Using the combination of React and Firebase, it’s possible for you to produce super responsive applications.
If you’re already familiar with React, learning how to integrate Firebase is an excellent next step.
Using that knowledge you could start creating scalable full-stack applications with little or zero backend code.

The process is easy if you’ve alreadycreated your React app.
Next, make a newfirebase_setupdirectory inside your projectsrcfolder.
Create afirebase.jsfile inside this folder.
You’ll use this across the app while making API requests.
Now, install thefirebaseanduuidlibraries in your React app.
TheaddDocmethod has the advantage that it instructs Firebase to generate a unique ID for each record.
So you’ll use it in the submit button.
Additionally, create a change handler.
This goes into the database.
A snapshot allows your app to listen to changes in the backend.
It updates the client automatically each time someone writes to the database.
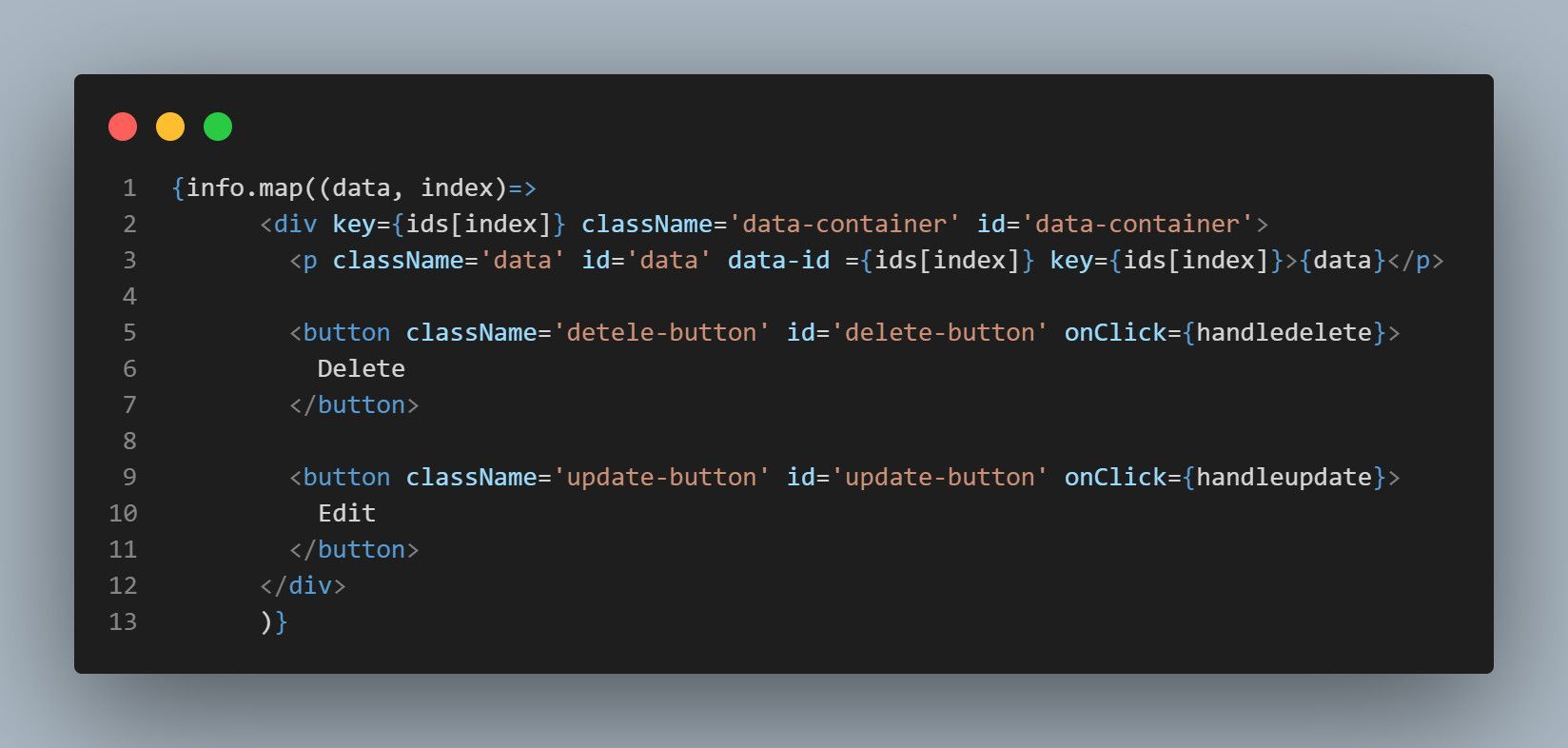
ThesetInfostate grabs the data in each document.
You’ll map through this (theinfoarray) while rendering to the DOM.
