Formatting numbers correctly can be a tricky task.
And formatting currencies brings additional challenges involving localization.
Fortunately, Go has features to help.

The Go standard library provides various tools for formatting numbers.
The strconv package includes functions for parsing and converting numbers to and from strings.
The strconv Package
Thestrconvpackage is a powerful tool for converting between numbers and strings.
you might use it to work with numbers in various formats.
It includes functions to work with integers and floating-point numbers.
Formatting Integers in Go
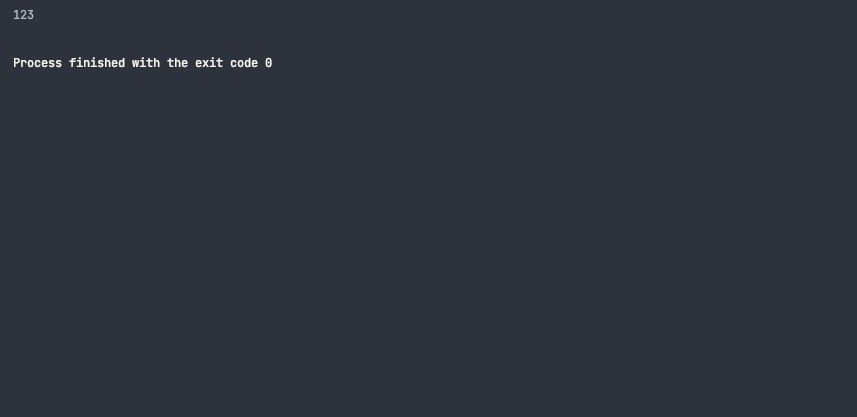
The strconv packagesItoafunction provides functionality for converting integers to strings.
TheItoafunction takes an integer and returns the string representation of that integer.
This code converts an integer value to a string usingItoa.
It then outputs the resulting string to the console using thefmtpackage.
It then passes the result toFormatInt, along with a base for conversion, in this case 10.
FormatInt returns a string whichPrintlnthen outputs to the console.
TheAppendIntfunction takes in a byte slice, anint64value, and a base.
Note that AppendInt receives a byte slice to append to, and returns the resulting byte slice.
Parsing Strings as Integers
TheAtoifunction converts strings to integers.
TheParseUintfunction parses the 12345 string as a base ten, unsigned integer.
The 0-bit size ensures it returns a standard int key in.
It returns the parsed value and an error.
you could use theParseFloatfunction to parse a string representation of a floating point number.
TheParseFloatfunction parses the string as a 64-bit floating point number and returns the string and an error jot down.
Formatting Currencies in Go
Building an tool that interacts with currencies requires number formatting and parsing.
Working with different currencies can be a challenge, but thestrconvandaccountingpackages can help you format them.
Recall that structs are one ofGos core object-oriented features, similar to classes from other languages.
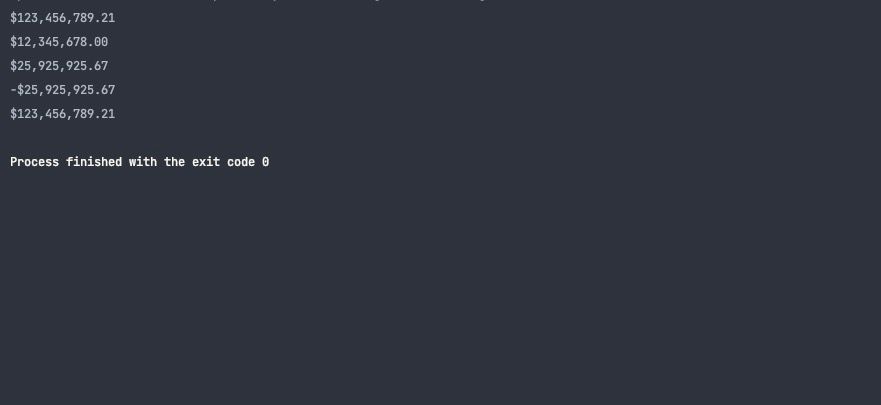
you might use theFormatMoneyfunction of the accounting package to format numbers into currencies.
Theacvariable is the accounting instance.
This program formats and prints monetary values using theFormatMoneyandFormatMoneyBigFloatmethods of the accounting instance.
TheNewRatfunction from thebigpackage creates a rational number given a numerator and denominator.
TheNewFloatfunction helps represent large floating point numbers.
The language also offers a powerful string formatting system.
The fmt packages C-inspired Sprintf function lets you create formatted strings using a special placeholder syntax.