What new knowledge did you gain whilst writing the book?
Simultaneously, money took the form of bits moving around the world, including the form of cryptocurrencies.
Thus, e-commerce encompasses physical or virtual goods (software, information, music, books, etc.

This initial phase includes advertising, discovery and negotiation of the price, and the terms and conditions.
There are instances, however, where the term mobile commerce implies specific characteristics.
The Federal Acquisition Streamlining Act of October 1994 required the use of EDI in all federal acquisitions.
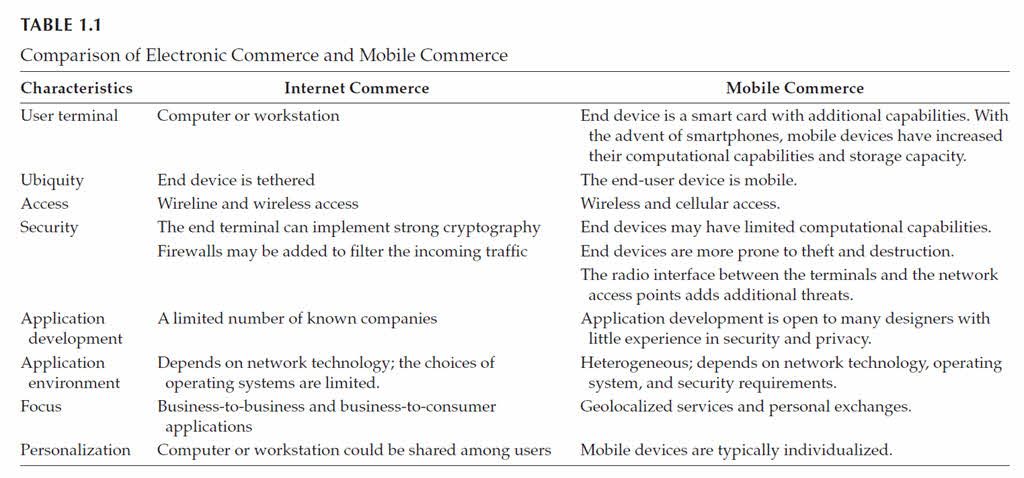
Interest in business-to-consumer e-commerce started to grow in the 1980s, although this interest varied across different countries.
In Germany, remote banking services were conducted through the Bildschirmtext (BTX) system.
The Minitel uses the kiosk mode of operation.

After collection of the funds, the operator compensates the content providers.
At the same time, the financial institutions benefit from having a unique interface to consolidateindividual transactions.
Let us now look closer at three business-to-consumer applications over the web.

