Broadband and fiber connections have created lightning-fast networks where high-definition media can be loaded in just a few seconds.
That’s not to say there isn’t room for improvement.
Changing your DNS controls is often cited as one of the easiest ways to optimize your internet speed.

Michal_Jesensky/Shutterstock
So, let’s take a look at how DNS works and how to change your DNS controls.
What Is DNS?
How Does Your Location Affect DNS Speed?
The infrastructure supporting the internet is a series of copper and optical cables connecting servers worldwide.
If a DNS server is located far away from you, then your browsing speeds will be impacted.
However, the reality of the internet is more complicated than simple distance calculations would have you believe.
These are known as anycast addresses, with multiple servers worldwide responding to requests from these addresses.
The servers responding to the requests vary throughout the day, depending on connection conditions and traffic.
Despite returning your queries from servers worldwide, it is consistently ranked as one of the fastest DNS servers.
In most cases, if you use a Canadian DNS server, the CDNs assume you are in Canada.
This impacts loading speeds, and the content you see will be optimized for a Canadian audience.
CDNs are essential to the operation of the internet.
Google and OpenDNSattach your IP address to the DNS requests.
This means that the data is loaded from a server local to you, improving your overall internet speed.
Does Changing Your DNS Increase Speed?
When planning a trip with Google Maps, you’re presented with several different travel options.
Some routes will take less time, even if they cover a greater distance.
