Windows has long been the worlds foremost desktop operating system.
More than a billion active devices run on the most recent Windows 11 and 10 systems.
Thus, the Windows series is the product that primarily made Microsoft the software giant it is today.
It is an OS series with a history that encompasses five decades dating back to the 1980s.
This is the story of the Windows OS series from the 1980s up to the present day.
The big M later changed that name to Windows 1.0 for its 1985 release.
Microsoft released 1.0 to go head-to-head with Apples graphical Lisa OS, but it had little industry impact.
Windows 1.0 bore little resemblance to the most recent platforms in its series.
However, it did include some of the programs and accessories that remain a part of the series today.
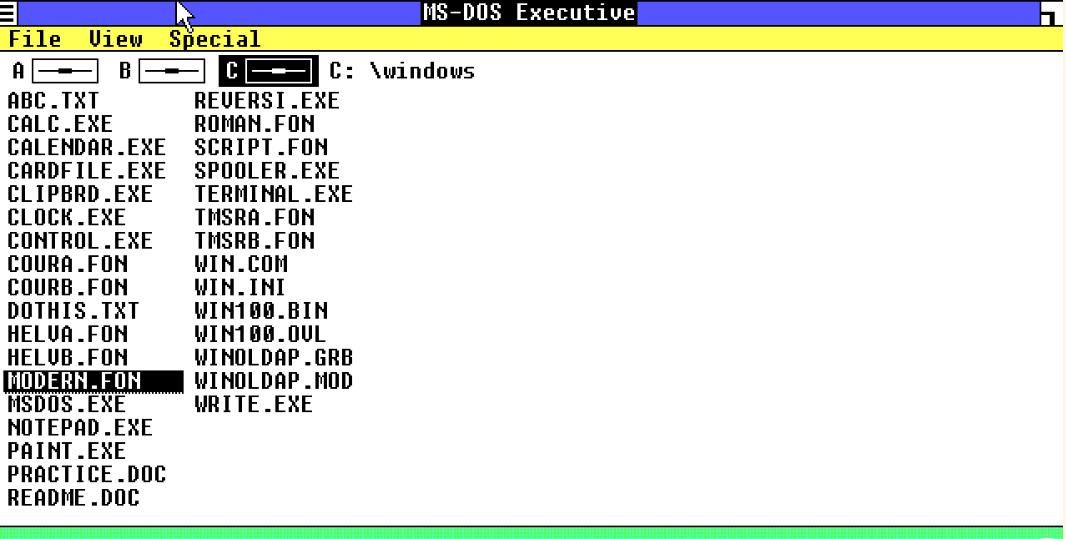
MS Paint, Calculator, Notepad, and the Control Panel were all there in Windows 1.0.
Users could also play a Reversi game included in 1.0.
Microsoft released Windows 2.0 in 1987.
With expanded memory management for software, Window 2.0s multitasking was altogether better.
Apple, however, wasnt impressed with Windows 2.0.
That case was eventually settled in 1994 with Apple losing most claims.
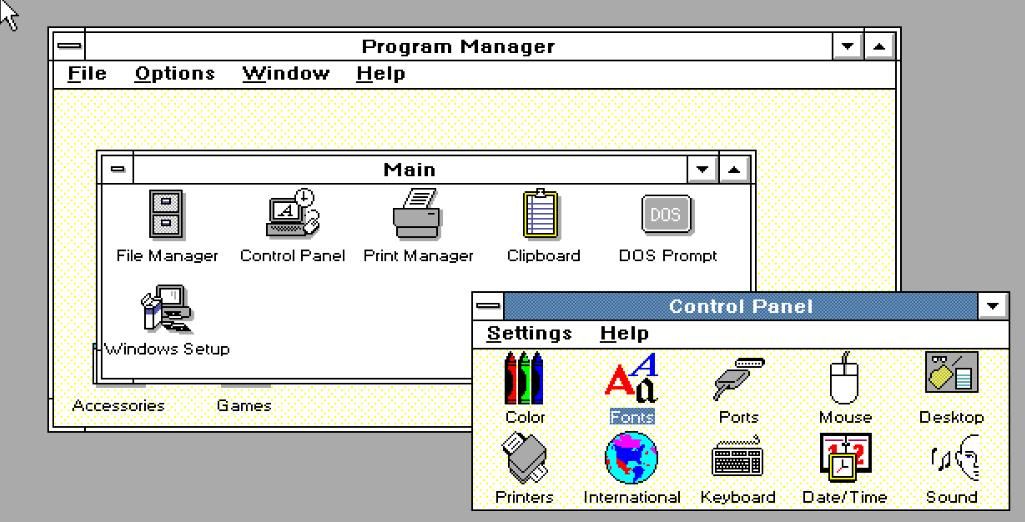
Windows 3 and 3.1
Microsoft kick-started the 90s with the release of Windows 3.0 in 1990.