These are the site auction eBay, Amazon, and Stamps.comTM or Neopost.
The auction site eBay illustrates a successful pure player that established a virtual marketplace.
It has established key relationships with the U.S. Neopost ranks number one in Europe and number two worldwide in mailroom equipment and logistics systems.
Both systems faced significant operational difficulties.
There is also a need to adapt to users software and to all printer models.
Finally, users must pay a surcharge of about 10% to the operator.
From an economic point, the offer may not be attractive for all cases.
However, the decision by the U.S.
Proximity commerce or face-to-face commerce is using several methods to replace cash.
Prepaid cards can be one of two types: closed-loop and open-loop cards.
In France, prepaid telephone cards have been widely used since the 1980s (Adams, 1998).
The principle is to share excess and idle capacity on a very short-term basis.
The payment can be directly from a bank account or a payment card (credit or debit).
Venmo, which is now part of PayPal, allows groups to split bills easily.
In general, handling small transfers between individuals is not a big or lucrative part of the financial system.
This pullback has opened the way to new approaches to the transfer of workers remittances.
For example, TransferWise, a UK company, operates in the following manner.
The customer selects a recipient and a currency and the amount to be transferred.
If this is not the case, then a system of brokers will be needed.
Other person-to-person lenders in the United Kingdom include Funding Circle, Zopa, and WorldRemit.
WebMoney is another global transfer service based in Moscow, Russia.
