An effective programmer needs a solid understanding of data structures and algorithms.
Technical interviews will often test your problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
Graphs are one of the many important data structures in programming.
In most cases, understanding graphs and solving graph-based problems does not come easy.
What is a graph, and what do you better know about it?
What Is a Graph?
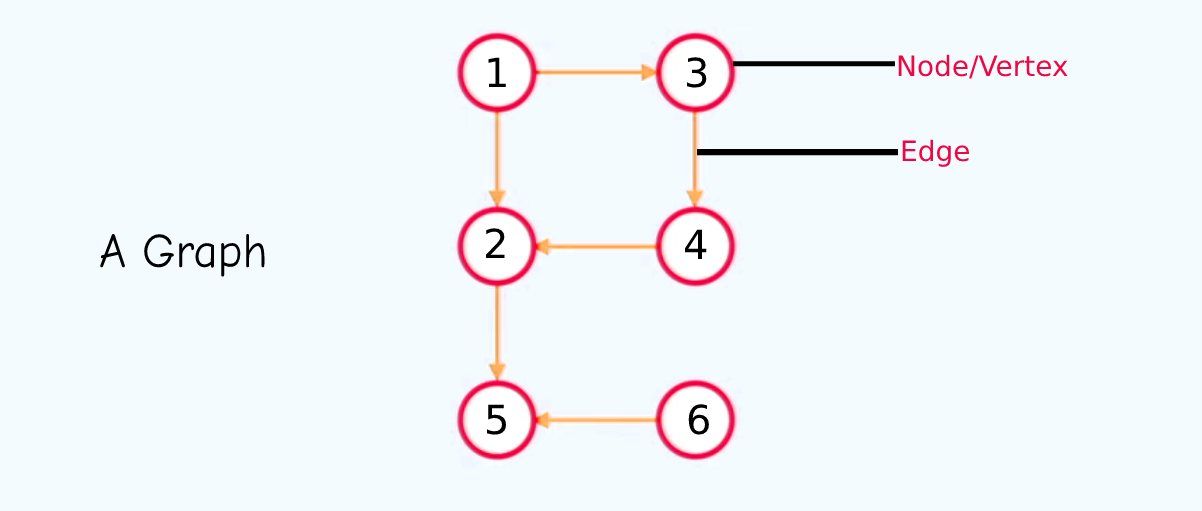
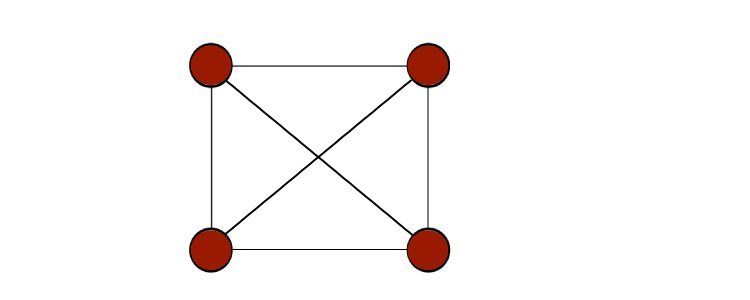
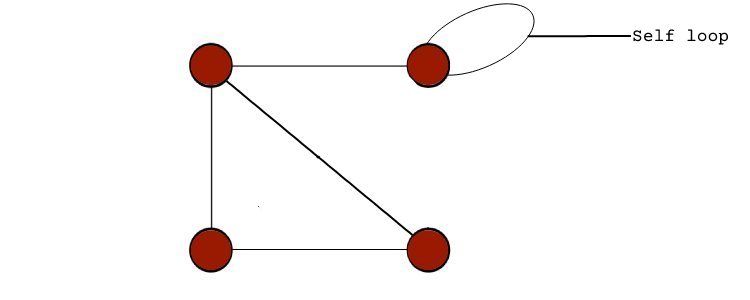
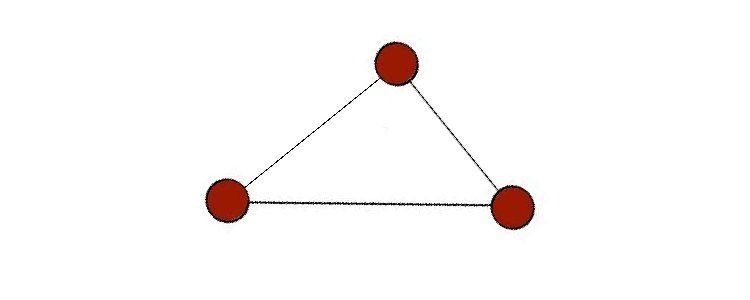
