JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a highly versatile and vastly popular data format.
Using Go, you could marshal native data structures into JSON.
And you might perform the reverse action, unmarshaling JSON data into Go variables.

If it encounters an error during the conversion process, it’ll return the error and an empty slice.
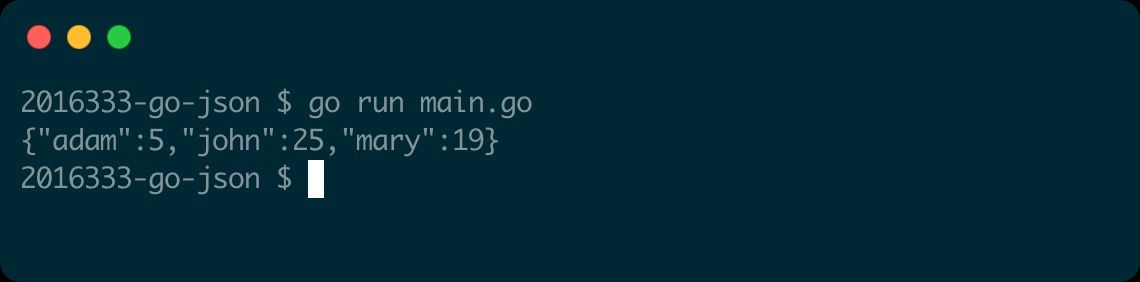
Here’s a code example that usesMarshalto convert a map to JSON.
Struct tags let you adjust the wayMarshaltreats the field the tag belongs to.
Struct tags (thatMarshalrecognizes) start with the substring “json:”.
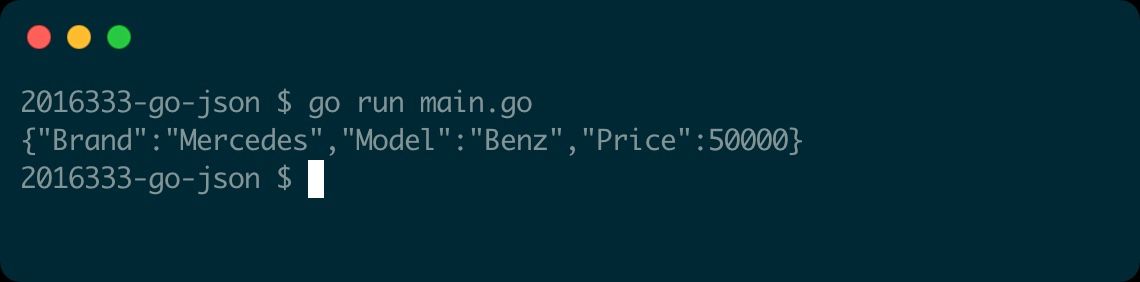
As an example, Say you have a structCarthat represents some information about a car.
This results in the JSON output fields starting with uppercase too.
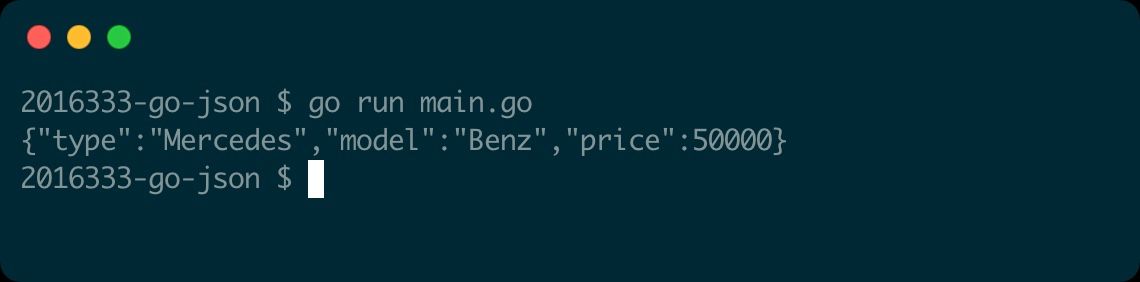
That’s where the struct tags come in.
The code also uses struct tags to rename the other struct fields.
it’s possible for you to read more about Marshal and struct tags in theGo documentation.
Unmarshaling From JSON in Go
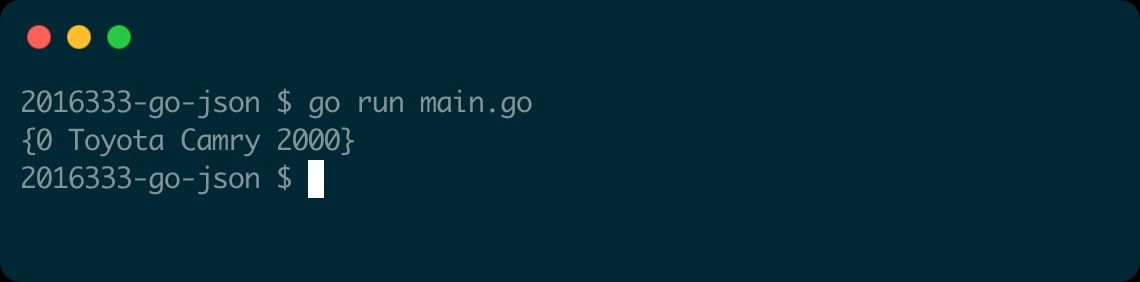
The encoding/json package provides an unmarshaling function as well, calledUnmarshal.
It has the following function signature:
UnlikeMarshal,Unmarshaldoesn’t return a value.
Converting data to JSON is a great way of sharing it with another program or process.
The format is so universal that JSON is as portable as can be.