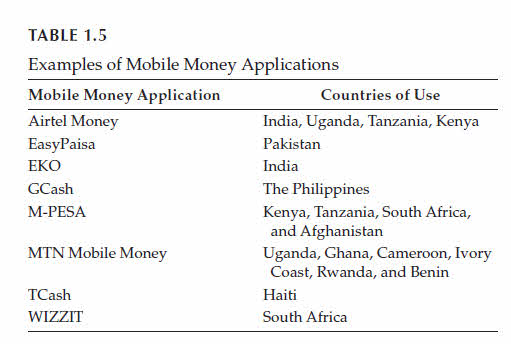
It is common in the Arab World, the Horn of Africa, and the Indian subcontinent.
Independently, the transfer initiator informs the recipient of that secret code.
The community spirit was translated into an economy of free advice or software freely shared.
Other impediments relate to concerns regarding the security of information, because security on the public Internet is afterthought.
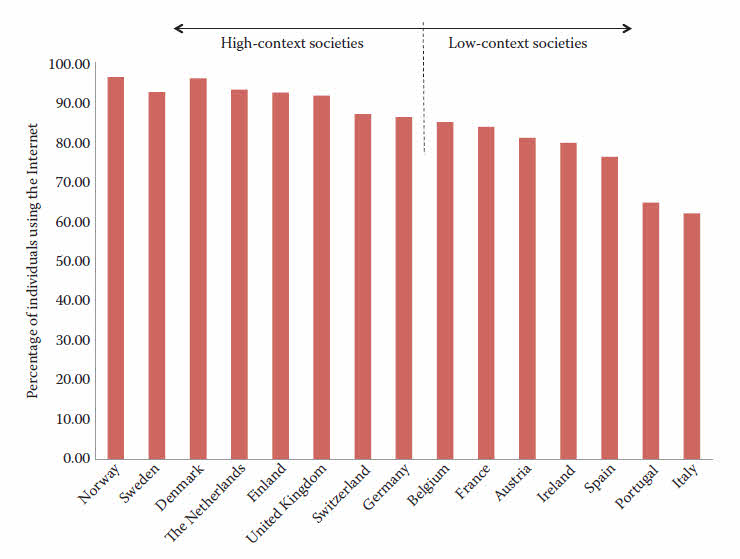
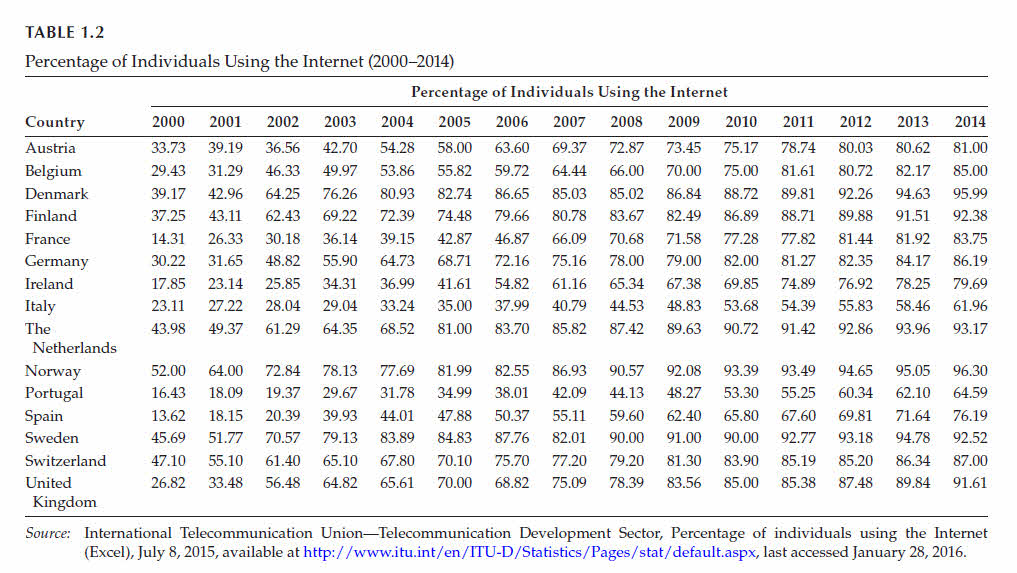
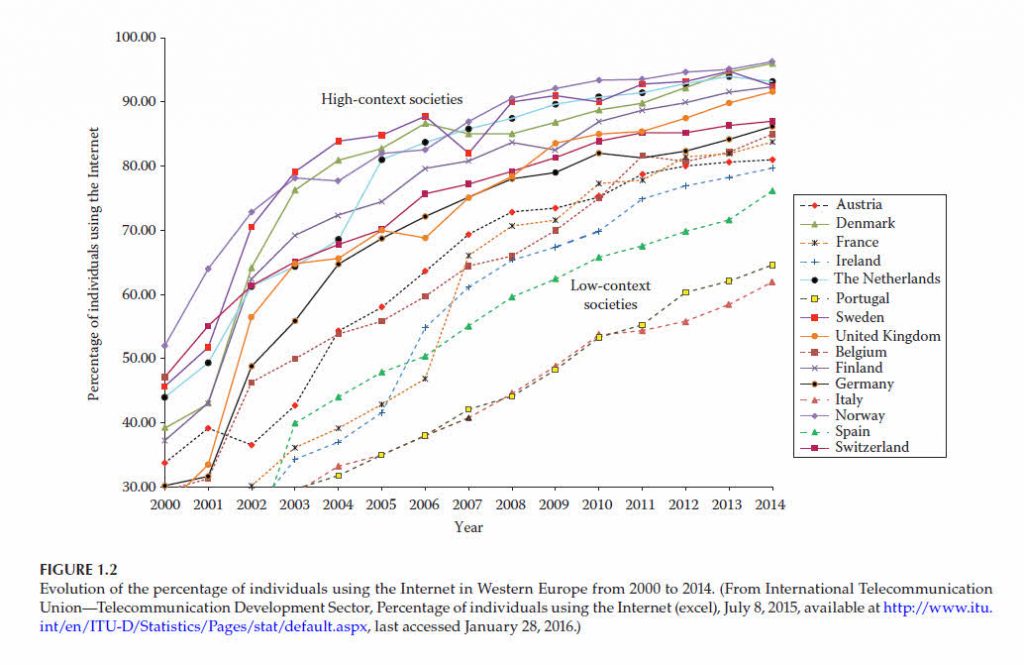
the Internet in Western European countries as of 2014, available from the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
In Figure 1.2, the dotted lines are reserved to countries with high-context cultures.
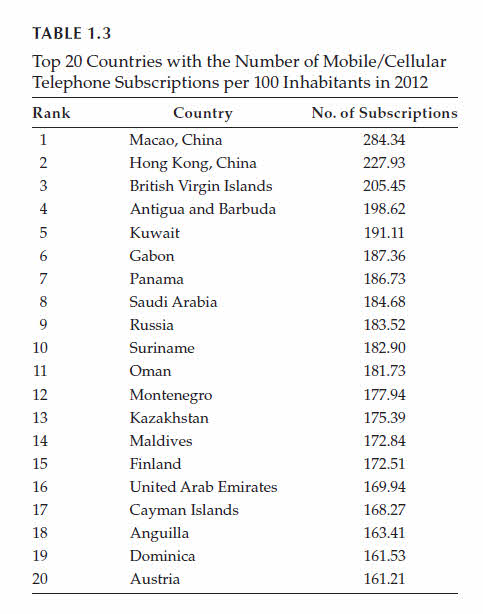
The situation is substantially different regarding mobile commerce.
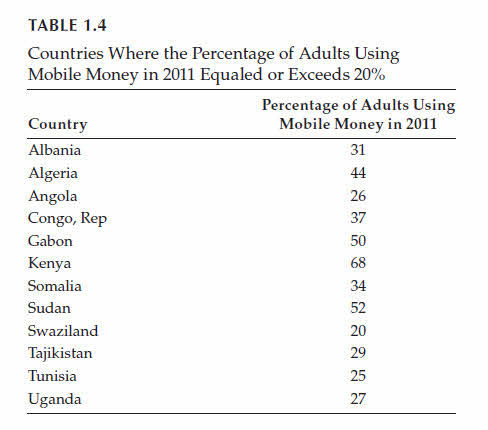
It is noted that 19 countries in the top 20 list are from the developing world.
Smartphones offer many additional features for mobile commerce.
This has security implications as well.
Furthermore, mobile devices have limited options for running protection software.
connectivity, and their openness to mobile applications (apps) that supplement the capabilities of the machine.
This has security implications as well.
Furthermore, mobile devices have limited options for running protection software.
connection access for remote communication can be through either a wireline or a wireless infrastructure.
The physical medium for wireline access can be copper cables, coaxial cables, and optical fibers.
The bit rates depend on the access technology.
Cable companies use the DOCSIS 3.0 technology to support rates up to 100 Mbit/s.