The third installment to the Windows series was the first to feature software and file icons.
This platform could handle more software simultaneously thanks to the introduction of virtual memory.

With such enhancements, this was the first OS in its series to shift more than a million copies.
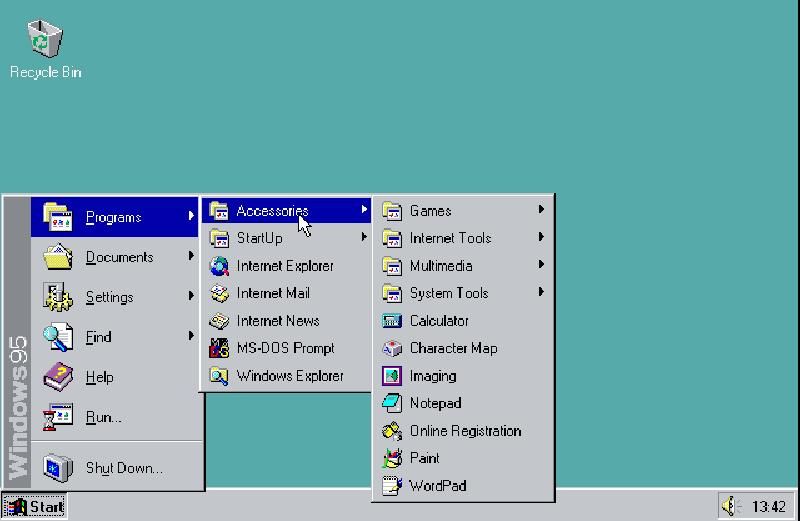
Windows 95 was the first platform in its OS franchise that wasnt subordinate to DOS.
The Start menu was Windows 95s revolutionary new feature.
That menu made all installed software much more accessible than before.
For the first time, users could find and open most of their software from a convenient menu.
The taskbar, which included theStartbutton, was the other significant new feature in Windows 95.
That feature enabled users to multitask by clicking rectangular window buttons.
It also incorporated a system tray clock and notification area as in the most recent Windows platforms.
Microsoft later released Windows 98 and Millennium in 1998 and 2000.
They were both essentially revamped Windows 95 versions that were much the same in terms of interface design.
Millennium was more like an upgraded edition of Windows 98.
However, System Restore was one notable feature it introduced to users.
Windows XP
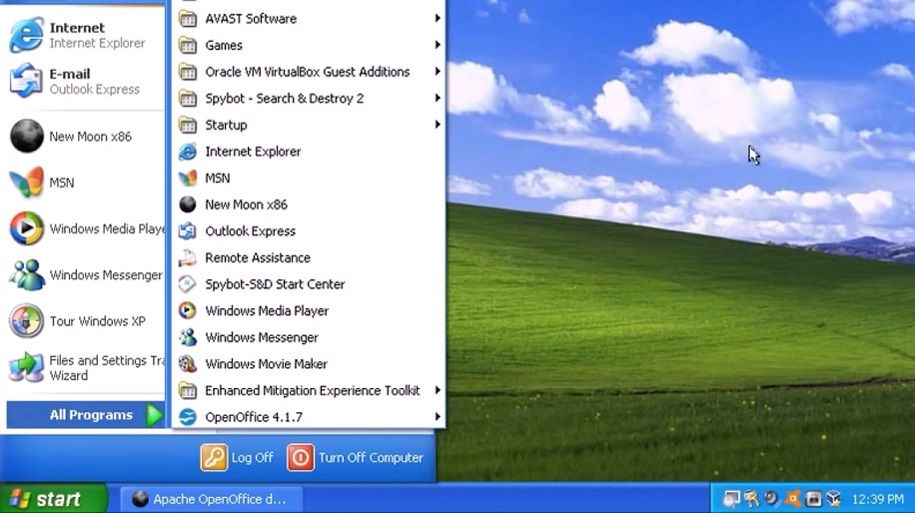
Windows XP became generally available to users during 2001.