ThesetIdsstate tracks all document IDs (passed as theIdsarray).
you’re free to use each ID to launch the Delete and Update queries on each document.
you could then pass each document ID as a DOM attribute while mapping through theinfoarray.
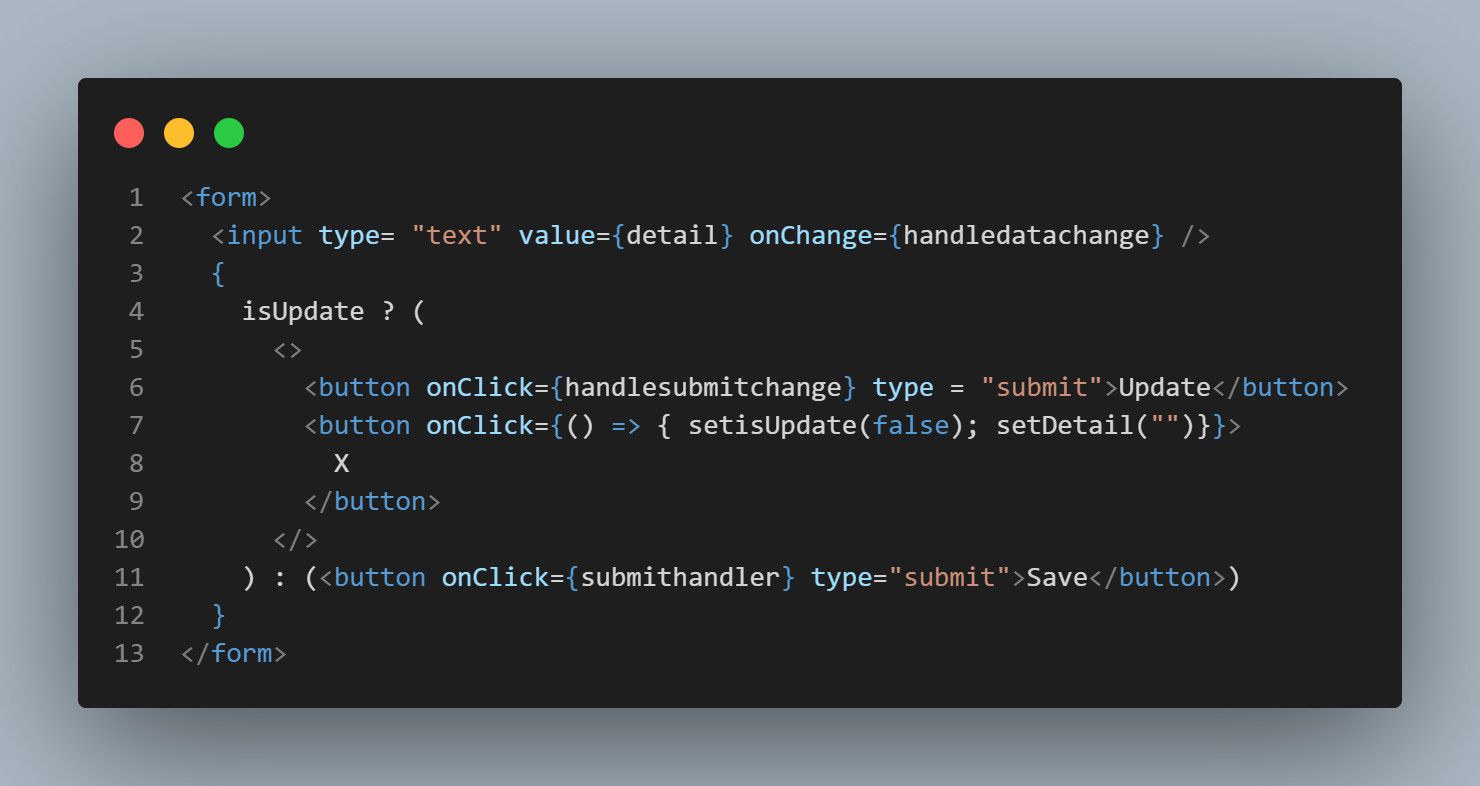
Define two handlers for the update action.
It uses this to query each document from the database for it to make changes.
The Edit button uses this function.
SoisUpdate(tracked by thesetisUpdatestate) returnstruewhen a user clicks the Edit button.
This action brings up the Update button, which submits the edited data when a user clicks it.
The extraXbutton closes the edit action when clickedby settingisUpdatetofalse.
IfisUpdateisfalse, the DOM retains the initial Save button instead.
Delete Data From Firestore
it’s possible for you to delete existing data from Firestore using thedeleteDocmethod.
It removes the data from the database and the DOM when a user clicks it.
Besides React, it supports other JavaScript frameworks, including Angular.js, Vue.js, and many others.