Gigabit passive optical networks (GPONs) carry all service types in addition to analog telephony.
The traffic of any service pop in can be encrypted using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
The deployment configuration depends on the reach of the optical fiber.
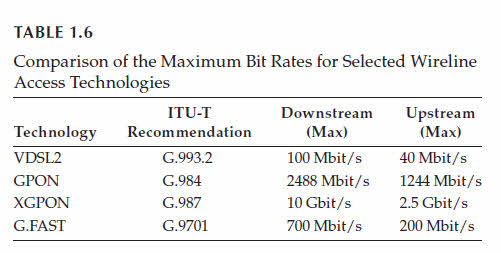
Table 1.6 summarizes the maximum transmission speeds of all these technologies.
Several protocols are available for wireless access.
Exchange Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) increased the rate to 473.6 kbit/s.
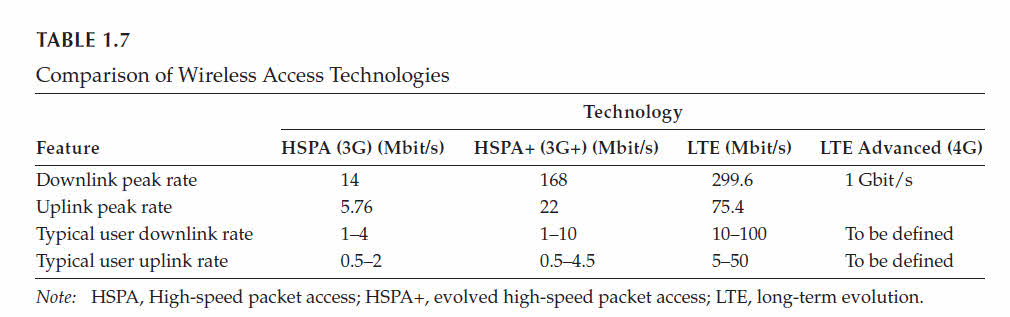
Newer generations of technologies have increased the rates, as shown in Table 1.7. optimal fashion and to enhance the information carrying capacity of the radio channels.
The peak download is 128 Mbit/s, and the peak upload is 56 Mbit/s.
These operate respectively at the various frequencies and theoretical bit rates (maximum throughputs).
The set of encoding rules is called barcode symbology.
Barcodes can be read with smartphones equipped with a digital camera.
One-dimensional codes have limited storage capacity and provide indices to backend databases.
Most consumer products today are equipped with black-and-white stripes or Global Trade Item Number (GTIN).
GTIN is a linear or 1D barcode that follows a specific standard.
Planet is used to track both inbound and outbound letter mail.
The Intelligent Mail Barcode (IM barcode) is a 65 barcode to replace both Postnet and Planet.
USPS GS1-128 (EAN-128) is used for special services such as delivery confirmation.
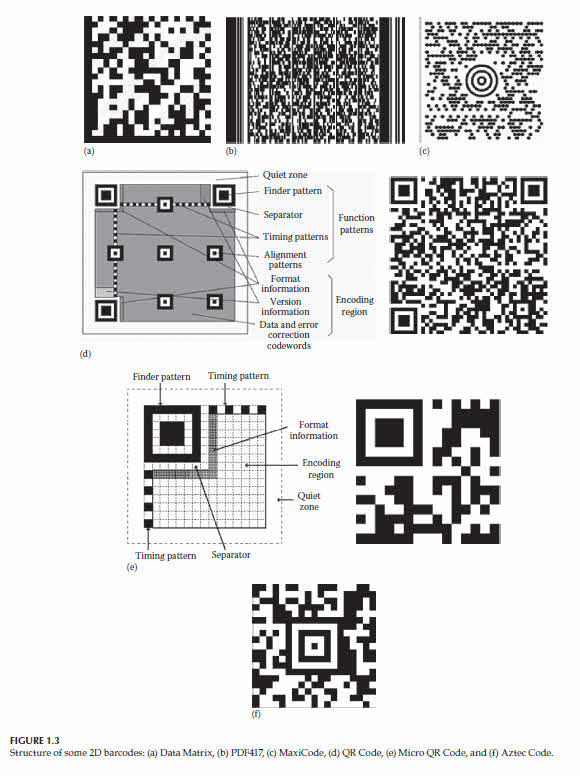
Data representation in matrix codes consists of a matrix of black and white squares or cells.