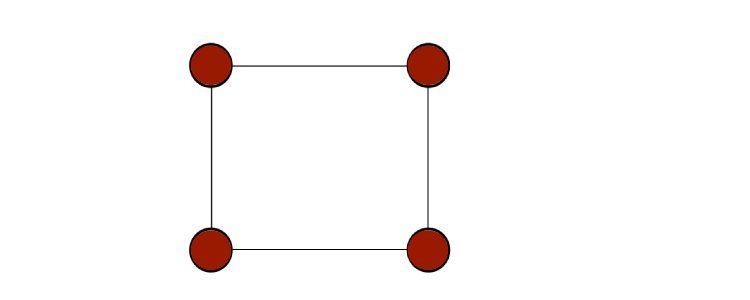
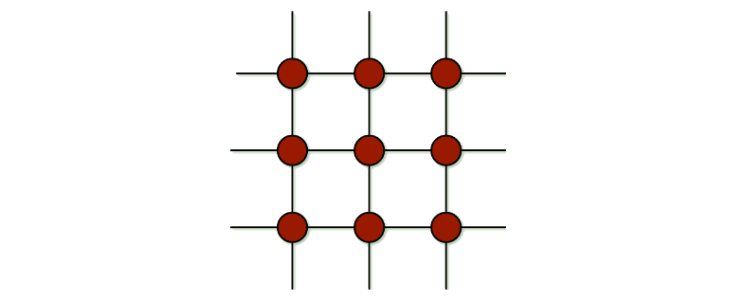
A graph is a non-linear data structure that has nodes (or vertices) with edges that connect them.
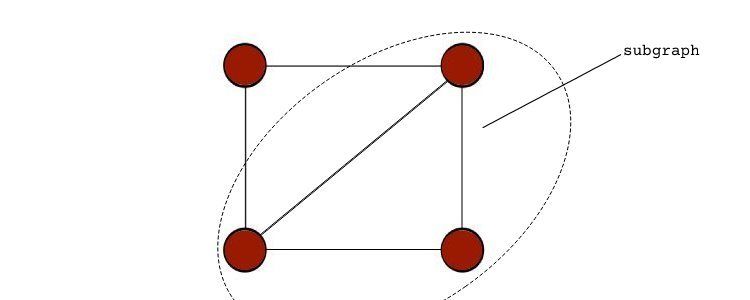
The most popular approaches areedge lists,adjacency lists, andadjacency matrices.
TheKhan Academy guide to representing graphsis a great resource for learning about how to represent a graph.
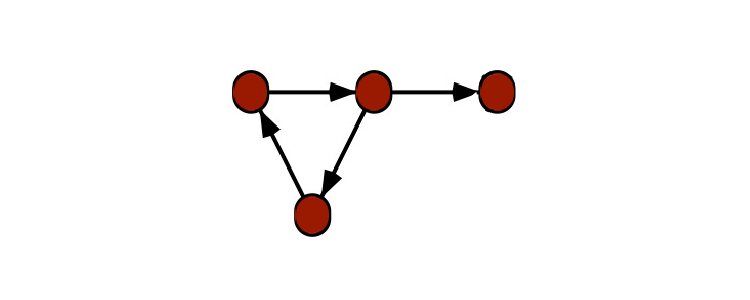
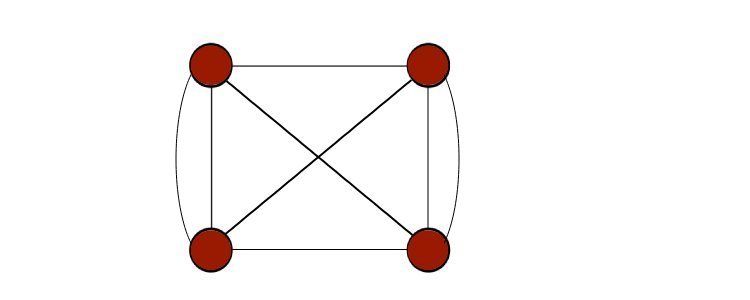
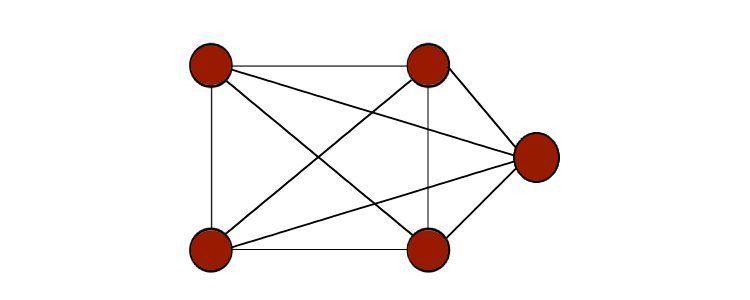
There are many different types of graphs.
