Here’s how to do it.
This file system determines how files are named, stored, and accessed.
The Disk Management tool in Windows makes it very easy to format drives.
Zoomik/Shutterstock
Before proceeding, however, see to it the drive does not contain any important data.
If it does, ensure youback up that data to a safe location.
Alternatively, you’re able to pressWin + Xto launch the Power Menu and then clickDisk Management.
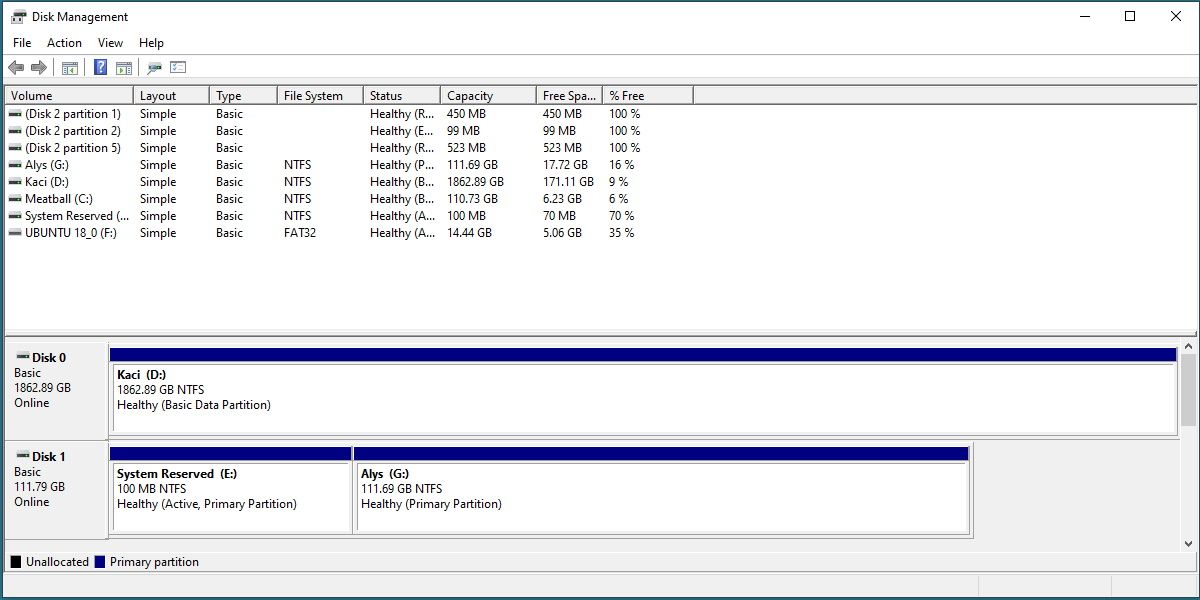
Windows would then recognize these partitions as separate drives (such as C: and D:).
Similarly, you could combine multiple partitions into one.
However, you should considerpartitioning your drivefor better organization.
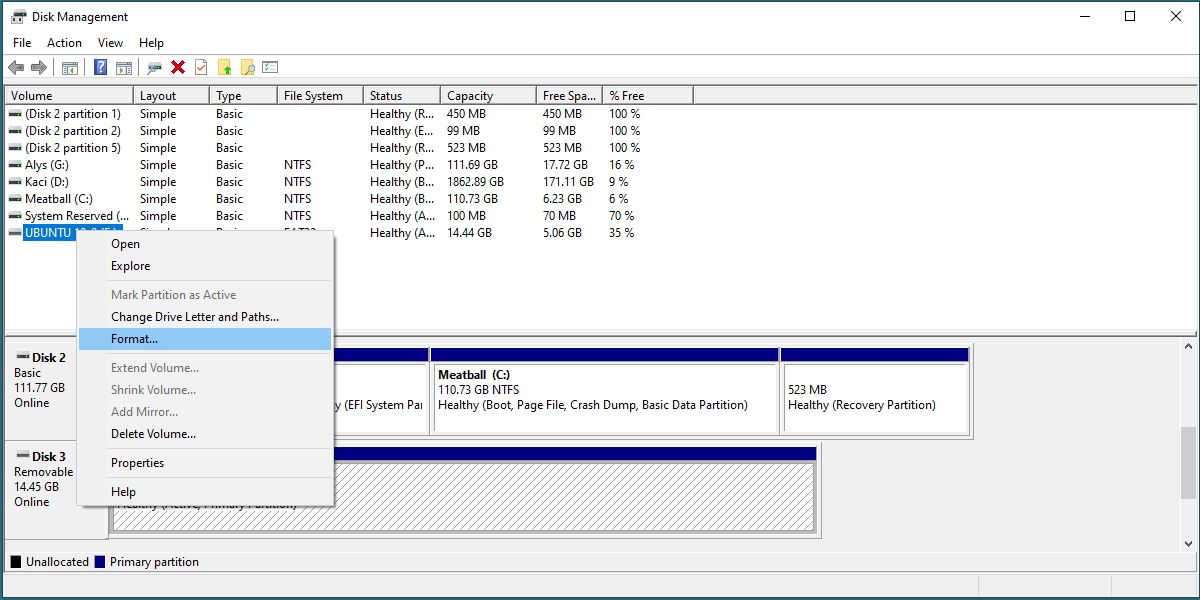
Linux drives are typically labeled EXT4.
Right-punch the drive and selectFormat.
Be absolutely sure that this is the drive you want.
Formatting the wrong drive could have disastrous consequences, ranging from lost personal data to an inoperable system.
