Docker is one of the most used containerization platforms and is highly loved among software engineers.
It comes with a powerful CLI tool for managing Docker containers and other related tasks.
By default, you need root privileges to run any Docker-related commands on Linux.

What Is the Docker Attack Surface?
As a rule of thumb, IT systems should have minimal attack surfaces to reduce security risks.
In general, Dockers attack surface is very minimal.
Containers run in a secure isolated environment and do not affect the host operating system unless otherwise.
In addition, Docker containers only run minimal services which makes it more secure.
you might configure your Linux system to control Docker without sudo privileges.
This can be convenient in development environments but can be a serious security vulnerability in production systems.
And here’s why you should never run Docker without sudo.
They have access to your Docker log files and can stop and delete containers at will, or accidentally.
You could also lose critical data which is vital for business continuity.
If you are using Docker containers in production environments, downtime results in a loss of business and trust.
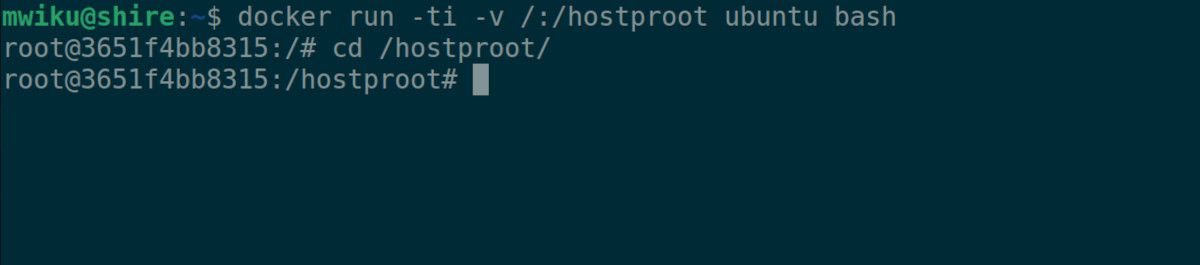
The aforementioned command will download and execute the latest Ubuntu image and mount it on the root directory.
Worse still, a malicious user could spread malicious code on your connection via Docker containers.
Secure Your Docker Containers on Linux
Docker is a powerful and secure platform.
Running Docker without sudo increases your attack surface and makes your system vulnerable.
In production environments, it is highly recommended that you should use sudo with Docker.
With so many users on a system, it becomes extremely hard to assign permissions to each user.
In such cases, following the best access control practices can help you maintain the security of your system.