Over the past few years, the term “NFC” has been popularized through smartphone-based contactless payments.
So, let’s debunk these myths and misconceptions and understand what NFC truly is.
The most well-known example of an NFC software is contactless smartphone payments.

In the process of NFC communication, a tag sends information to a receiver.
NFC tends to max out at about a four-centimeter distance, though certain factors can affect this figure.
As previously mentioned, the connection range of NFC is incredibly short, sitting at around four centimeters.

This may even be possible over tens of meters, which is something to keep in mind.
NFC stems from something called RFID (radio frequency identification).
NFC technology was officially invented in 1983 by Charles Watson, though many individuals contributed to its creation.

Like NFC, RFID allows for wireless connection, using tags and readers for identification and tracking.
The tag acts as the object or gadget identification while the reader recognizes it.
The two communicate with each other using radio waves.

From this earlier technology, NFC was later born.
RDIF and NFC are certainly very similar, but there are some particularly important differences between the two.
Firstly, while RFID uses radio waves for communication, NFC uses a magnetic field.

But this is not the case.
Other devices can use NFC, including computers, tablets, and even smartwatches.
After all, many smartwatches now offer a contactless payment option, and NFC is a requirement for this.

It’s also worth noting that your contactless payment cards use RFID, which is very similar to NFC.
Contactless payment cards contain small chips and antennas that communicate with payment terminals.
This technology has parameters to protect your data, including encryption capabilities.
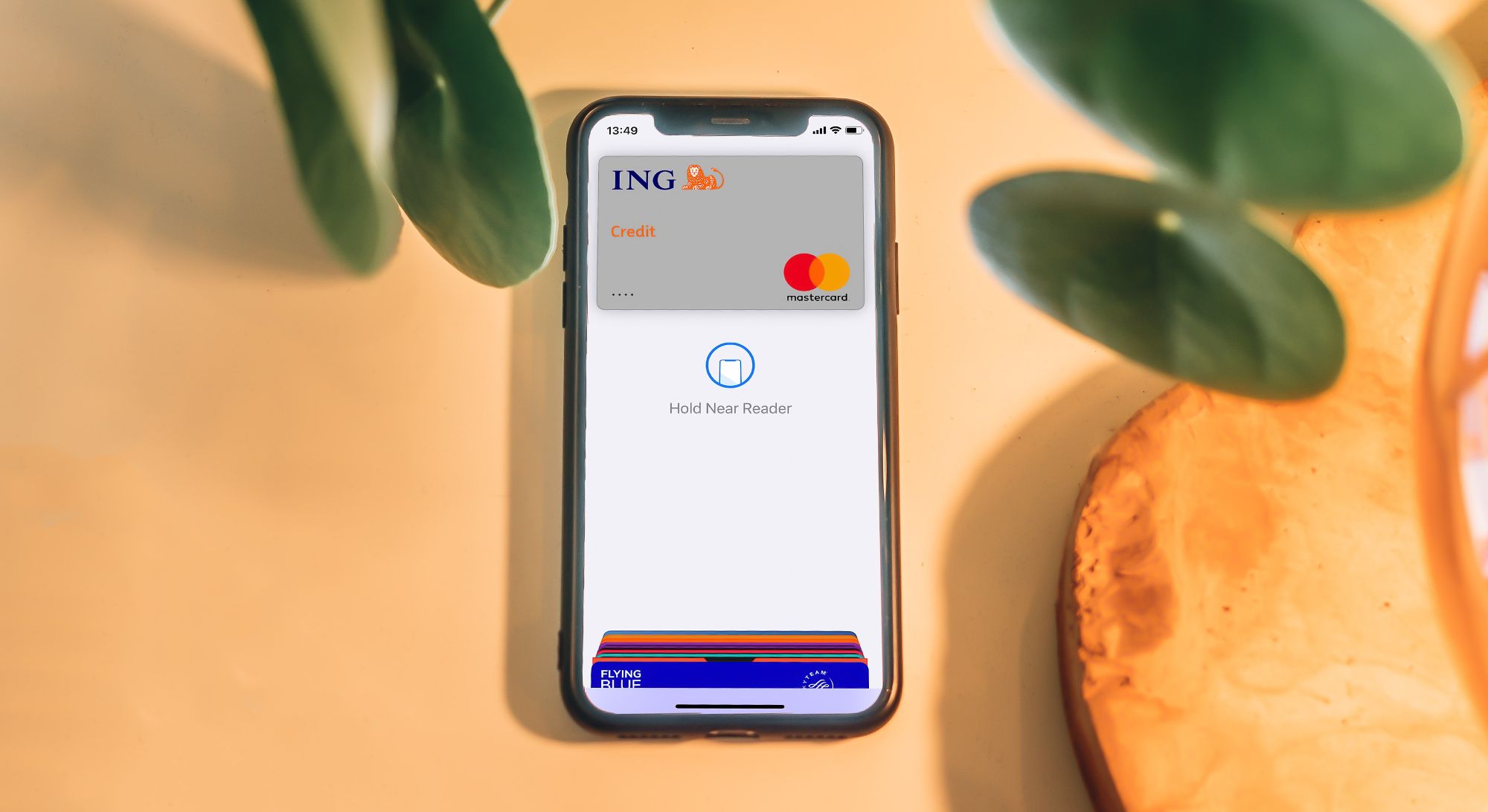
NFC also uses tokenization to protect your data and funds.
Every time you use your chosenNFC payment appon your phone, your payment details are tokenized upon payment.
A token cannot be hacked, which therefore safeguards your sensitive data.
However, NFC security is not airtight.
While NFC payments are encrypted, software vulnerabilities may allow cybercriminals to exploit your unit or payment information.
But things don’t stop there.
Using NFC, this can be done quickly and easily.
But remember that a very short range is required for NFC data transfers, which you may find limiting.
So should you be worried about a malicious actor replicating your NFC-based payment method for their own use?
In short, no.
NFC payments cannot be replicated for unauthorized use.
Along with encryption, this makes NFC card duplication essentially impossible.
Remember, NFC can be hacked and isn’t a completely secure technology.
So it is only card duplication that is not possible here.
But it has many benefits that can aid you in your daily life.