You cannot format the Windows system drive (typically the C: drive, but not always).
Formatting the Windows drive requires more complex methods, which are beyond the scope of this article.
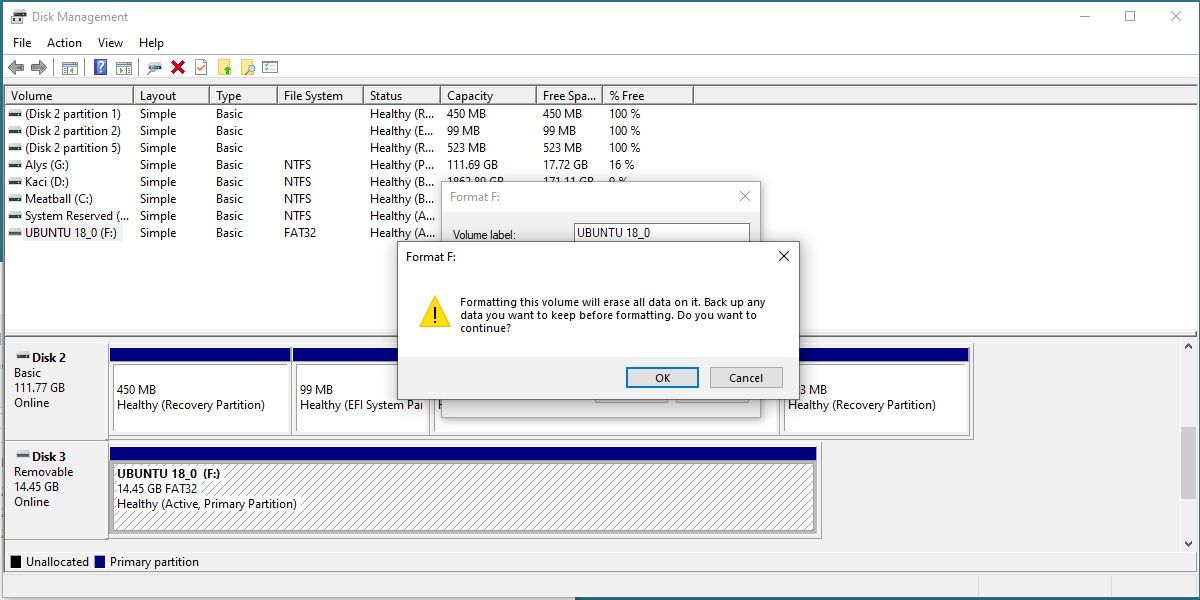
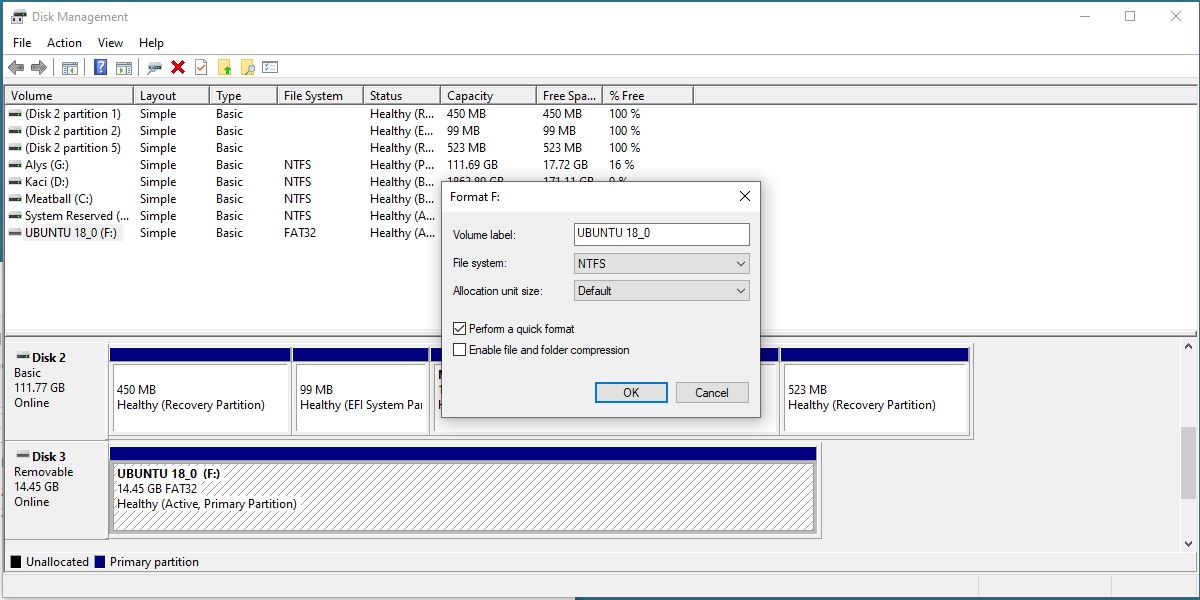
you might name it anything you prefer, as long as you use letters and numbers only.
For theFile System, you’ll want to choose NTFS.
Don’t worry aboutAllocation Unit Sizeand leave it onDefault.
It’s best to uncheck thePerform a quick formatoption.
Leaving it enabled means Windows will assume the drive is error-free.
Unchecking the option will initiate a standard format, which will overwrite the entire drive with zeros.
The only downside is that it takes longer.
We also recommend unchecking theEnable file and folder compressionoption, as it can negatively impact your day-to-day drive performance.
There areother methods to format a driveas well, but the Disk Management tool is the most straightforward option.