A two-hour-long movie would hog over 1.7 Terabytes of storage when uncompressed.
What Is a Video Codec?
Put simply, video is nothing but a set of still images replacing each other quickly.

This high resolution of images enables a video shot in 4K to deliver a great video experience.
To solve this problem, we have video codecs.
Short for coder/decoder or compression/decompression, a video codec compresses the stream of images into bits of data.
Image credits:Janke at English Wikipedia/Wikimedia Commons
As the name suggests, the compression bit in a codec reduces the size of each image.
The decompression, on the contrary, works oppositely and renders the video using the compressed information.
To solve this problem, CPUs and GPUs come with special hardware which can run these compression algorithms.

How Does a Video Codec Work?
The difference in rods and cones prevents the eyes from detecting color changes when comparing compressed and uncompressed images.
After that, the algorithm reduces the amount of color in the image based on compression levels.
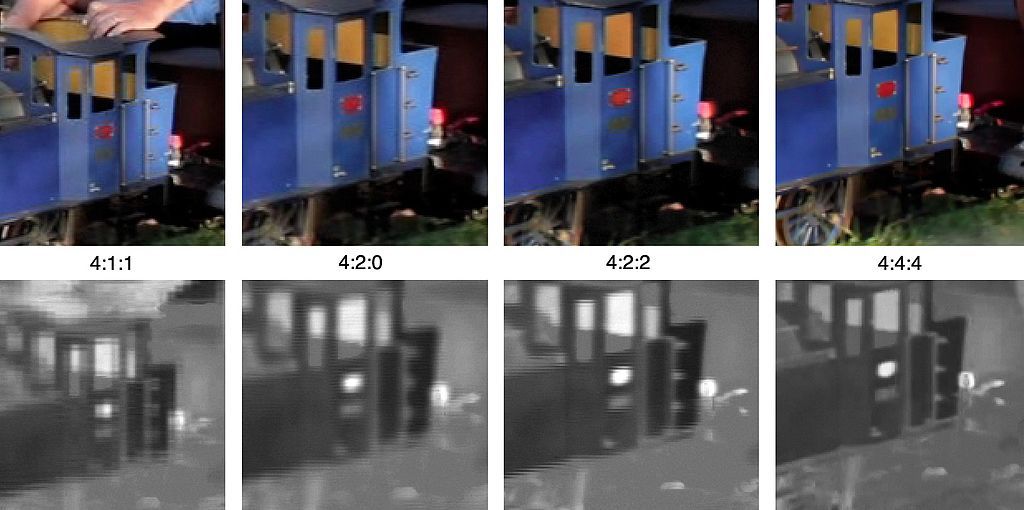

Image credits:Janke at English Wikipedia/Wikimedia Commons
For example, imagine a video with a person speaking against a fixed background.
In such a case, all the frames in the video have a similar composition.
Therefore all the images are not needed to render the video.
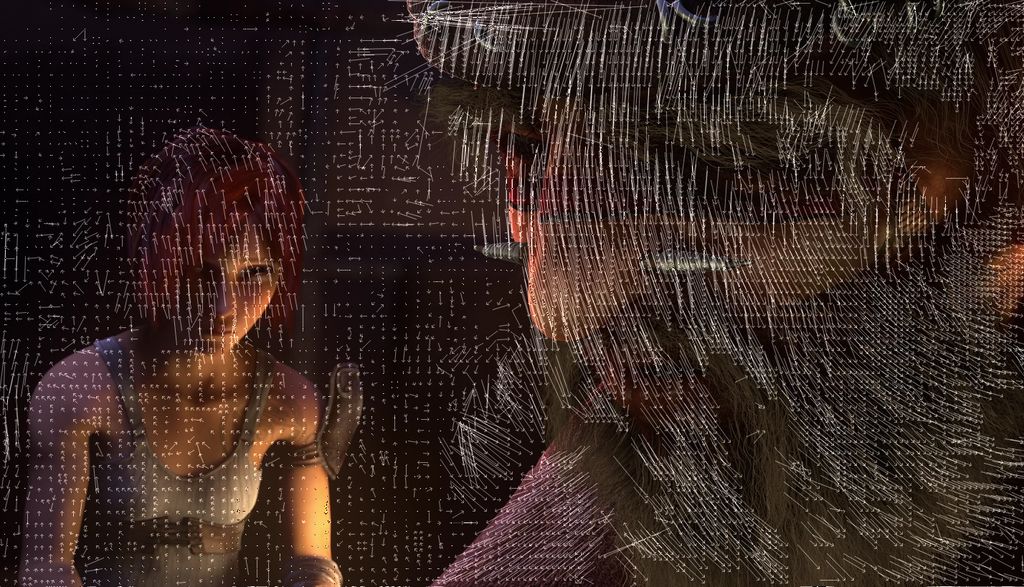

Image Credits: Blender Foundation/Wikimedia
Here I frames are the ground truth and are used to create P frames.
A part of the video compression algorithm which helps create the P frames using the I frames.
To do this, the compression algorithm breaks the I frame into blocks known as macro-blocks.
Image Credits: Redor/Wikimedia
Video compression algorithms use the Discrete Cosine Transform to reduce the high-frequency component.
Here is how it works.
It then removes these data points from the imagereducing the size of the video.
This encoded data is stored on a system, enabling it to render a video easily.
AV1 vs. HEVC vs. VP9: Which Codec Is Best?
However, you also need to consider that the quality it delivers decreases as you keep compressing the video.
For example, a 24-bit uncompressed 4K video running at 60 frames has a bitrate of 11.9 Gb/s.
Compatibility
As explained earlier, a video compression algorithm encodes a video once it’s compressed.
Now to play this video, your rig needs to decode the same.
Instead, users must install additional add-ons from the Windows store to run such videos.
Which Codec Should You Choose?
If you are looking for the best video quality, go for AV1.
Finally, H.265 codec is a great fit if you need good quality and compression without encoding overheads.