Summary
An SSH key lets you keep your remote server accounts safe while granting passwordless access.
It’s easy to generate one on Linux.
What Is an SSH Key?

HAKINMHAN /Shutterstock
An SSH key is a cryptographically generated key that lets youlog on to remote machines.
An SSH key is a “key pair” containing a public key and a private key.
you might copy the public key to remote machines, and they will use it to authenticate you.
The private key, as its name implies, is private and should stay on your local machine.
Don’t share your private SSH key with anyone!
At login time, the remote server will use SSH to compare your public key with your private one.
If they match, you’re authorized to enter the remote system.
This key pair system lets you set up accounts easily while maintaining security.
The passphrase allows you to add an extra layer of security to your key.

If you use a passphrase, don’t forget it!
You won’t be able to get in using that key if you forget it.
If you want to sign in without a password, just leave the passphrase blank.
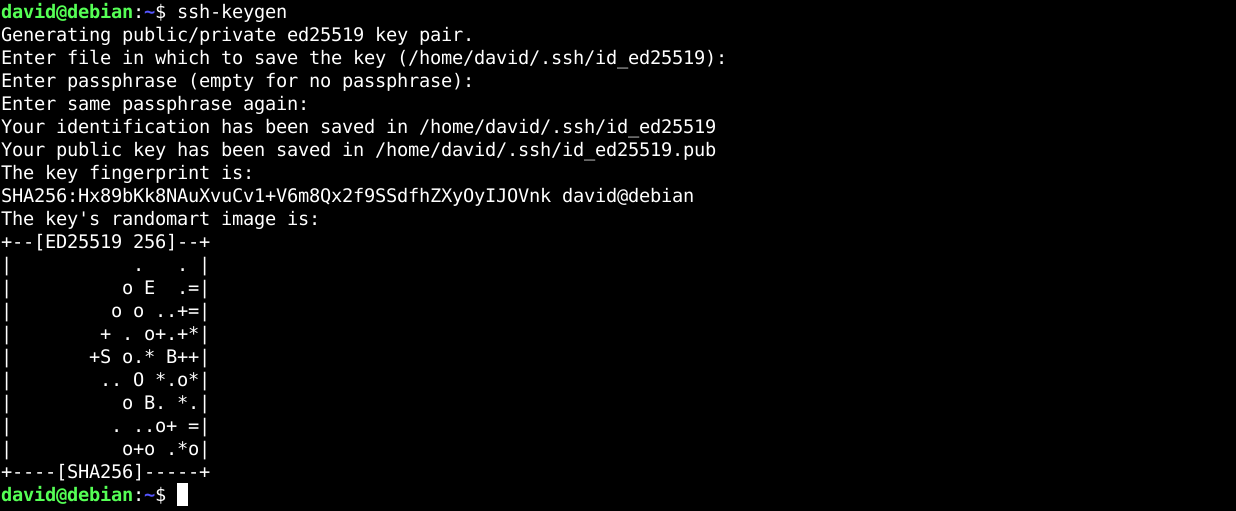
By default, ssh-keygen uses the Ed25519 algorithm.
This is sufficient for most cases because it’s very secure.
you could specify the key in of algorithm you want using the -t flag.
You shouldn’t normally need to do this unless the server doesn’t support whatever algorithm you’ve used.
you’ve got the option to read thessh-keygen manual pageto learn how to generate a different key pair.
There are two ways to do this.
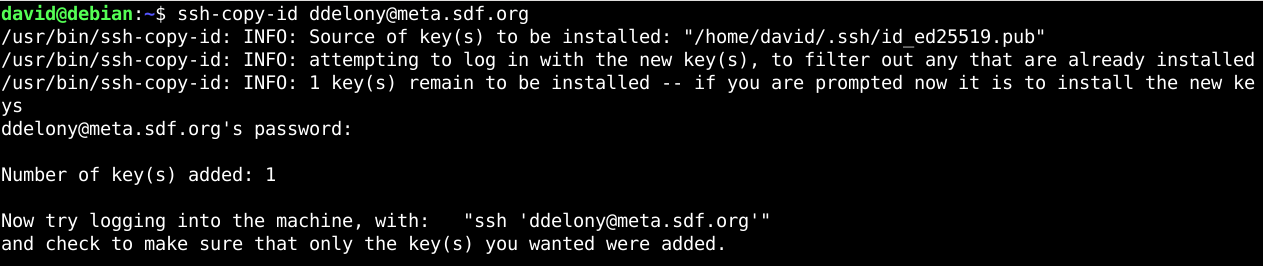
The first and easiest is to use thessh-copy-idutility.
Your public key will bea file ending in “.pub"in the .ssh directoryin your home directory.
Open it and copy and paste what’s in it into the.ssh/authorized_keysfile on the remote machine.
Save the file, and you’ll now be able to log on to the server using SSH.
check that that the file is only writeable by you, oryou may run into errors.