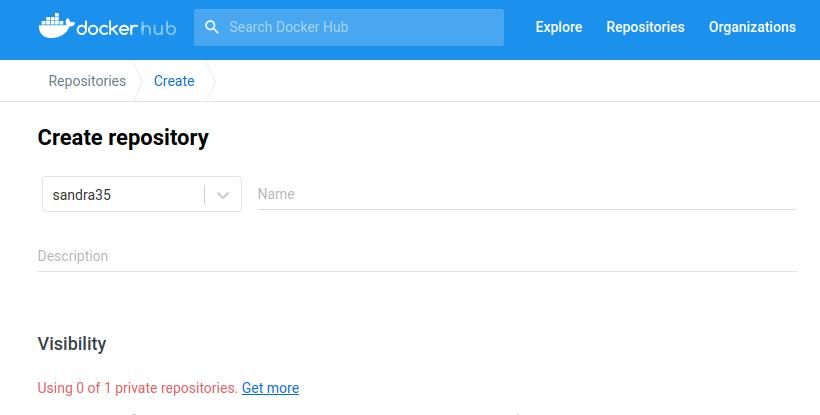
punch theCreate repositorybutton, then provide aNameandDescriptionof the repository.
you’re able to choose whether to make your repository public or private.
The Docker registry gives you access to one free private repository and multiple public ones.
Pull a Docker Image
To test the process, pull a sample Docker Image from Docker Hub.
you could pull an Ubuntu image using this command:
Ubuntu is one of the official Docker images.
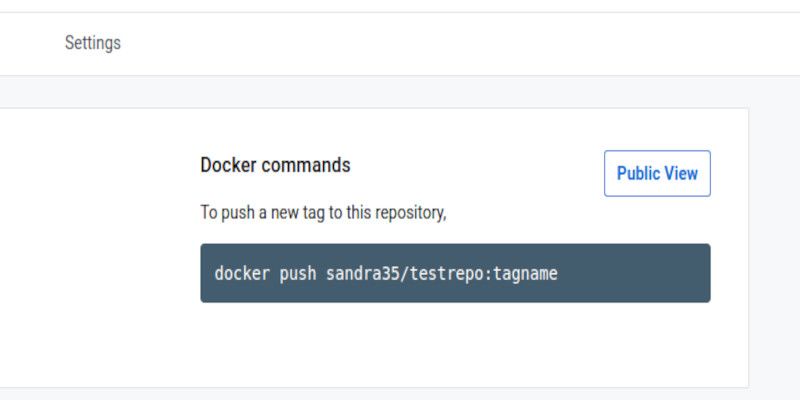
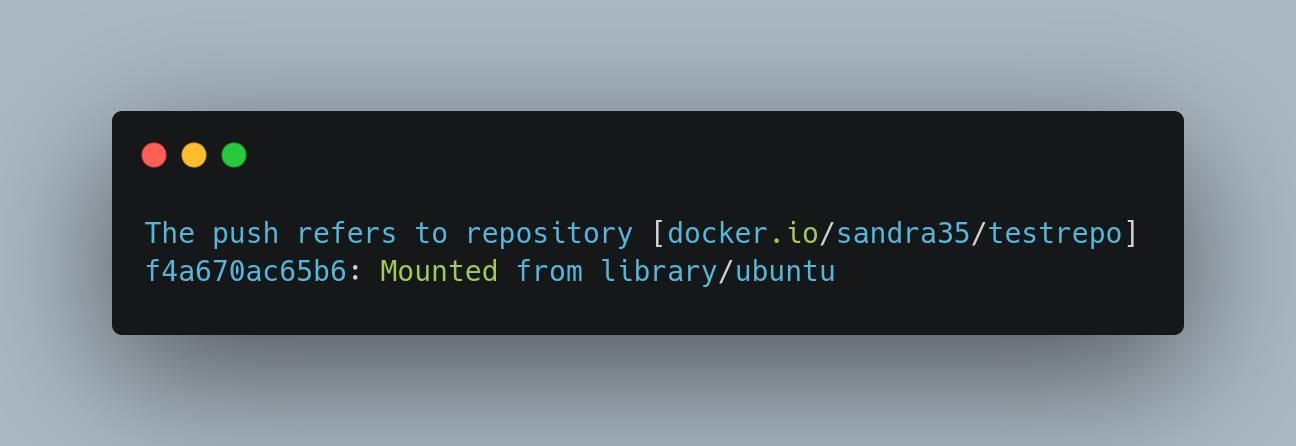
Next, you should probably push it into your own Docker repository.
All repositories contain instructions on how to push images into them.
You’ll need to use this specific syntax to structure your local image before pushing it to your repository.
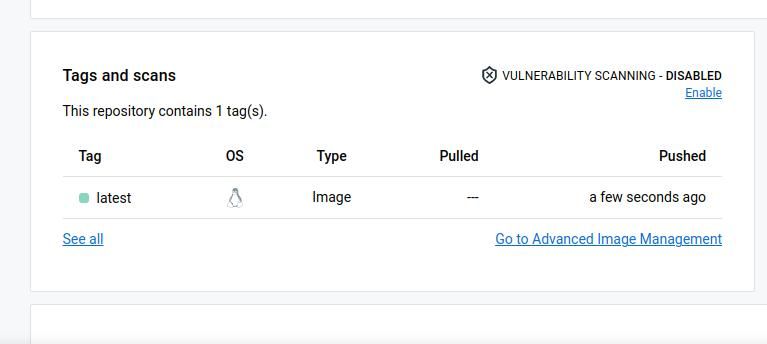
You should see the image in the repository when you refresh the page.
Congratulations, you have successfully hosted an image on the Docker registry!
you could check the app logs by clicking on the image.
Using the same method, you’re able to host your own applications.
The size of your program will increase the volume of the hosted image.
The registry stores the image until you delete it.
you’ve got the option to share your image with anyone on the internet.
The registry optimizes the storage and distribution of images online.
you’ve got the option to quickly build containerized applications and ship them online.
The Docker registry hosts an unlimited number of applications on its public repositories.
Alternatively, you’re able to create paid private repositories restricted to a particular audience.
Start using the Docker registry and change the way you store and share applications.