Matrix codes have larger storage capacity than stacked codes.
Some of the 2D barcodes that can be read from mobile phones are presented next.
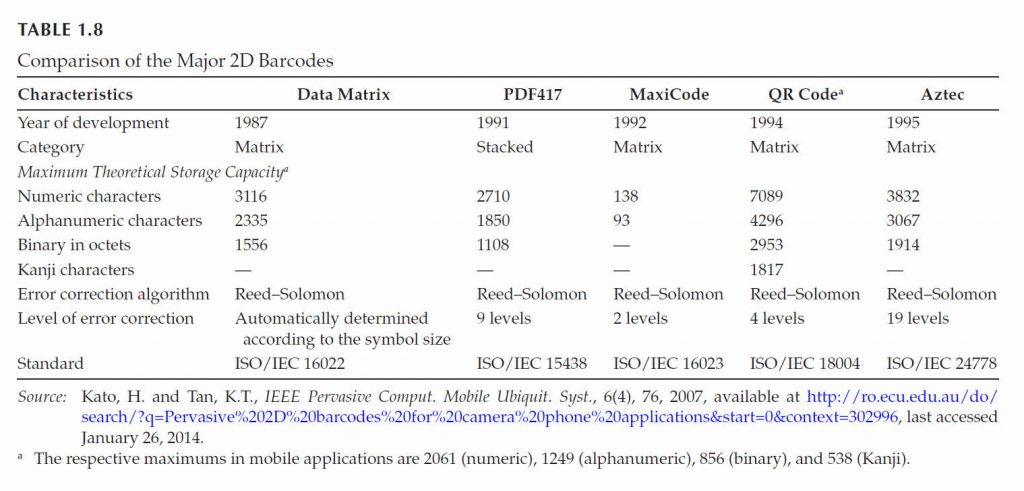
Data Matrix was developed in 1987 and standardized finally in 2006 as ISO/IEC 16022:2006.