This could be due to many factors, such as traffic, transport changes, and average speed.
When selecting a DNS server to increase your internet speeds, you’ll face a similar range of factors.
Choosing the most advantageous path is known as route optimization.
Some DNS servers, like those provided by ISPs, will experience heavy traffic, especially during peak times.
Some servers have outdated records or inefficiently route your data.
The complex interplay between servers and connections makes route optimization integral to improving your internet speeds.
Your ISP’s DNS server may be located close by.
However, its one-size-fits-all approach is unlikely to offer you the best performance.
This is where a tool like Google’sNamebenchcomes in handy.
It offers a free speed test to help you find the fastest DNS to optimize your internet speed.
Namebench analyzes your connection and recommends the best DNS servers explicitly tailored to you.
Furthermore, DNS doesn’t only dictate speed.
you’re able to choose a specific DNS provider toimprove your online safety and security.
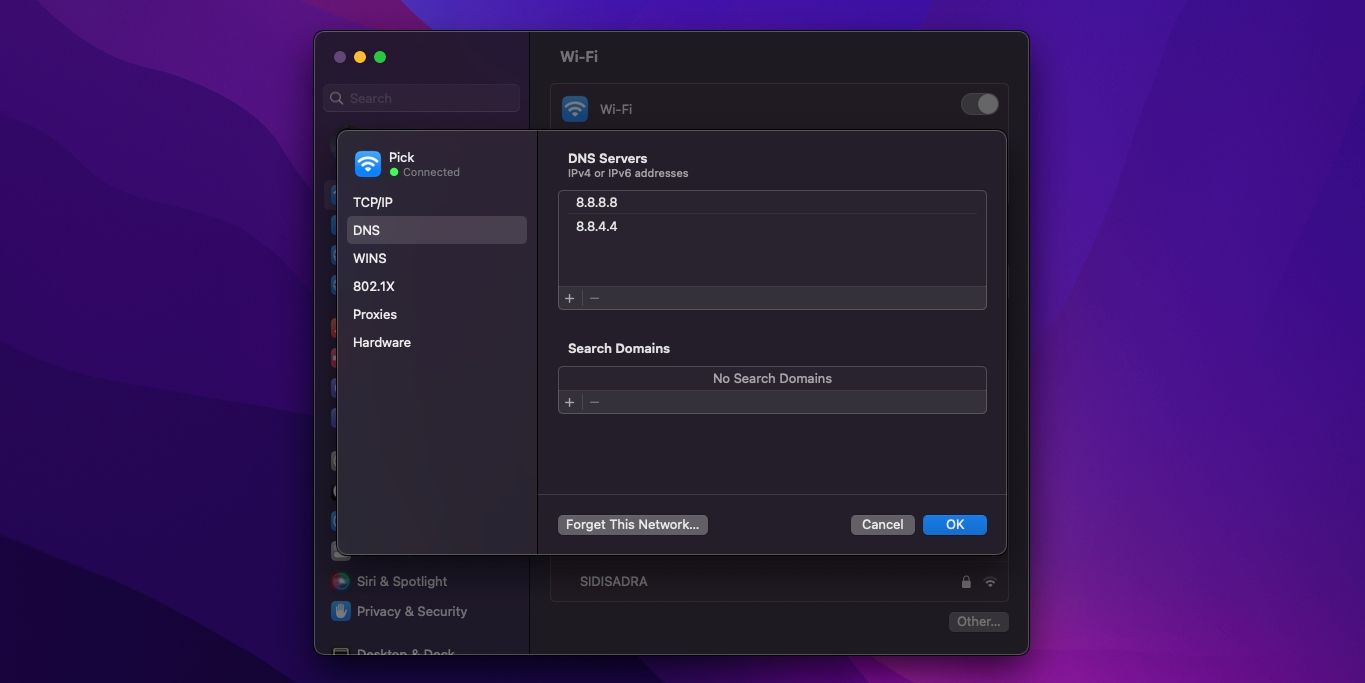
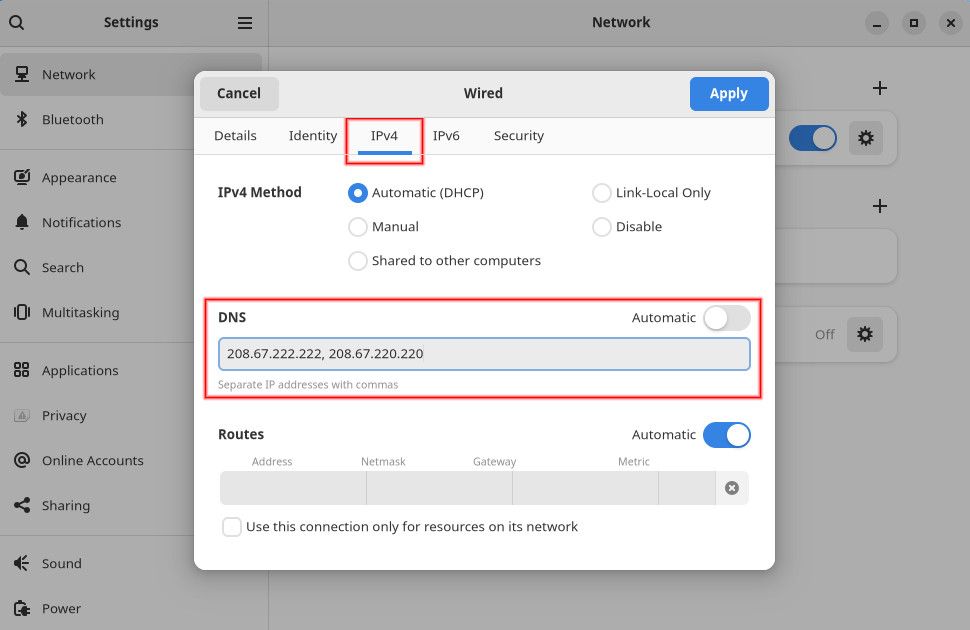
Instead, you’ll want to change your operating system’s DNS parameters.
There are several alternative DNS providers, including Google DNS, OpenDNS, Cloudflare DNS, and Quad9.
Then, you’re able to close all parameters windows and return to regular internet browsing.
Once you confirm those options, you’ll begin using your new DNS servers.
you’re free to also choose between changing the prefs using the Linux GUI or the command line.
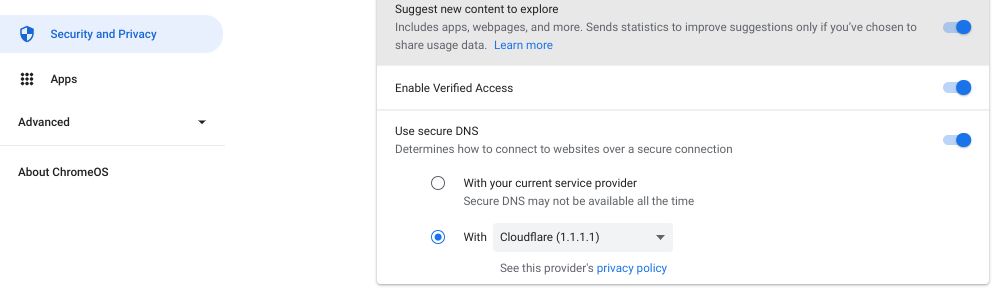
It’s a relatively simple task to change the DNS prefs on ChromeOS.
Your new DNS configs will work on any connection you connect your Chromebook to.