Many open-source architectural standards exist for building and distributing applications.
RESTful APIs are the most used API architectural standard.
If youve written complex RESTful APIs with many endpoints, youve likely realized how complicated they can be.
This is especially true if there are only slight differences between the endpoints.
You may also encounter problems with data fetching since RESTful APIs are not flexible enough to select specific data.
GraphQL solves these problems of RESTful APIs.

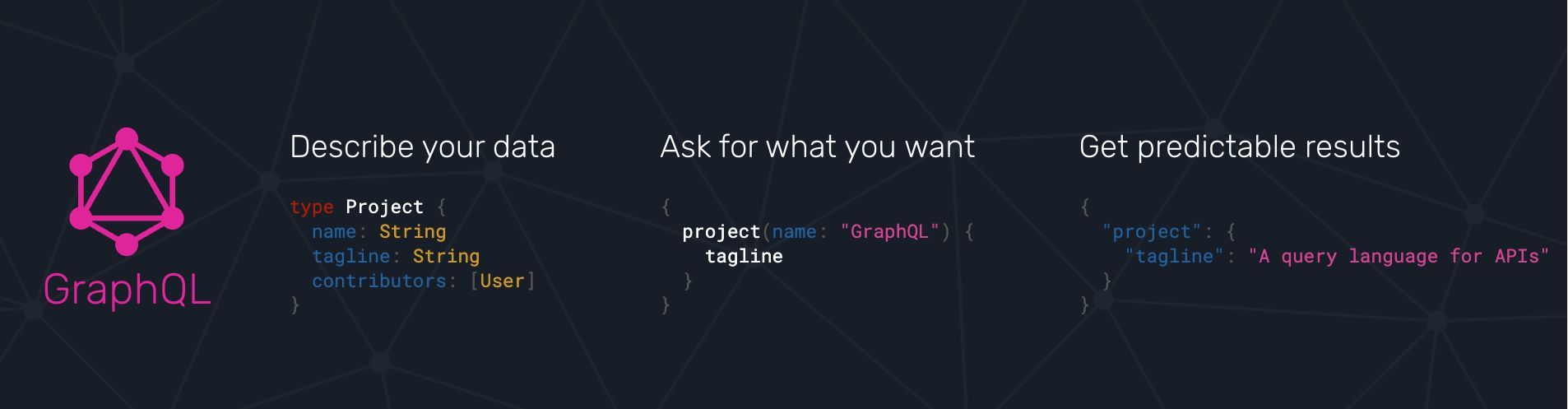
What Is GraphQL?
GraphQL (Graph Query Language) is a query language and runtime for building APIs.
Unlike REST APIs with many endpoints for consuming data, GraphQL APIs have one entry point.
you’re free to fetch specific data by describing it in queries.
TheGraphQL specificationdefines the query language and how GraphQL servers operate.
Meta built GraphQL in 2012 as an alternative to REST for building on HTTP.
They released GraphQL as an open-source standard in 2015.
Today, the GraphQL foundation oversees the development of the GraphQL specification.
GraphQL is fairly new, with low adoption, and there are hidden costs to using it.
Building GraphQL APIs can be unnecessarily complex, especially for small projects with a few endpoints.
Also, all GraphQL requests eventually return a status code of 200 regardless of the state of the request.
How Does GraphQL Work?
Youll be able to use various features depending on theGraphQL package or libraryyou choose to use.
GraphQL schemas include object types that define the requestable object and its available fields.
Why Should You Use GraphQL?
REST is an easy-to-use standard, and most programming languages have tools for building RESTful APIs fast.
However, there are many issues with building and consuming RESTful APIs.
Here are some of the issues with REST that makes developers prefer GraphQL for some use cases.
Inefficient Data Fetching
RESTful APIs relay data based on the endpoints specification.
They arent flexible enough to retrieve data beyond what is hard coded in the handler function of the endpoint.
you could parse the valuable resource manually, which eventually takes more time.
The GraphQL query above queries auserschema for entries where theagefield is 89.
The query has an embedded query for entries where thealivefield evaluatestrue.
It returns the name, bio, and nationality fields from the schema.
Consuming GraphQL APIs is not as tedious as RESTful APIs.
In REST, different endpoints give access to different resources, unlike GraphQL, where theres a single endpoint.
This yields flexibility and performance, and queries can call different resolver functions.
The GraphQL SDL syntax is easy to read and understand.
Youll specify the structure of your schema in a file with the.graphqlor.graphqlsextension.
The GraphQL code above is the schema for a GraphQL API defining the structure of the API for requests.
The schema defines CRUD functionality for the API.
Heres an example of querying theHumanschema.
The query above would return the human schema’snameandagefield data.
GraphQL mutations have a fairly different syntax in contrast to queries.
Heres an example mutation operation on theHumanschema.
The mutation code inputsnameandagefields to the client and returns the data from the fields.
Youll need a data store for persistence when youre building your GraphQL API.
Youll have to find a library with the features you need for your project.
Most libraries take either a schema-first or a code-first approach.
In the former, you define a GraphQL schema, and the library generates resolvers and boilerplate code.
For the latter, you hard-code the resolvers without defining a schema.
These can reduce the development time for smaller and medium projects.