Its main characteristic is its small symbol size to fit on tiny drug packages.
PDF417 is a stacked code, developed in 1991 and standardized in 2006 as ISO/IEC 15438.
Figure 1.3b shows the structure of a printed PDF417 barcode symbol.

Error correction is based on the ReedSolomon algorithm.
The U.S. Department of Homeland Security has selected PDF417 for RealID-compliant driver licenses and state-issued identification cards.
PDF417 and Data Matrix can be used to print postages accepted by the U.S. MaxiCode was developed by UPS in 1992 for the highspeed sorting and tracking of units.

It has a fixed size and a limited data capacity.
One of its characteristic features is a circular finder pattern made up of three concentric rings.
It was standardized in ISO/IEC 16023:2000.

Model 1 QR Code is the original version of the specification.
5160, 226230).
Versions differ by the amount of data that can be stored and by the size of the 2D barcode.

The resolution of the camera phone puts a practical limit on the versions that mobile applications can use.
During scanning, these pattern blocks are the first to be detected.
Micro QR Code is a small-sized QR Code for applications where less space and data storage capacity are required.

The Aztec Code is another 2D matrix symbology defined in ISO/IEC 24778:2008, as shown in Figure 1.3f.
It was developed in 1995 to use less space than other matrix barcodes.
One simple check is to verify visually that the tag is printed with the poster and not inserted afterward.

Reliability refers to the consistency of the measurement across repetitions.
Speed, typically less than 5 seconds for user acceptance.
The quality of the user interface.

As of now, there is no standardized procedure to assess the performance of scanners.
In the 1990s, they started to be used in health-care systems in Belgium, France, and Germany.
In these cards, several applications may coexist within the same card but in isolation (sandboxing).

), or logical security (software, confidential data repositories, etc.).
These cards are often associated with a display to show dynamic passwords.
105106; Lindley, 1997, pp.

3637, 95111).
Duration of card usage, which distinguishes disposable cards from rechargeable cards.
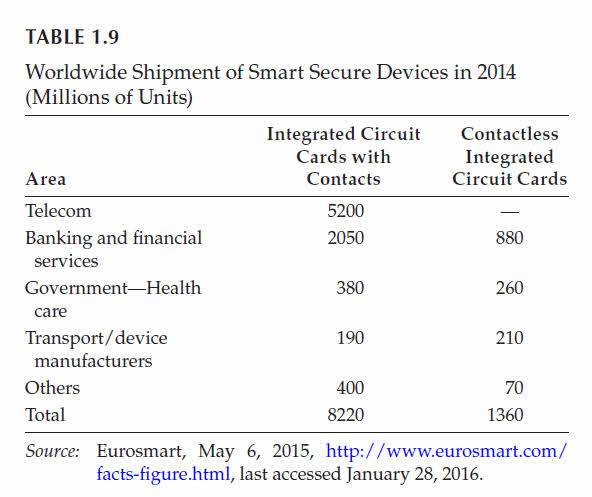
The technology of contactless integrated circuit cards is also known as radio-frequency identification (RFID).

Characteristic tool of the card, which differentiates monoapplication cards from multiapplication cards.
In contrast, a contactless card requires only close proximity to a reader.
Both the reader and the card are equipped with antennae and establish communication using radio frequencies.

Contactless cards derive their power from this electromagnetic link through induction.
The contactless chip and its antenna can be embedded in mobile devices such as smartphones.
RFID cards are used for tracking and access control.