XP had a completely overhauled user interface design that gave it an entirely new look compared with its predecessors.
It was a welcome visual change that enhanced the platforms aesthetic appeal.
Aside from its new look, XP introduced some notable new features to the Windows series.
XP was the first in its series to have a program Compatibility mode.
The XP Professional edition had a new Remote Desktop app for remotely connecting to PCs.
Automatic Windows updates were also a new thing in XP.
With a more appealing design and good new features, many users fell in love with XP.
XP remained the latest addition to the Windows series until 2007.
It retained a loyal user base long after Microsoft stopped supporting the platform.
Windows Vista
After XP came Windows Vista, which disappointed some users.
Microsoft added a new Windows Aero interface design to Vista.
Aero gave Vista a transparent glass theme and Flip 3D task switcher along with other glossy effects.
This was also the first Windows OS to have thumbnail previews on its taskbar for open software.
Yet, all the fancy effects bloated Vistas system requirements.
The gadget sidebar was another big new thing in Vista.
However, it also had some security vulnerabilities that convinced Microsoft to scrap it from later Windows platforms.
Vista also introduced User Account Control, which remains a part of Windows today.
That feature enabled users to approve/disallow programs to make changes.
Windows 7 addressed many of the performance issues that had blighted its predecessor.
Windows 7 had a revamped taskbar with smaller, square icons replacing rectangular titled ones for minimized software.
Microsoft also expanded Windows 7s taskbars thumbnail previews to display multiple windows from the same software.
Windows 7 came with a variety of new themes and sound schemes.
It also introduced the desktop slideshow customization feature for periodically changing the background.
With mobile computing on the rise, Windows 8 was a more touchscreen-optimized OS than its predecessors.
It had a whole new Metro UI design that gave the platform a more modern look.
Windows 8 replaced the Start menu with a Metro Start Screen that included customizable tiles to open software with.
It also introduced Windows Store from which users could download apps.
The result was a somewhat uneasy compromise between a desktop and tablet operating system.
Windows 8 was hardly ideal for users upgrading with older PCs for which its touchscreen features werent suitable.
Windows 10 (The Last Windows Version)
Microsoft revealed Windows 10 in 2015.
Then one Microsoft developer said it would be the last Windows version.
Windows 10 was a more desktop PC-focused OS than its predecessor.
It included a completely redesigned Start menu with integrated app tile shortcuts.
For the first time, users couldset up multiple virtual desktops, which helped reduce taskbar clutter.
The built-in Cortana virtual assistant app was another new stand-out feature of Windows 10.
Later build updates added timeline, clipboard history, and dark mode features to Windows 10.
Most users seemed to prefer Windows 10 to 8 at least.
Microsoft released Windows 10 with a one-year free upgrade offer, which increased migration to the OS.
It remains the biggest Windows platform in terms of user base today.
Windows 11 primarily ushered in a visual redesign of its predecessor.
It has centralized taskbar icons, rounded windows corners, and new-style context menus.
Windows 11 includes a revamped File Explorer with a new command bar interface.
The big Ms latest desktop OS also has redesigned prefs and Microsoft Store apps.
Thus, many of the changes in Windows 11 are cosmetic ones.
However, Microsofts latest desktop platform does boast some notable new features.
ItsWidgetstaskbar button has revived desktop gadgets in a more limited form.
Snap Layouts is also a useful feature addition that enables users to select different window layouts.
The Windows series currently has an approximate 75 percent desktop OS market share.