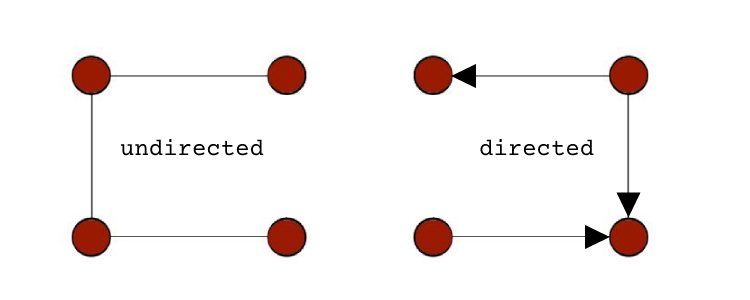
One common distinction is betweendirectedandundirectedgraphs; these come up a lot in coding challenges and real-life uses.
Therefore, aself-loopis a loop over only one graph node, as seen in a pseudo graph.
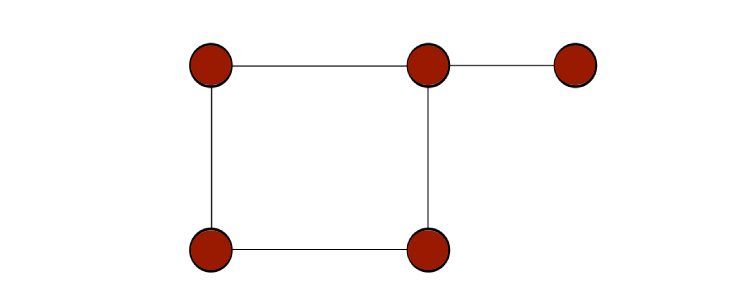
Traversing a graph means going through and exploring each node given there is a valid path through the edges.
Graph traversal algorithms are mainly of two types.
Depth-first search is mostly recommended when you want to visit every node in the graph.
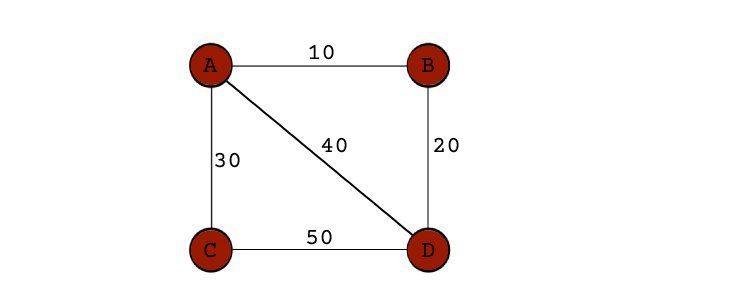
A simple illustration can help understand both algorithms better.
It will find the connection betweenXandYin a short time without having to explore the whole country.
Another major difference between these two algorithms is in the way they are implemented in code.
Below is some pseudocode demonstrating the implementation of both algorithms.
Breadth-First Search
Depth-First Search
A few other graph-traversal algorithms derive from breadth-first and depth-first searches.
These are just a few of the many popular graph-based interview problems.
you’re free to try them out onLeetCode,HackerRank, orGeeksforGeeks.
Understanding Graph Data Structures and Algorithms
Graphs arent just useful for technical interviews.
They have real-world use cases as well, such as innetworking, maps,andairline systemsfor finding routes.
They are also used in the underlying logic of computer systems.
Graphs are excellent for organizing data and for helping us visualize complex problems.
Graphs should only be used when absolutely necessary, though, to prevent space complexity or memory issues.