These comply with the ISO/IEC 14443 standards.
Furthermore, ISO/IEC 7501-1:2008 defines the specifications of electronic passports including globally interoperable biometric data.
This tag would then be read at various intervals up to its point of sale.
Some airport baggage handling systems use RFID tags to improve the accuracy and speed of automatic baggage routing.
A growing number of new cars sold today contain an RFID-based vehicle immobilization system.
It includes an RFID reader in the steering column and a tag in the ignition key.
Urban transportation systems with high commuter traffic constitute a large market for contactless payments.
The value is preloaded value, and the deduction per ticket is recorded on the card itself.
An antenna is integrated in the surface of the card and operates at the carrier frequency of 13.56 MHz.
Furthermore, location-based services can generate additional revenues to transportation operators.
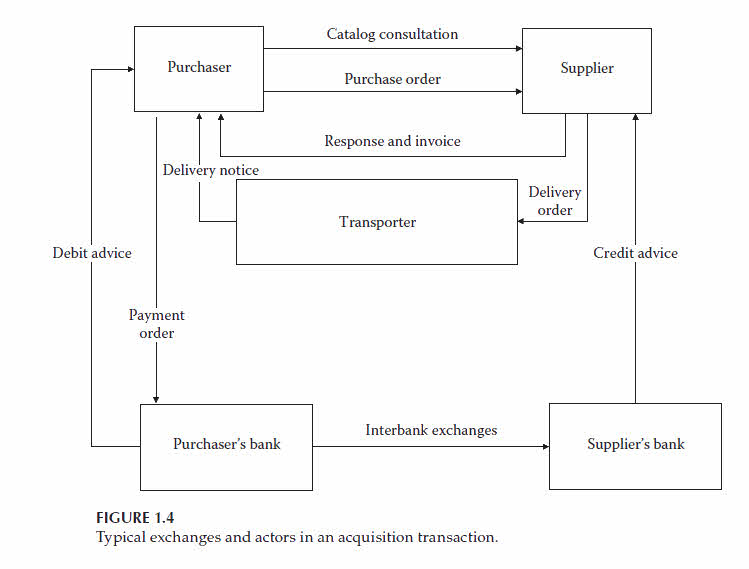
Documentation on the merchandise2.
Agreement on the terms and conditions of the sale3.
The delivery of electronic or digital objects such as files, images, or software can be achieved online.
Interconnecting elements or middleware may mask this heterogeneity at the cost of complexity and inefficiency.
1.6.2 Payment Intermediaries
Payment intermediaries convert purchase requests into financial instructions to banks and card schemes.
They provide several functions such as payment aggregation, gateway functionalities, and payment processing.
Some also intervene to manage the security of the payment infrastructure.
Ultimately, these aggregators may be able to perform some banking functions.
This alleviates the burden on the merchant of incorporating multiple payment methods into their website and streamlining payment operations.
Some payment gateways also help merchants identify risk factors to address customer queries about rejected payments.
A payment processor relays the issuer banks decision back to the merchant.
At the end of each day, payment processors initiate the settlements among the banks.
These intermediairies are part of the security infrastructure of online payments.
1.6.3 Providers and Manufacturers
The efficiency and security of electronic transactions may require specialized hardware.
The software may also be managed through third parties (i.e., as through cloud services).
Other specialized functions may be needed in backoffice operations.
1.7 Security
The maintenance of secure digital commerce channels is a complex enterprise.
The pressures for speed and to cut cost are driving reliance on third parties that may compromise security.
1.7.2 Loss of Confidentiality
Electronic commerce provides many opportunities to profit from malfeasance.
Online inventories expand the possible audience of any given shopkeeper.
Parts of the Internet economy are nonmonetary in the form of open source or free software.
Also, some of the value of electronic commerce comes from the value of learning by searching.
Questions
1.
What are the goods sold in digital commerce (electronic or mobile)?3.
Compare the roles of barcode technology with RFID technology in supply chain management.5.
Discuss the role of standards in electronic commerce.
Consider standards at the terminals, networks, and applications.
Provide advantages and disadvantages of standards.7.
Compare at least three characteristics of business-to-business commerce with business-to-consumer commerce.8.
Describe the kiosk business model.9.
What are the main benefits and main costs related to business-to-business e-commerce?10.
List two anticompetitive issues that may arise in electronic procurement.11.
What are the three aspects of security from a users viewpoint?
hey, comment on how to improve this article.
